EMBEDDED Intel486™ PROCESSOR HARDWARE REFERENCE MANUAL
4-52
shown in Table 4-8 on page 4-27. The burst order for reads is the same as the burst order for
writes. (See Section 4.3.4.2, “Burst and Cache Line Fill Order.”)
An attempted line fill caused by a read miss is indicated by the assertion of CACHE# and W/R#.
For a line fill to occur, the system must assert KEN# twice: one clock prior to the first BRDY#
and one clock prior to last BRDY#. It takes only one deassertion of KEN# to mark the line as
non-cacheable. A write-back cycle of a cache line, due to replacement or snoop, is indicated by
the assertion of CACHE# low and W/R# high. KEN# has no effect during write-back cycles.
CACHE# is valid from the assertion of ADS# through the clock in which the first RDY# or
BRDY# is asserted. CACHE# is deasserted at all other times. PCD behaves the same in Enhanced
Bus mode as in Standard Bus mode, except that it is low during write-back cycles.
The Write-Back Enhanced IntelDX4 processor samples WB/WT# once, in the same clock as the
first BRDY#. This sampled value of WB/WT# is combined with PWT to bring the line into the
internal cache, either as a write-back line or write-through line.
4.4.3 Cache Consistency Cycles
The system performs snooping to maintain cache consistency. Snoop cycles can be performed
under AHOLD, BOFF#, or HOLD, as described in Table 4-11.
The snoop cycle begins by checking whether a particular cache line has been “cached” and inval-
idates the line based on the state of the INV pin. If the Write-Back Enhanced IntelDX4 processor
is configured in Enhanced Bus mode, the system must drive INV high to invalidate a particular
cache line. The Write-Back Enhanced IntelDX4 processor does not have an output pin to indicate
a snoop hit to an S-state line or an E-state line. However, the Write-Back Enhanced IntelDX4 pro-
cessor invalidates the line if the system snoop hits an S-state, E-state, or M-state line, provided
INV was driven high during snooping. If INV is driven low during a snoop cycle, a modified line
is written back to memory and remains in the cache as a write-back line; a write-through line also
remains in the cache as a write-through line.
After asserting AHOLD or BOFF#, the external bus master driving the snoop cycle must wait for
two clocks before driving the snoop address and asserting EADS#. If snooping is done under
HOLD, the master performing the snoop must wait for at least one clock cycle before driving the
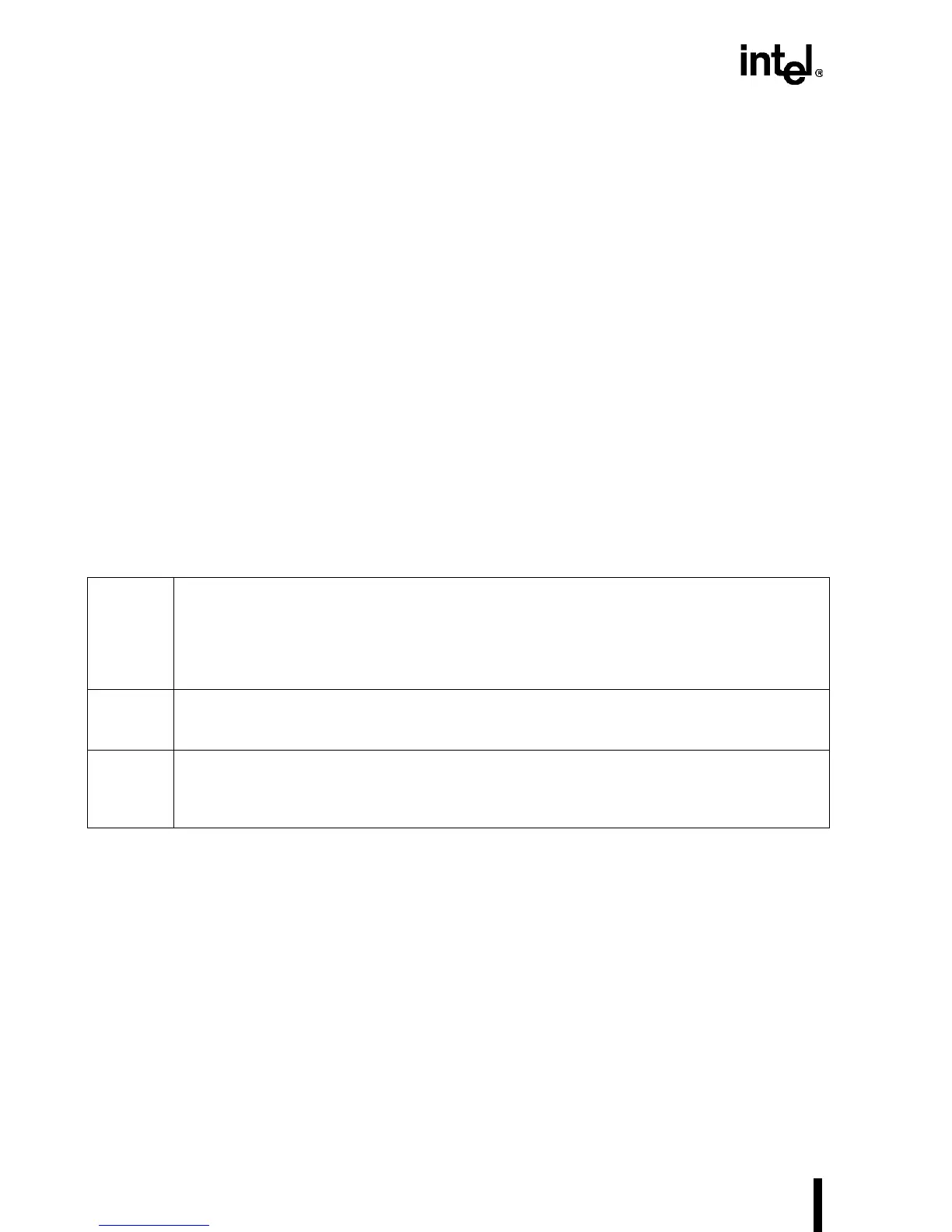
Table 4-11. Snoop Cycles under AHOLD, BOFF#, or HOLD
AHOLD
Floats the address bus. ADS# is asserted under AHOLD only to initiate a snoop write-back cycle.
An ongoing burst cycle is completed under AHOLD. For non-burst cycles, a specific non-burst
transfer (ADS#-RDY# transfer) is completed under AHOLD and fractured before the next
assertion of ADS#. A snoop write-back cycle is reordered ahead of a fractured non-burst cycle
and the non-burst cycle is completed only after the snoop write-back cycle is completed,
provided there are no other snoop write-back cycles scheduled.
BOFF#
Overrides AHOLD and takes effect in the next clock. On-going bus cycles will stop in the clock
following the assertion of BOFF# and resume when BOFF# is de-asserted. The snoop write-back
cycle begins after BOFF# is de-asserted followed by the backed-off cycle.
HOLD
HOLD is acknowledged only between bus cycles, except for a non-cacheable, non-burst code
prefetch cycle. In a non-cacheable, non-burst code prefetch cycle, HOLD is acknowledged after
the system asserts RDY#. Once HOLD is asserted, the processor blocks all bus activities until
the system releases the bus (by de-asserting HOLD).
 Loading...
Loading...











