6-15
CACHE SUBSYSTEM
receives stale data. This can be implemented with chip select logic or with the high order address
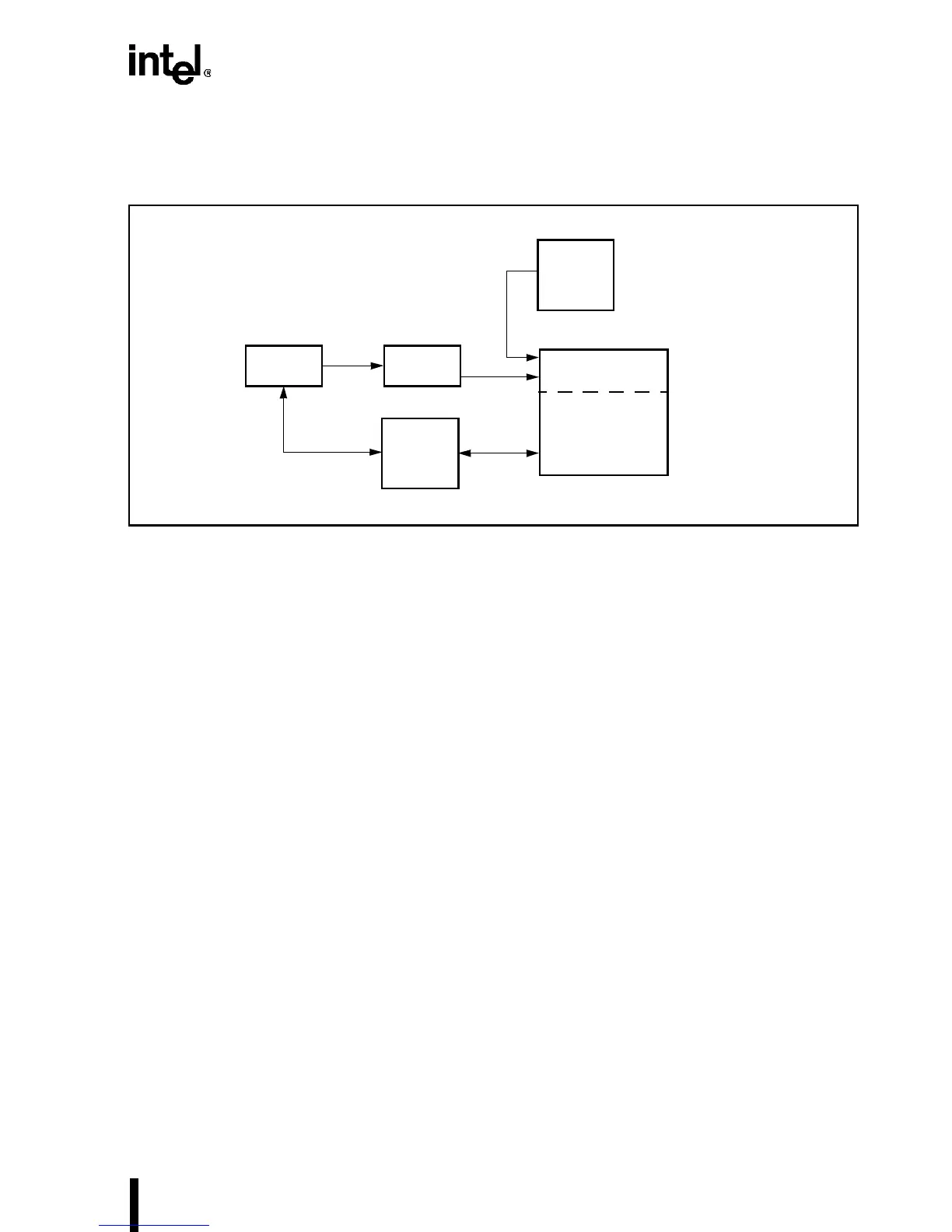
bits. Figure 6-9 shows non-cacheable memory.
Figure 6-9. Non-Cacheable Share Memory
In cache flushing, all cache locations with set dirty bits are written to main memory (for write-
back systems), then cache contents are cleared. If all of the devices are flushed before another bus
master writes to shared memory, cache consistency is maintained.
Combinations of various cache coherency techniques may be used in a system to provide an op-
timal solution. A system may use hardware transparency for time critical I/O operations such as
paging, and it may partition the memory as non-cacheable for slower I/O operations such as print-
ing.
6.5 NON-CACHEABLE MEMORY LOCATIONS
To avoid cache consistency problems, certain memory locations must not be cached. The PC ar-
chitecture has several special memory areas which may not be cached. If ROM locations on add-
in cards are cached, for example, write operations to the ROM can alter the cache while main
memory contents remain the same. Further, if the mode of a video RAM subsystem is switched,
it can produce altered versions of the original data when a read-back is performed. Expanded
memory cards may change their mapping, and hence memory contents, with an I/O write opera-
tion. LAN or disk controllers with local memory may change the memory contents independent
of the Intel486 processor. This altering of certain memory locations can cause a cache consisten-
cy problem. For these reasons, the video RAM, shadowed BIOSROMs, expanded memory
boards, add-in cards, and shadowed expansion ROMs should be non-cacheable locations. De-
pending on the system design, ROM locations may be cacheable in a second-level cache if write
protection is allowed.
CPU
Decoder
Other
Bus
Master
Cache
Non-cacheable
Cacheable
 Loading...
Loading...











