EMBEDDED Intel486™ PROCESSOR HARDWARE REFERENCE MANUAL
4-32
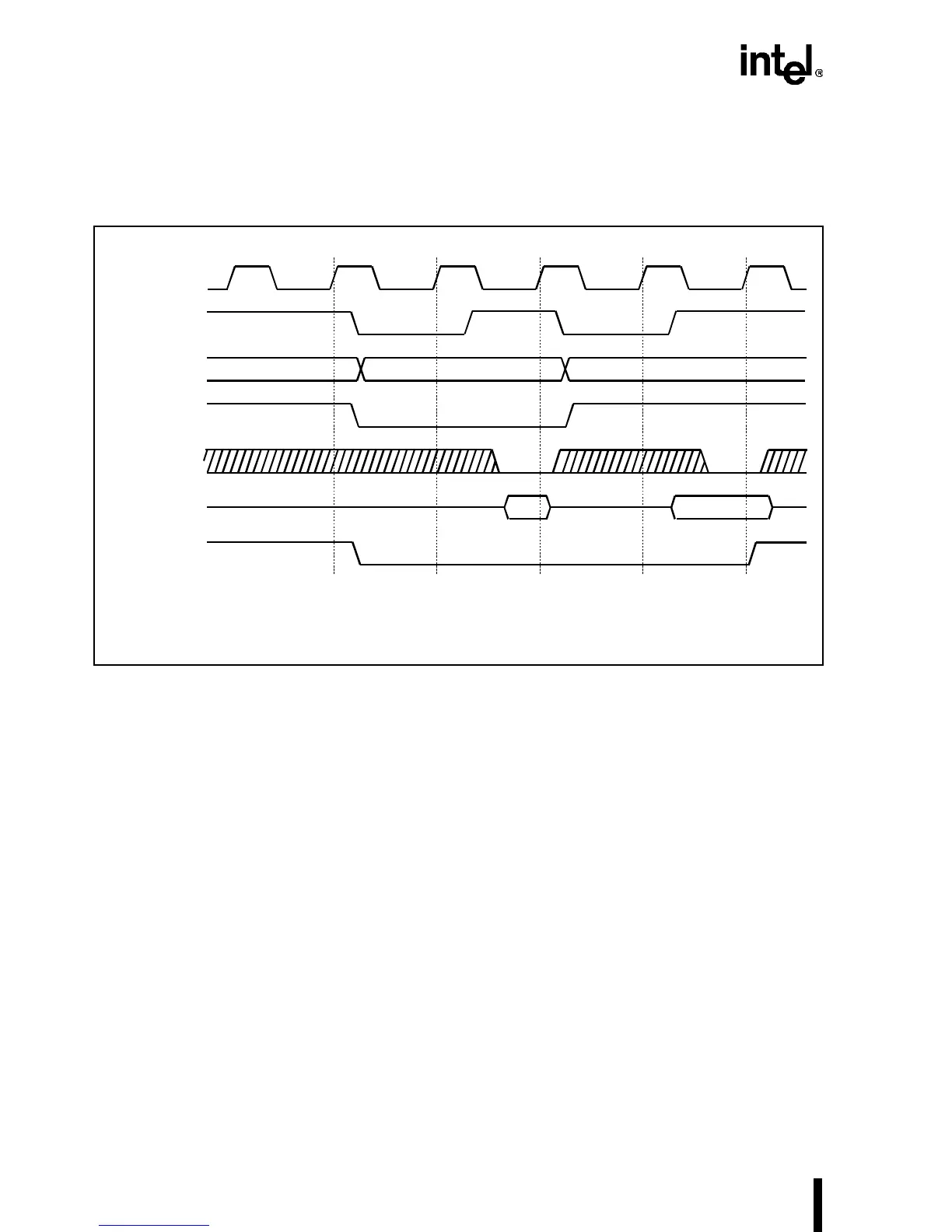
When LOCK# is asserted, the Intel486 processor recognizes address hold and backoff but does
not recognize bus hold. It is left to the external system to properly arbitrate a central bus when the
Intel486 processor generates LOCK#.
Figure 4-23. Locked Bus Cycle
4.3.7 Pseudo-Locked Cycles
Pseudo-locked cycles assure that no other master is given control of the bus during operand trans-
fers that take more than one bus cycle.
For the Intel486 processor, examples include 64-bit description loads and cache line fills.
Pseudo-locked transfers are indicated by the PLOCK# pin. The memory operands must be
aligned for correct operation of a pseudo-locked cycle.
PLOCK# need not be examined during burst reads. A 64-bit aligned operand can be retrieved in
one burst (note that this is only valid in systems that do not interrupt bursts).
The system must examine PLOCK# during 64-bit writes since the Intel486 processor cannot
burst write more than 32 bits. However, burst can be used within each 32-bit write cycle if BS8#
or BS16# is asserted. BLAST is de-asserted in response to BS8# or BS16#. A 64-bit write is driv-
en out as two non-burst bus cycles. BLAST# is asserted during both 32-bit writes, because a burst
is not possible. PLOCK# is asserted during the first write to indicate that another write follows.
This behavior is shown in Figure 4-24.
242202-080
TiT2T1T2T1Ti
CLK
ADS#
A31–A2
M/IO#
D/C#
BE3#–BE0#
W/R#
RDY#
DATA
LOCK#
To Processor
From Processor
Read Write
‡
†
†
‡
 Loading...
Loading...











