7-5
PERIPHERAL SUBSYSTEM
The BS16# and BS8# inputs allow external 16- and 8-bit buses to be supported using fewer ex-
ternal components. The Intel486 processor samples these pins every clock cycle. This value is
sampled on the clock before RDY# to determine the bus size. When BS8# or BS16# is asserted,
only 16-bits or 8-bits of data are transferred in a clock cycle. When both BS8# and BS16# are
asserted, an 8-bit bus width is used.
Dynamic bus sizing allows the power-up or boot-up programs to be stored in 8-bit non-volatile
memory devices (e.g., PROM, EPROM, E2PROM, Flash, and ROM) while program execution
uses 32-bit DRAM or variants.
7.1.3 Address Decoding for I/O Devices
Address decoding for I/O devices resembles address decoding for memories. The primary differ-
ence is that the block size (range of addresses) for each address signal is much smaller. The min-
imum block size depends on the number of addresses used by the I/O device. In most processors,
where I/O instructions are separate, I/O addresses are shorter than memory addresses. Typically,
processors with a 16-bit address bus use an 8-bit address for I/O.
One technique for decoding memory-mapped I/O addressed is to map the entire I/O space of the
Intel486 processor into a 64-Kbyte region of the memory space. The address decoding logic can
be reconfigured so that each I/O device responds to a memory address and an I/O address. This
configuration is compatible with software that uses either I/O instructions or memory-mapped
techniques.
Addresses can be assigned arbitrarily within the I/O or memory space. Addresses for either I/O-
mapped or memory-mapped devices should be selected so as to minimize the number of address
lines needed.
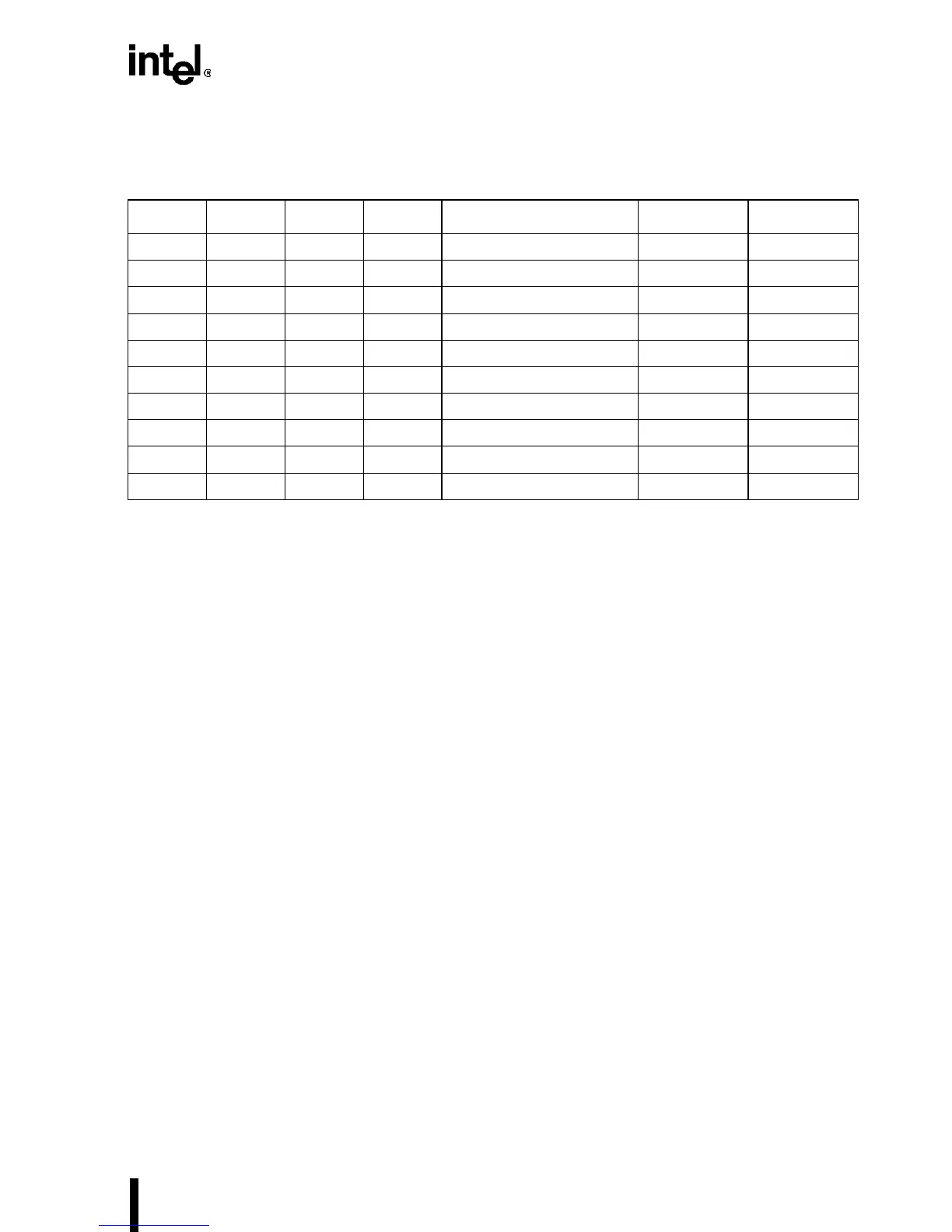
Table 7-2. Valid Data Lines for Valid Byte Enable Combinations
BE3# BE23 BE1# BE0# w/o BS8#/BS16# w BS8# w BS16#
1110 D7–D0 D7–D0 D7–D0
1100 D15–D0 D7–D0D15–D0
1000 D23–D0 D7–D0D15–D0
0000 D31–D0 D7–D0D15–D0
1101 D15–D8 D15–D8D15–D8
1001 D23–D8 D15–D8D15–D8
0001 D31–D8 D15–D8D15–D8
1011 D23–D16 D23–D16D23–D16
0011 D31–D16 D23–D16D31–D16
0111 D31–D24 D31–D24D31–D24
 Loading...
Loading...











