94
Configuring basic DHCP snooping
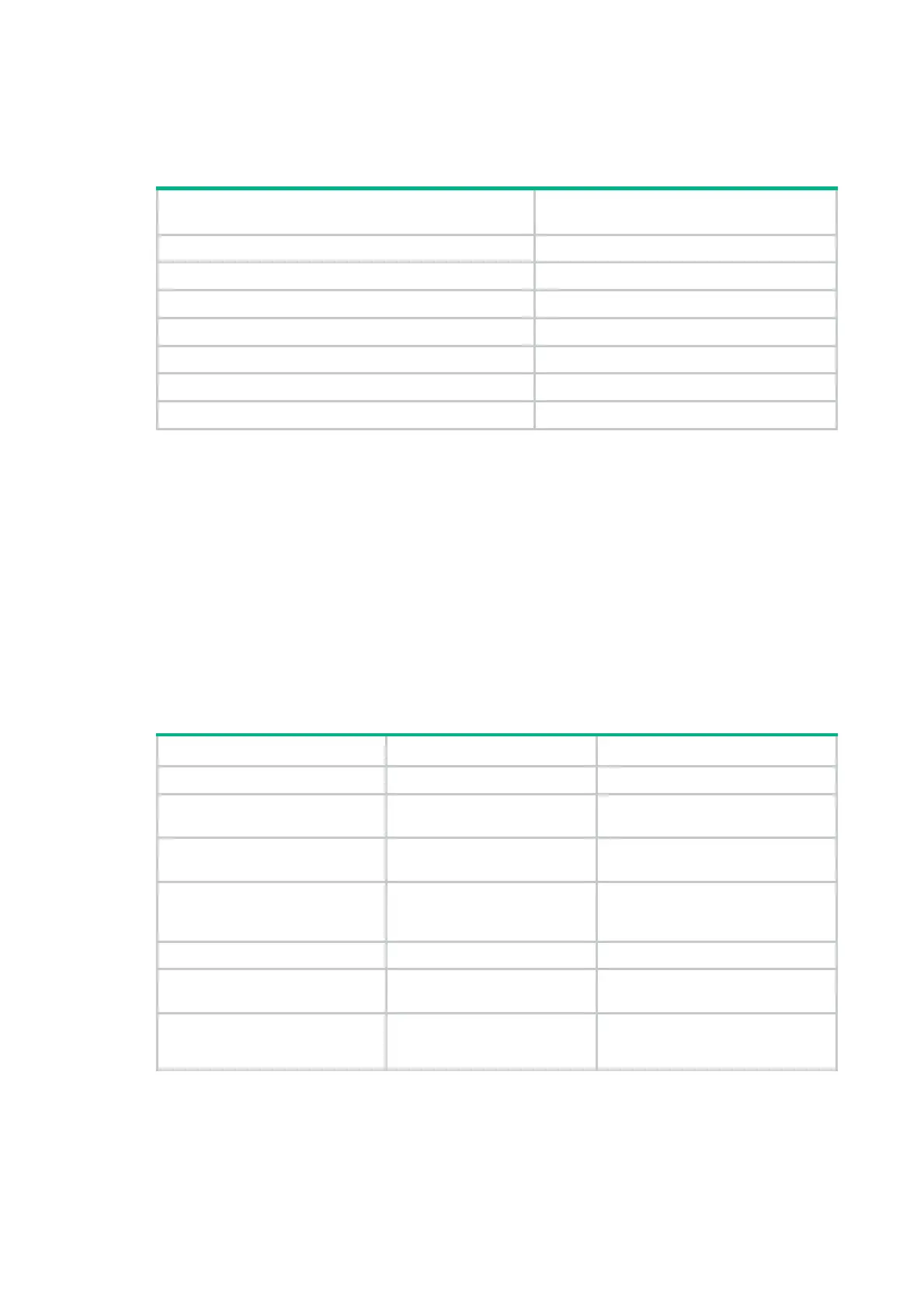
The following matrix shows the feature and hardware compatibility:
Hardware
DHCP snooping entry recording
compatibility
MSR954(JH296A/JH297A/JH298A/JH299A/JH373A) No
MSR958(JH300A/JH301A) No
MSR1002-4/1003-8S Yes
MSR2003 Yes
MSR2004-24/2004-48 Yes
MSR3012/3024/3044/3064 Yes
MSR4060/4080 Yes
Follow these guidelines when you configure basic DHCP snooping:
• Specify the ports connected to authorized DHCP servers as trusted ports to make sure that
DHCP clients can obtain valid IP addresses. The trusted ports and the ports connected to
DHCP clients must be in the same VLAN.
• You can specify the following interfaces as trusted ports: Layer 2 Ethernet interfaces and Layer
2 aggregate interfaces. For more information about aggregate interfaces, see Layer 2—LAN
Switching Configuration Guide.
• The DHCP snooping configuration on a Layer 2 Ethernet interface that has been added to an
aggregation group does not take effect unless the interface leaves the aggregation group.
• DHCP snooping can work with QinQ to record VLAN tags for DHCP packets received from
clients. For more information about QinQ, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
To configure basic DHCP snooping:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enable DHCP snooping.
dhcp snooping enable
By default, DHCP snooping is
disabled.
3. Enter interface view.
interface
interface-type
interface-number
This interface must connect to the
DHCP server.
4. Specify the port as a trusted
port.
dhcp snooping trust
By default, all ports are untrusted
ports after DHCP snooping is
enabled.
5. Return to system view.
quit
N/A
6. Enter interface view.
interface
interface-type
interface-number
This interface must connect to the
DHCP client.
7. (Optional.) Enable the
recording of DHCP snooping
entries.
dhcp snooping binding
record
By default, the recording of DHCP
snooping entries is disabled.
 Loading...
Loading...




