4-69
BUS OPERATION
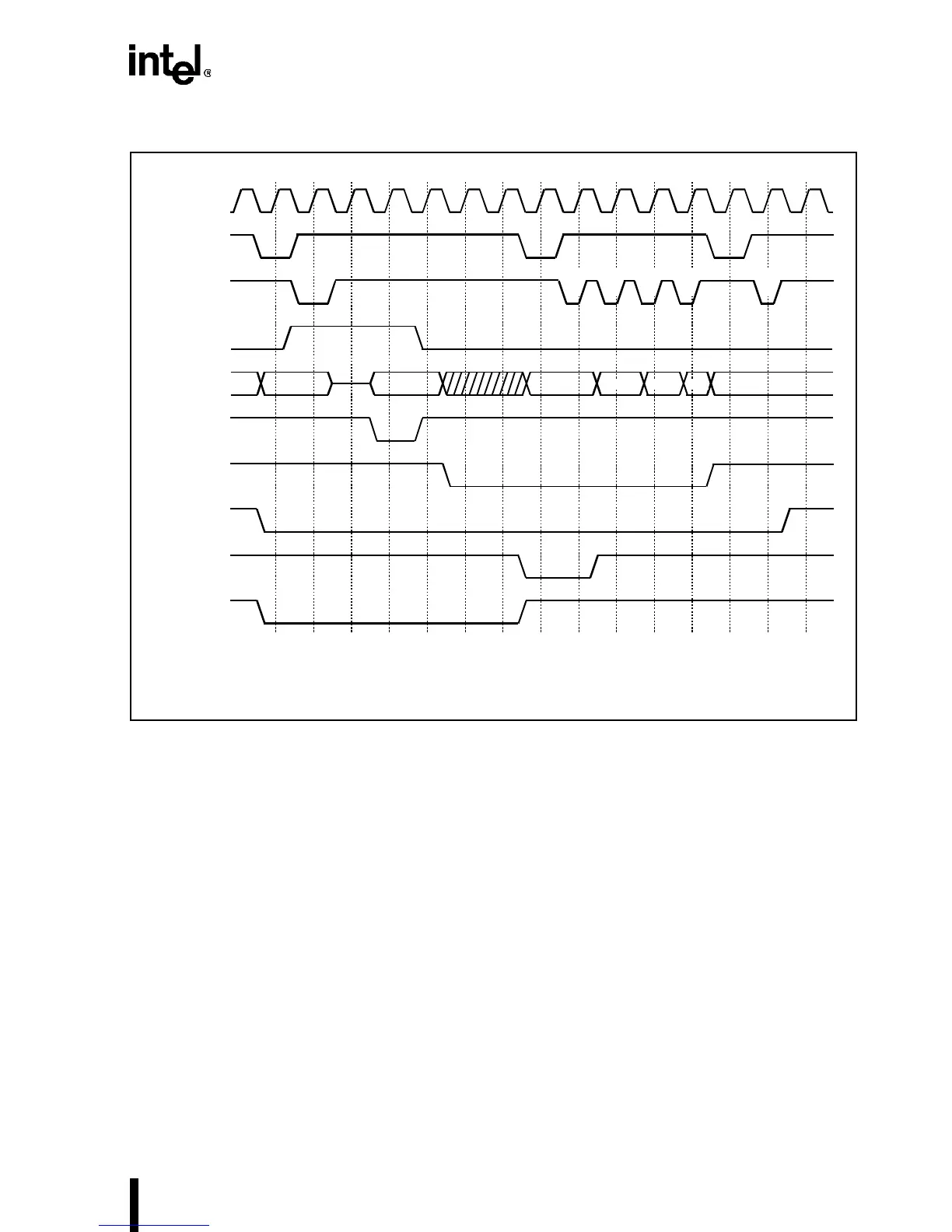
Figure 4-47. Snoop Cycle Overlaying a Locked Cycle
4.4.5 Flush Operation
The Write-Back Enhanced IntelDX4 processor executes a flush operation when the FLUSH# pin
is asserted, and no outstanding bus cycles, such as a line fill or write back, are being processed.
In the Enhanced Bus mode, the processor first writes back all the modified lines to external mem-
ory. After the write-back is completed, two special cycles are generated, indicating to the external
system that the write-back is done. All lines in the internal cache are invalidated after all the
write-back cycles are done. Depending on the number of modified lines in the cache, the flush
could take a minimum of 1280 bus clocks (2560 processor clocks) and up to a maximum of 5000+
bus clocks to scan the cache, perform the write backs, invalidate the cache, and run the flush ac-
knowledge cycles. FLUSH# is implemented as an interrupt in the Enhanced Bus mode, and is rec-
ognized only on an instruction boundary. Write-back system designs should look for the flush
acknowledge cycles to recognize the end of the flush operation. Figure 4-48 shows the flush op-
eration of the Write-Back Enhanced IntelDX4 processor when configured in the Enhanced Bus
mode.
242202-159
CLK
ADS#
RDY#
BRDY#
AHOLD
ADDR
EADS#
HITM#
W/R#
To Processor
From Processor
12345678910111213141516
Write
0 4 8 C
CACHE#
LOCK#
WB1 WB2 WB3 WB4
Write
Read
WB
†
‡
‡
†‡
 Loading...
Loading...











