444
IPv4-initiated communication
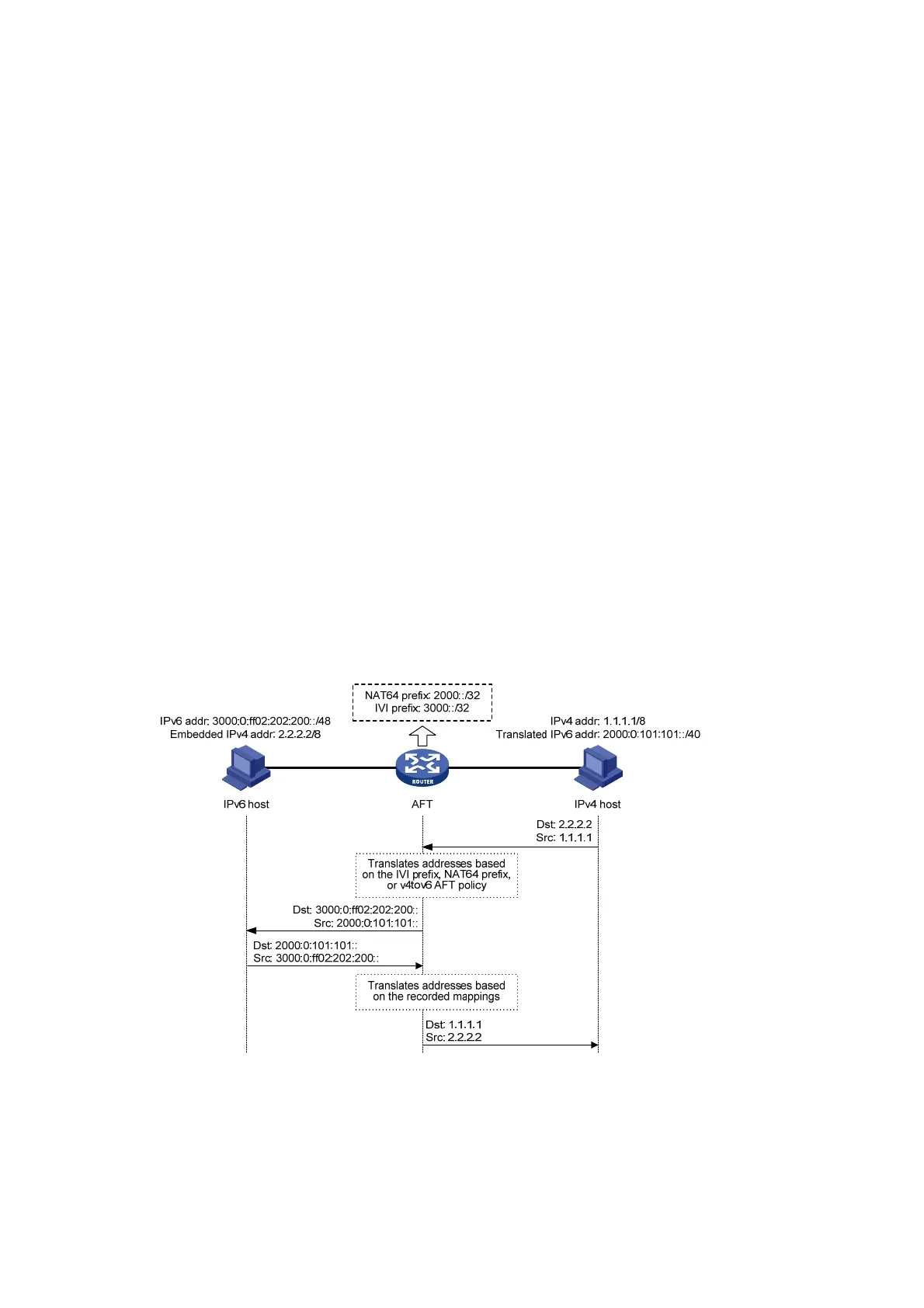
As shown in Figure 160, when the IPv4 host initiates access to the IPv6 host, AFT operates as
follows:
1. Upon receiving a packet from the IPv4 host, AFT compares the packet with IPv4-to-IPv6
destination address translation policies.
{ If a matching policy is found, AFT translates the destination IPv4 address according to the
policy.
{ If no matching policy is found, AFT does not perform address translation.
2. AFT performs the pre-lookup to determine output interface for the translated packet. PBR is not
used for the pre-lookup.
{ If a matching route is found, the process goes to step 3.
{ If no matching route is found, AFT discards the packet.
3. AFT compares the source IPv4 address with IPv4-to-IPv6 source address translation policies.
{ If a matching policy is found, AFT translates the source IPv4 address according to the
policy.
{ If no matching policy is found, AFT discards the packet.
4. AFT forwards the translated packet and records the mappings between IPv4 addresses and
IPv6 addresses.
5. AFT translates the IPv6 addresses in the response packet header to IPv4 addresses based on
the address mappings before packet forwarding.
For more information about IPv4-to-IPv6 destination address translation policies, see "Configuring
an IPv4-to-IPv6 destinatio
n address translation policy."
For more information about IPv4-to-IPv6 source address translation policies, see "Configuring an
IPv4-to-IPv6 sou
rce address translation policy."
Figure 160 AFT process for IPv4-initiated communication
 Loading...
Loading...




