480
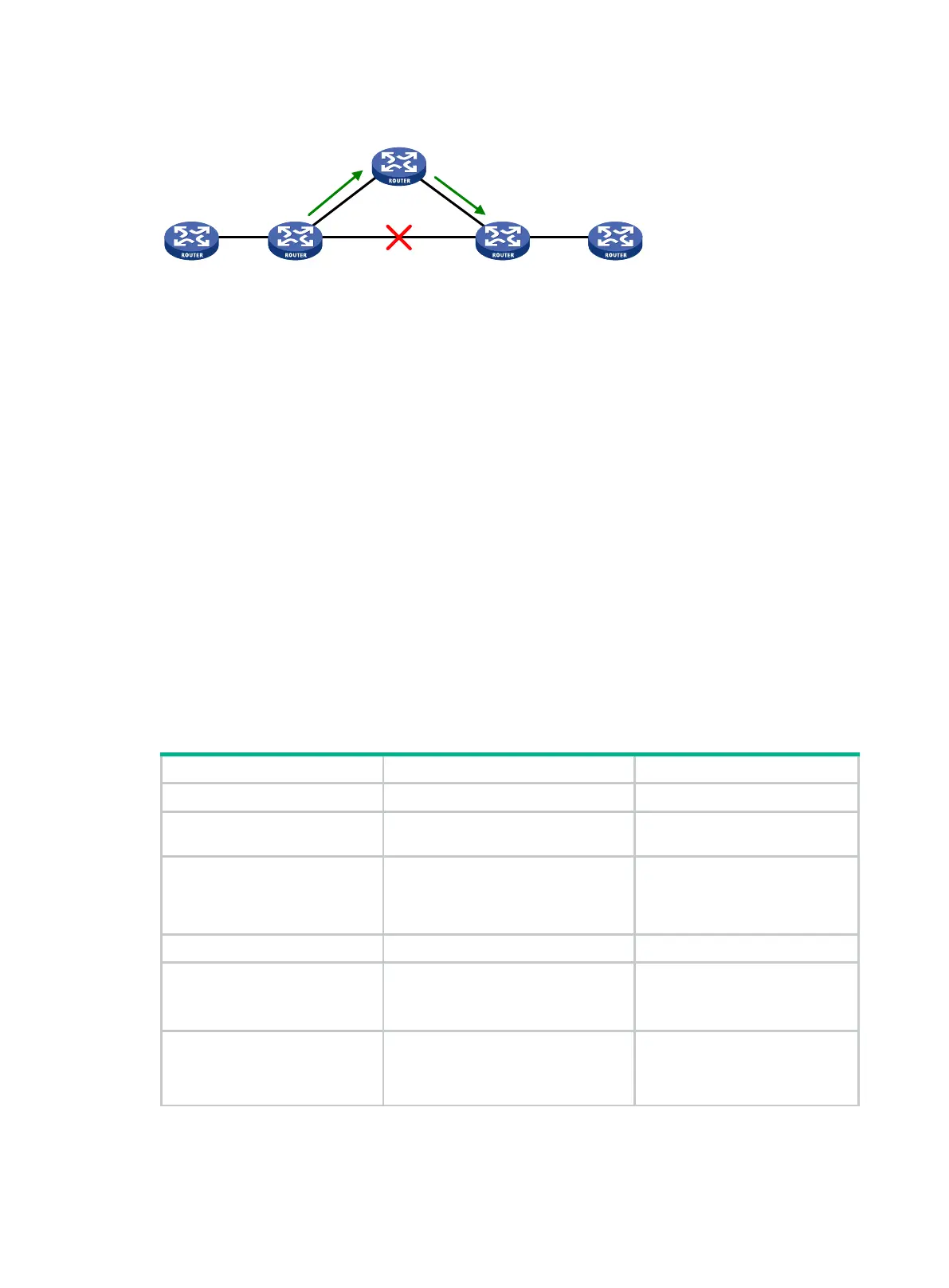
Figure 110 Network diagram for IPv6 IS-IS FRR
In Figure 110, after you enable FRR on Router B, IPv6 IS-IS FRR automatically calculates or
designates a backup next hop when a link failure is detected. In this way, packets are directed to the
backup next hop to reduce traffic recovery time. Meanwhile, IPv6 IS-IS calculates the shortest path
based on the new network topology, and forwards packets over the path after network convergence.
You can assign a backup next hop for IPv6 IS-IS FRR in the following ways:
Enable IPv6 IS-IS FRR to calculate a backup next hop through Loop Free Alternate (LFA)
calculation.
Designate a backup next hop with a routing policy for routes matching specific criteria.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure IPv6 IS-IS FRR, complete the following tasks:
Configure IPv6 addresses for interfaces to ensure IP connectivity between neighboring nodes.
Enable IPv6 IS-IS.
Make sure the backup next hop is reachable.
Configuration procedure
Configuring IPv6 IS-IS FRR to calculate a backup next hop through LFA calculation
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter interface view.
interface
interface-type
interface-number
N/A
3. (Optional.) Disable LFA
calculation on the interface.
isis ipv6 fast-reroute lfa-backup
exclude
By default, the interface
participates in LFA calculation
and can be elected as a backup
interface.
4. Return to system view.
quit
N/A
5. Enter IS-IS IPv6 unicast
address family view.
isis
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ]
[
]
N/A
6. Enable IPv6 IS-IS FRR to
calculate a backup next
hop through LFA
calculation.
fast-reroute lfa
By default, IPv6 IS-IS FRR is
disabled.
Backup next hop: Router C
Router ENext hop: Router D
Router B

 Loading...
Loading...











