277
Data Movement Instructions Section 5-18
Example
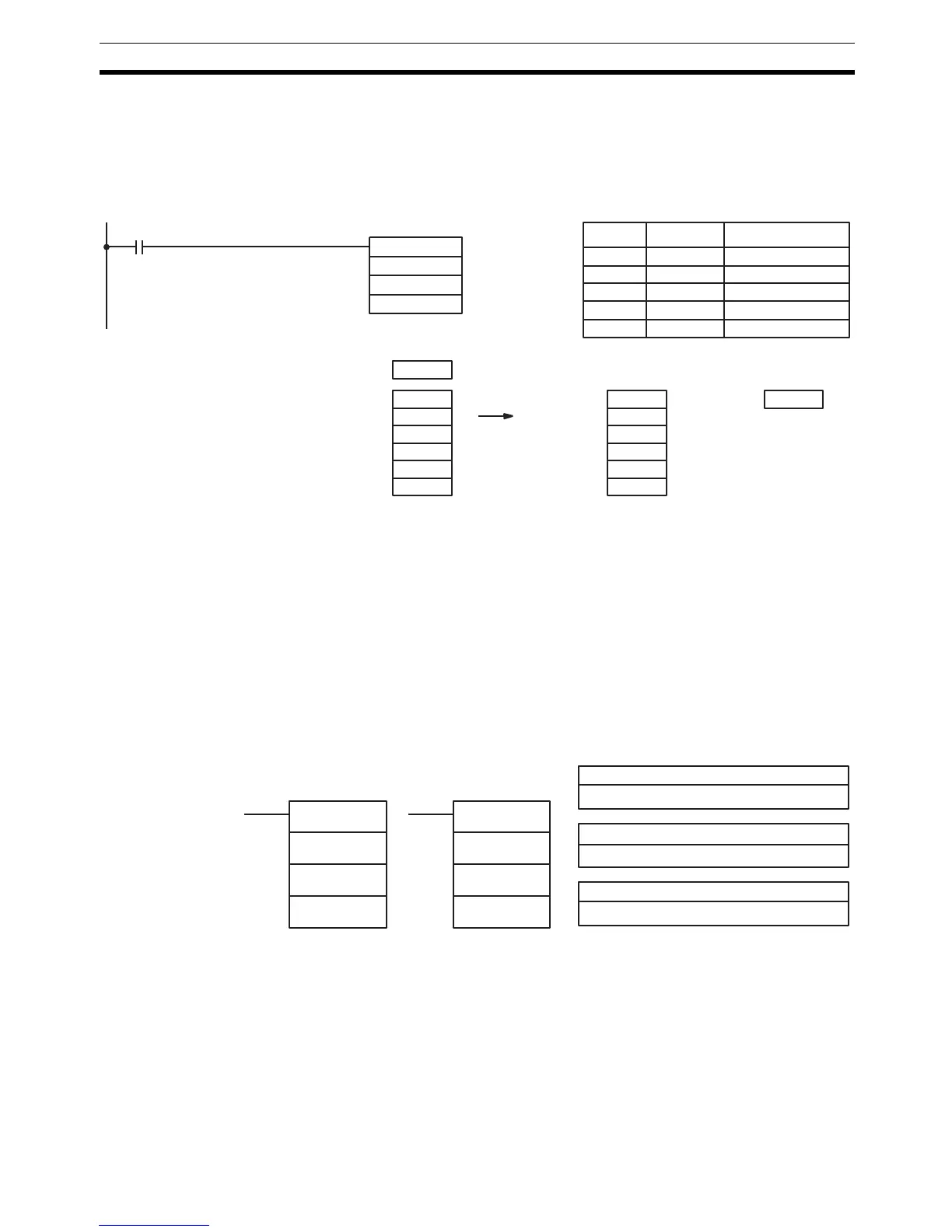
The following example shows how to use COLL(81) to create a stack between
DM 0001 and DM 0005. DM 0000 acts as the stack pointer.
When IR 00000 goes from OFF to ON, COLL(81) copies the content of
DM 0005 (DM 0000 + 5) to IR 001. The content of the stack pointer (DM 0000)
is then decremented by one.
Flags ER: The offset or stack length in the control word is not BCD.
Indirectly addressed EM/DM word is non-existent.
(Content of *EM/*DM word is not BCD, or the EM/DM area boundary
has been exceeded.)
During stack operation, the value of the stack pointer exceeds the
length of the stack; an attempt was made to write to a word beyond
the end of the stack.
EQ: ON when the content of S is zero; otherwise OFF.
5-18-8 MOVE BIT – MOVB(82)
Limitations The rightmost two digits and the leftmost two digits of Bi must each be
between 00 and 15.
DM 6144 to DM 6655 cannot be used for Bi or D.
@COLL(81)
DM 0000
216
001
00000
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00000
00001 @COLL(81)
DM 0000
216
001
DM 0000 0005
DM 0001 AAAA
DM 0002 BBBB
DM 0003 CCCC
DM 0004 DDDD
DM 0005 EEEE
Stack pointer
decremented
IR 216 8005
DM 0000 0004
DM 0001 AAAA
DM 0002 BBBB
DM 0003 CCCC
DM 0004 DDDD
DM 0005 EEEE
IR 001 EEEE
S: Source word
IR, SR, AR, DM, EM, HR, LR, #
Bi: Bit designator (BCD)
IR, SR, AR, DM, EM, HR, TIM/CNT, LR, #
Ladder Symbols
Operand Data Areas
D: Destination word
IR, SR, AR, DM, EM, HR, LR
MOVB(82)
S
Bi
D
@MOVB(82)
S
Bi
D
 Loading...
Loading...