EMBEDDED Intel486™ PROCESSOR HARDWARE REFERENCE MANUAL
6-12
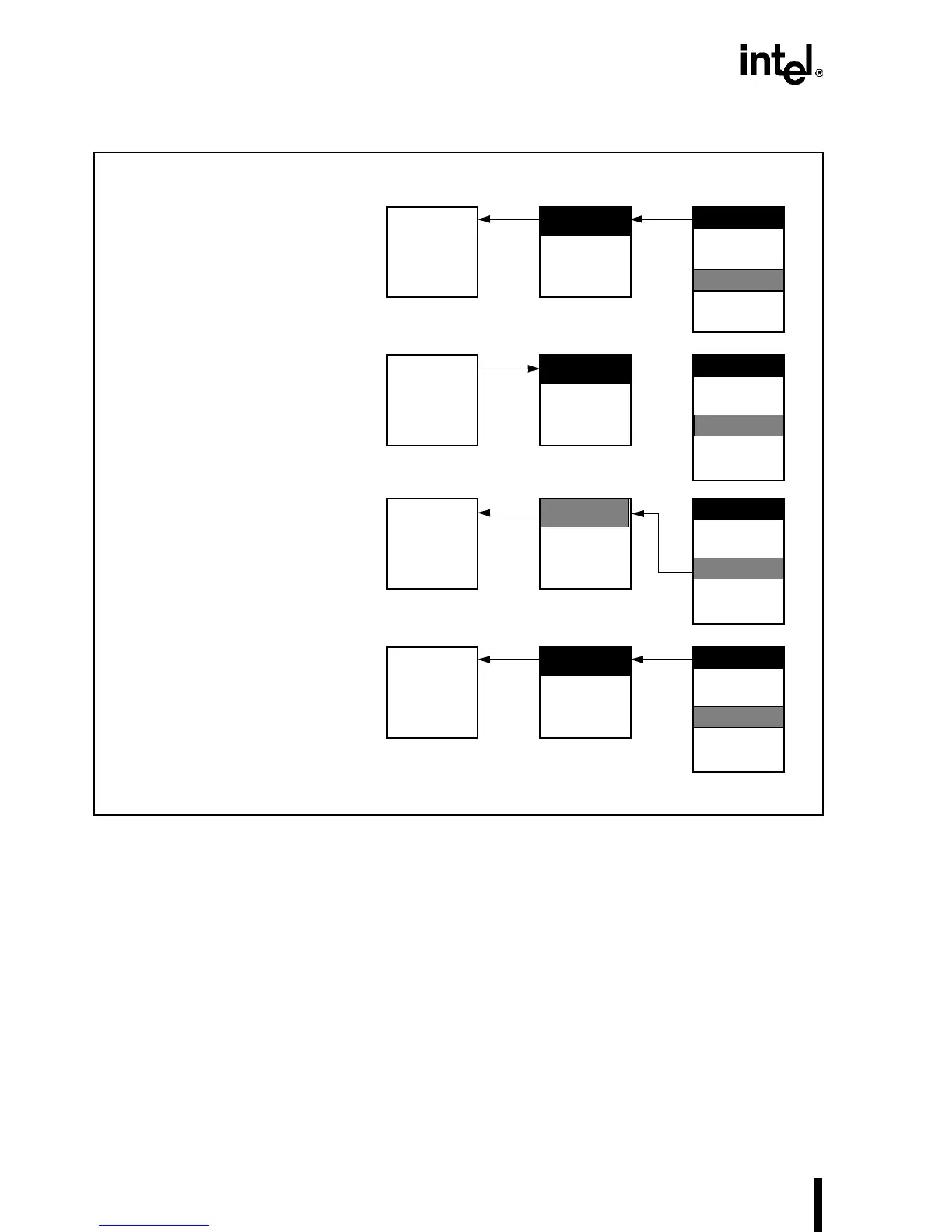
Figure 6-6. Stale Data Problem in the Cache/Main Memory
6.4.1 Write-Through and Buffered Write-Through Systems
In a write-through system, data is written to the main memory immediately after or while it is
written into the cache. As a result, the main memory always contains valid data. The advantage
to this approach is that any block in the cache can be overwritten without data loss, while the hard-
ware implementation remains fairly straightforward. There is a memory traffic trade-off, howev-
er, because every write cycle increases the bus traffic on a slower memory bus. This can create
contention for use of the memory bus by other bus masters. Even in a buffered write-through
scheme, each write eventually goes to memory. Thus, bus utilization for write cycles is not re-
duced by using a write-through or buffered write-through cache.
Main Memory
Cache
CPU
1
Processor reads data into cache
from main memory.
2
The data is processed and
modified and stored in the cache
(not in the main memory).
3
Later, another read overwrites the
cache data and the modified data is
overwritten and lost before the
main memory is updated.
3
The processor reads data from
memory as in the first step, but
stale data is copied in the cache, as
the correct data shown in Step 2
was not sent to the main memory.
 Loading...
Loading...











