337
Step Command Remarks
3. Specify an IPv4 address
for the tunnel interface.
ip address
ip-address { mask |
mask-length } [
sub
]
By default, no IPv4 address is
specified for the tunnel interface.
4. Specify the source
address or source
interface for the tunnel.
source
{ ipv6-address |
interface-type interface-number }
By default, no source address or
interface is specified for the tunnel.
The specified source address or the
lowest IPv6 address of the specified
source interface is used as the source
IPv6 address of tunneled packets.
5. Return to system view.
quit
N/A
6. Enter the view of the
interface that is connected
to the IPv4 public network.
interface
interface-type
interface-number
N/A
7. Enable DS-Lite tunneling
on the interface.
ds-lite enable
By default, DS-Lite tunneling is
disabled.
Only after you use this command, the
AFTR can tunnel IPv4 packets from
the public IPv4 network to the B4
router.
Configuration example
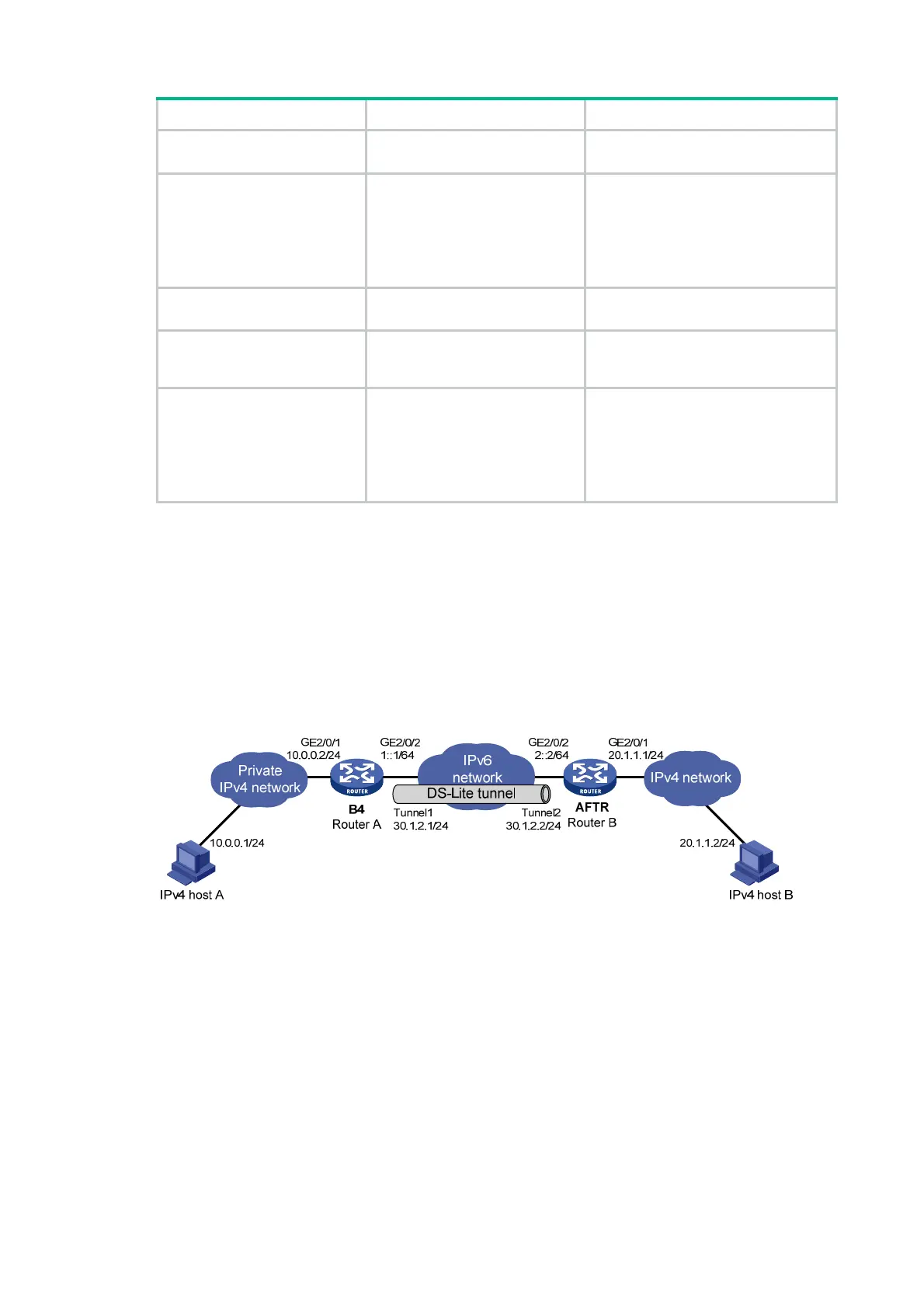
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 131, to enable hosts in the private IPv4 network to access the public IPv4
network over the IPv6 network, perform the following tasks:
• Configure a DS-Lite tunnel between Router A and Router B.
• Configure NAT on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 on the AFTR.
Figure 131 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
Make sure Router A and Router B can reach each other through IPv6.
• Configure Router A:
# Specify an IPv4 address for GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Specify an IPv6 address for GigabitEthernet 2/0/2, which is the physical interface of the
tunnel.
 Loading...
Loading...




