169
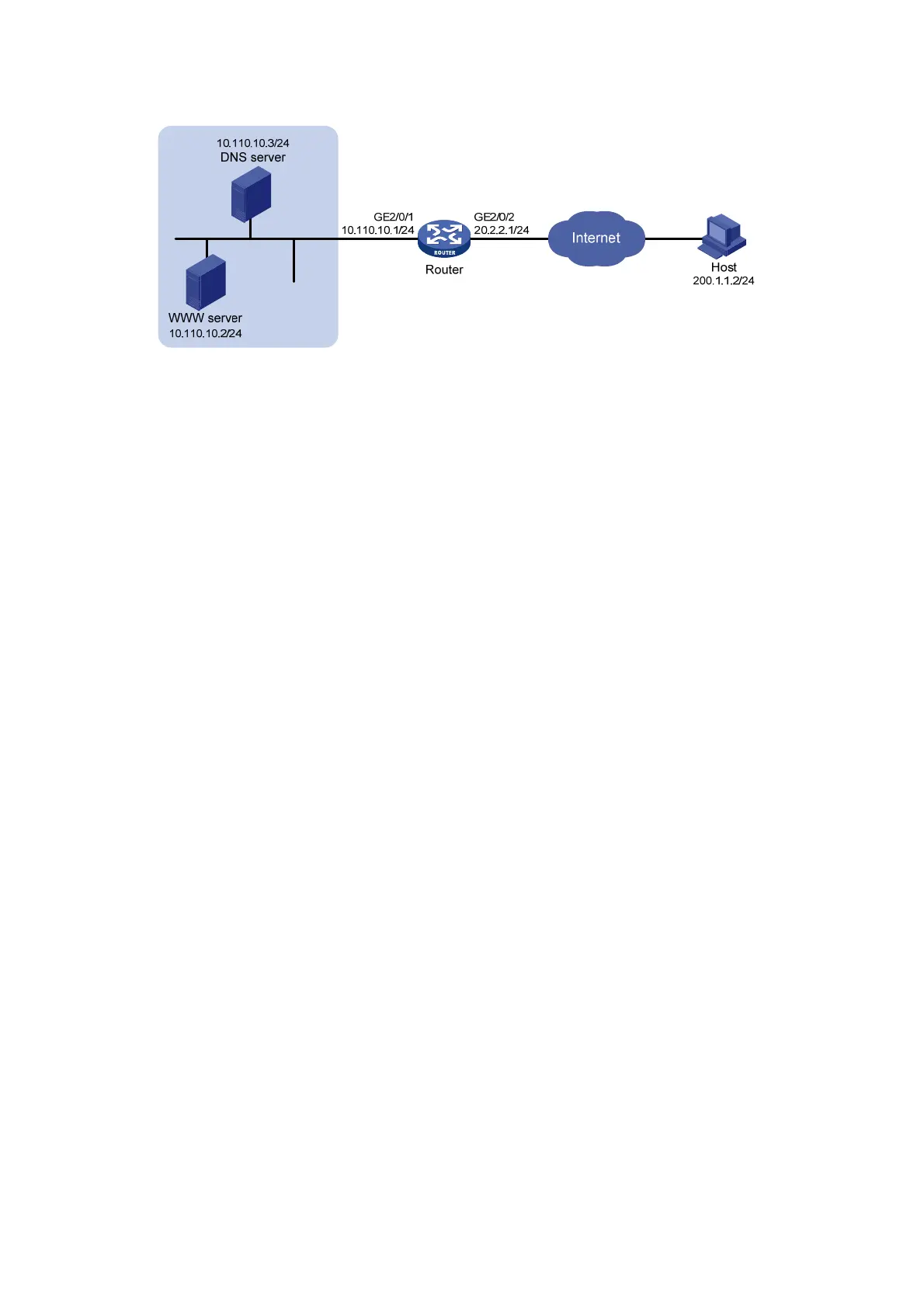
Figure 68 Network diagram
Requirements analysis
To meet the network requirements, you must perform the following tasks:
• Configure NAT Server to map the private IP address and port of the DNS server to a public
address and port. NAT Server allows the external host to access the internal DNS server for
domain name resolution.
• Enable ALG for DNS and configure outbound dynamic NAT to translate the private IP address
of the Web server in the payload of the DNS response packet into a public IP address.
Configuration procedure
# Specify IP addresses for the interfaces on the router. (Details not shown.)
# Enable NAT with ALG for DNS.
<Router> system-view
[Router] nat alg dns
# Configure ACL 2000, and create a rule to permit packets only from 10.110.10.2 to pass through.
[Router] acl basic 2000
[Router-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 10.110.10.2 0
[Router-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] quit
# Create address group 1.
[Router] nat address-group 1
# Add address 202.38.1.3 to the group.
[Router-address-group-1] address 202.38.1.3 202.38.1.3
[Router-address-group-1] quit
# Configure NAT Server on interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/2 to map the address 202.38.1.1 to
10.110.10.3. External users can access the internal DNS server.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/2
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] nat server protocol udp global 202.38.1.2 inside
10.110.10.3 dns
# Enable outbound NO-PAT on interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/2. Use the address in address group 1
to translate the private address in DNS response payload, and allow reversible NAT.
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] nat outbound 2000 address-group 1 no-pat reversible
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the host on the external network can access the internal Web server by using the
server's domain name. (Details not shown.)
 Loading...
Loading...




