Model 2701 User’s Manual Scanning 7-29
Reference
a. ROUTe:SCAN <clist> — Channels will be scanned in the order that they are
listed. The following example shows the proper format for specifying channels in a
scan list for a sequential scan:
ROUT:SCAN (@101:110,201,204,206)
For the above scan list, the scan will run starting with the lowest numbered channel
(101) and then sequence up (forward) to the highest numbered channel (206).
Remote programming can also be used to run non-sequential scans. Any scan list
configured to scan backward is considered a non-sequential scan. The following
examples configure non-sequential scan lists:
Example 1) ROUT:SCAN (@101:105,103,106:110)
Example 2) ROUT:SCAN (@110:101)
Example 1 — The scan starts with channel 101 and proceeds to channel 105. After
channel 105 is scanned, the unit backs up to scan channel 103, then proceeds
forward to scan channels 106 through 110.
Example 2 — The scan starts with channel 110 then proceeds backward to
channel 101.
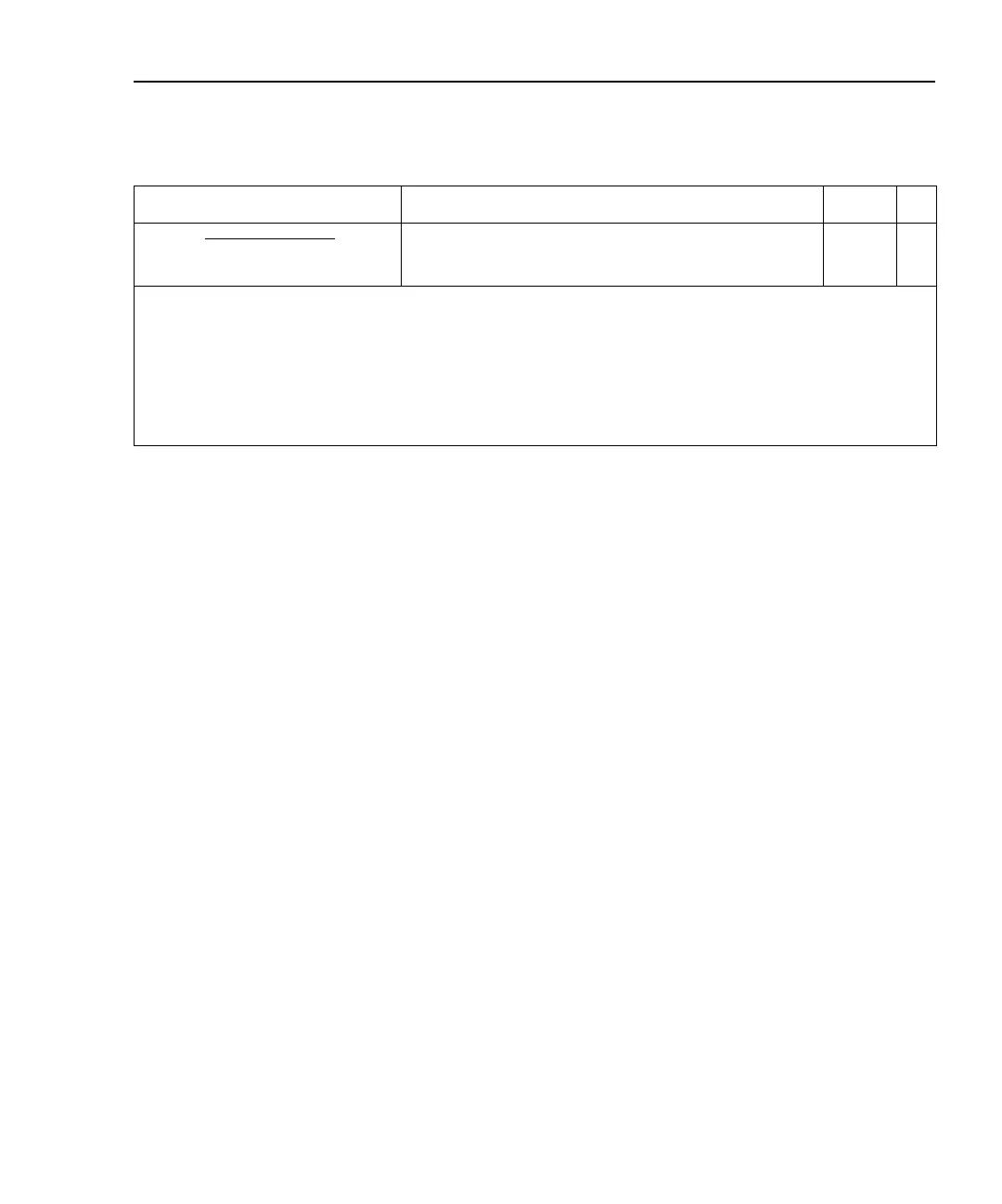
Commands Description Default Ref
Buf
fer commands
TRACe:DATA? Read buffer readings.
TRACe:CLEar Clear buffer.
Channel list parameter:
<clist> = (@SCH)
where: S = Mainframe slot number (1 or 2)
CH = Switching module channel number (must be 2 digits)
Examples: (@101) = Slot 1, Channel 1
(@101, 203) = Slot 1, Channel 1 and Slot 2, Channel 3
(@101:110) = Slot 1, Channels 1 through 10
Notes:
1. Not affected by *RST and SYSTem:PRESet. Front panel factory default is OFF.
2. *RST sets count to 1, and SYSTem:PRESet sets count to INFinity.
3. The default value depends on which switching module is installed.
Table 7-1 (continued)
Scanning commands
 Loading...
Loading...