8
Configuration procedure
# Create VLAN 10.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] vlan 10
[RouterB-vlan10] quit
# Add interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 to VLAN 10.
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] port access vlan 10
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 10 and configure its IP address.
[RouterB] interface vlan-interface 10
[RouterB-vlan-interface10] ip address 192.168.1.2 8
[RouterB-vlan-interface10] quit
# Configure a long static ARP entry that has IP address 192.168.1.1, MAC address 00e0-fc01-0000,
and output interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 in VLAN 10.
[RouterB] arp static 192.168.1.1 00e0-fc01-0000 10 gigabitethernet 2/0/1
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that Router B has a long static ARP entry for Router A.
[RouterB] display arp static
Type: S-Static D-Dynamic O-Openflow R-Rule I-Invalid
IP address MAC address VLAN Interface Aging Type
192.168.1.1 00e0-fc01-0000 10 GE2/0/1 N/A S
Short static ARP entry configuration example
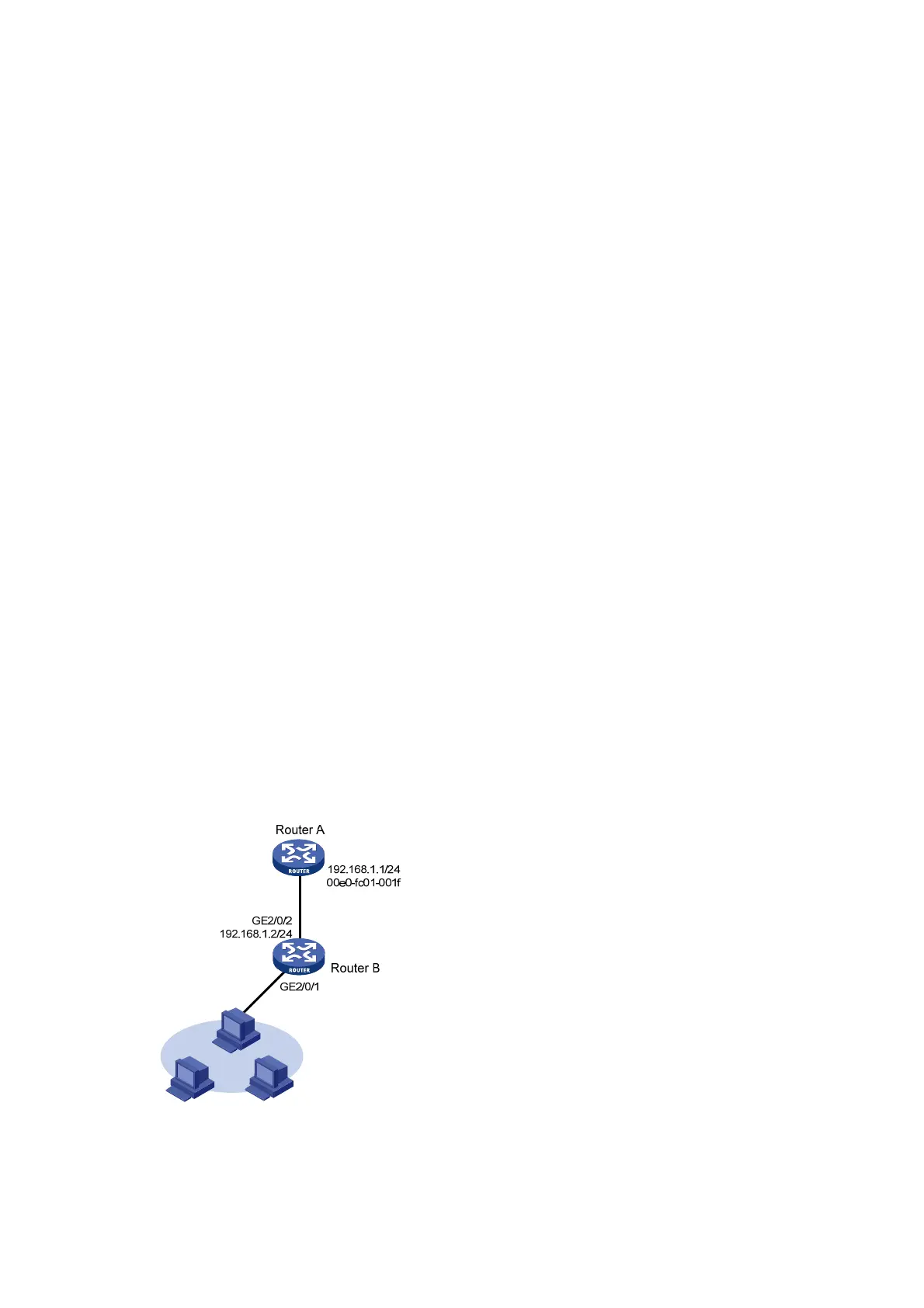
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 4, hosts are connected to Router B. Router B is connected to Router A through
GigabitEthernet 2/0/2.
To ensure secure communications between the Router A and Router B, configure a short static ARP
entry for Router A on Router B.
Figure 4 Network diagram
 Loading...
Loading...




