363-206-285
A SONET Overview
Issue 3 June 2001
A-15
Synchronous Multiplexing 1
SONET's method of
byte-interleaving
DS1s to a higher signal rate permits
economical extraction of a single DS1 without the need to demultiplex the entire
STS-1 SPE. In addition, SONET provides overhead channels for use by OAM&P
groups.
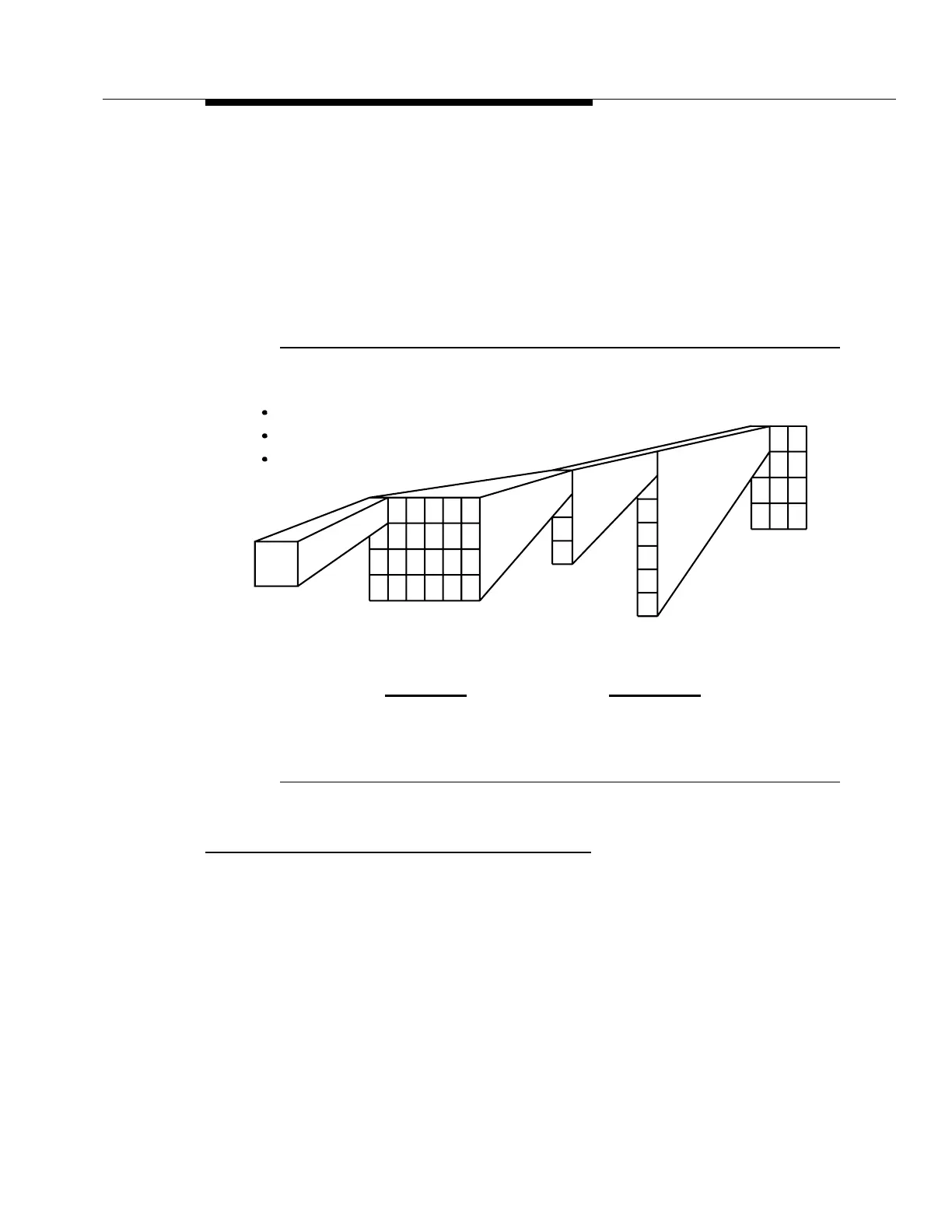
In SONET, a single asynchronous DS3 signal is mapped into an STS-1 SPE
(Figure A-12).
Figure A-12. Synchronous Multiplexing
Virtual Tributary Signals 1
Sub-DS3 asynchronous signals (DS1, DS1C, DS2 and E1) are
byte-interleaved
into a digital signal called a virtual tributary (VT). The VT is a structure designed
for the transport and switching of sub-DS3 payloads. Like the STS-1 signal, the
VT signal has a floating pointer that allows each VT SPE to move within the VT
structure. There are four sizes of virtual tributaries (VT1.5, VT2, VT3, VT6). Higher
rate payloads are transported as one or more concatenated STS-1 signals.
1 VF Circuit = 1 DSO
Byte Interleaving above DS1
DS1 Observable above DS1
Standard End-To-End Overhead Channel
4VT1.5s =VT-G 7VT-Gs
+ STS-1 Path OH
+ STS-1 Line OH
+ STS-1 Section OH
1 STS-1
24 DS0s = 1 DS1
24 DS0s
+ 3 DS0s (VT OH)
1VT1.5
STS-1 X N = OC-N

 Loading...
Loading...