EMBEDDED Intel486™ PROCESSOR HARDWARE REFERENCE MANUAL
7-6
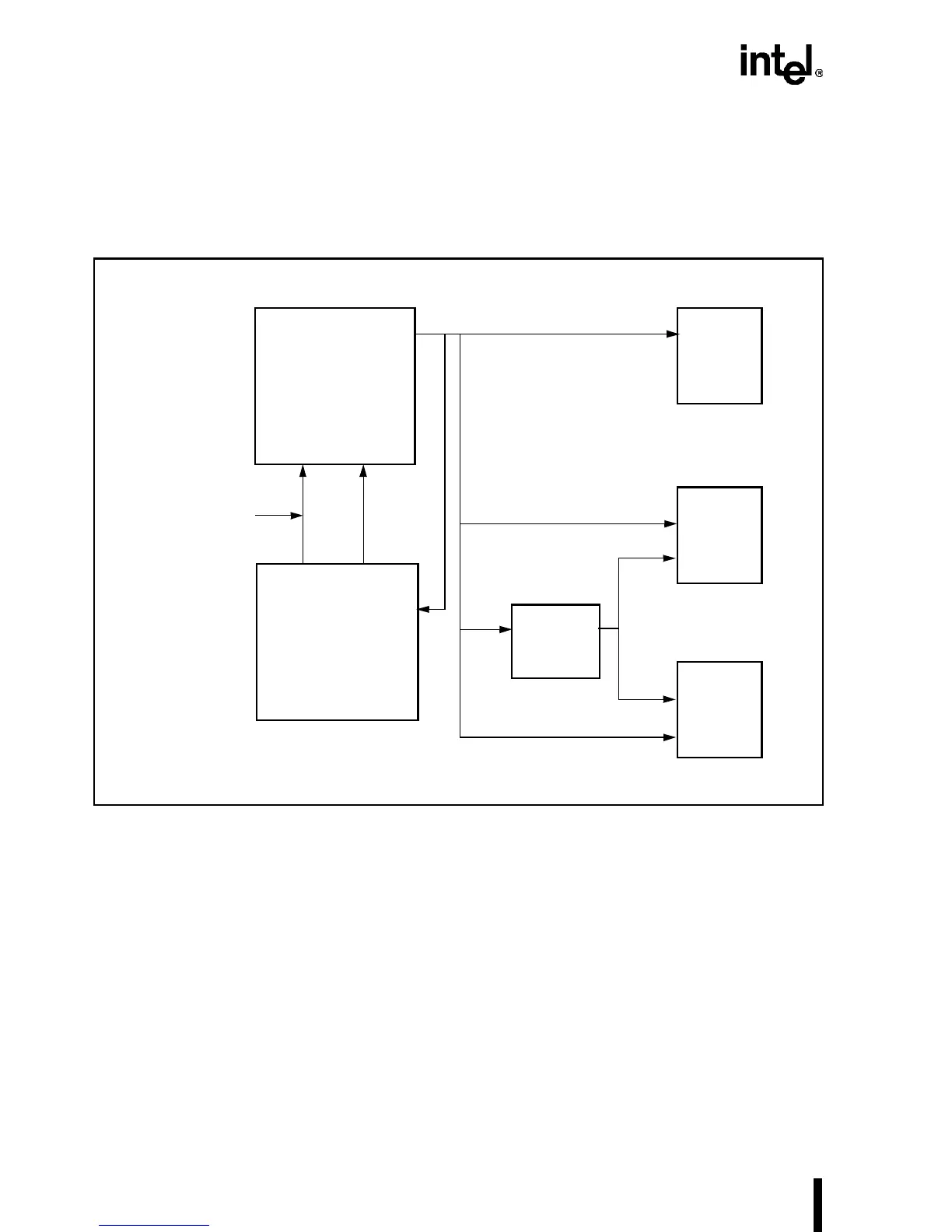
7.1.3.1 Address Bus Interface
Figure 7-2 shows the Intel486 processor address interface to 32-, 16- and 8-bit devices. To ad-
dress 16-bit devices, the byte enables must be decoded to produce A1, BHE# and BLE# (A0) sig-
nals.
Figure 7-2. Intel486™ Processor Interface to I/O Devices
To access to 8-bit devices, the byte enable signals must be decoded to generate A0 and A1. Be-
cause A0 and BLE# are the same, the same generation logic can be used. For 32-bit memo-
ry/mapped devices A31–A2 can be used in conjunction with BE3#–BE0#. This logic is shown in
Figure 7-3.
Address Bus
(A31–A2, BE3#–BE0#)
32-Bit
I/O
Devices
16-Bit
I/O
Devices
8-Bit
I/O
Devices
A31–A2
BE3#–
BE0#
Byte
Select
BHE#,
BLE#,
A1
A0(BLE#), A1
Address
Decoder
Intel486™
BS8#
BS16#
BS8# = BS16# = HIGH
for 32-Bit Addressing
A31–A2
Processor
 Loading...
Loading...











