203
Polyend Tracker Manual
202
Polyend Tracker Manual
NOTESNOTES
Flanger
Flanger follows similar principles to delay by doubling the audio and
introducing a slight phase shift and delay between the audio signals when
playing back. Flangers offer an evolving sweeping sound.
Equalizer, Compressor and Limiter.
The three effects, Equalizer, Compressor and Limiter are used for mixing
and nalising a sample rather than creative variations. In music production
they often nd themselves towards the end of a signal chain and are used
to polish and nish off a track, gluing tracks together, developing a
combined tonal balance, managing loudness and mastering a nal release.
In the context of Tracker sample editing, the process operates at an
individual sample level. However the same principles can be applied as
those in general music production, to nish off and generate a nal output
sample. While these effects are applied individually they can also optionally
be performed sequentially in order depending on what the objective is. An
example shown below.
Balances tonal elements in
a sound.
Provides harmonic
emphasis to elements and
makes space for others.
Can x stray frequencies
that affect the sound
Reduces dynamic range between
high peaks and low troughs,
allows overall level adjustment.
Can help sounds sit into a mix
better. Layered compressed /
uncompressed adds punch.
Create headroom.
Restricts and tames excessive
audio peaks in a sound.
Maximises output levels and
introduces a perceived loudness.
Protects digital integrity of a
sample by avoiding clipping.
Equalizer Compressor Limiter
Example of Effect Chain / Order
Audio
8
Audio
8
BackLength
2 ms
Depth
3
Rate
1.000 Hz
Offset
50 %
ApplyPreview
Sample Editor Flanger
8.beats
Depth
Amount of anger effect applied.
Tweak by Ear
While the anger and perhaps other effects have labelled functions, it is much more useful to tune these
parameters by ear rather than by numerical positioning. The application of each parameter will give a different
output depending on the source audio material. Sounds ranging from subtle tremolo to glitchy rhythms can be
found by tweaking the anger parameters by ear. The same applies to all of the creative audio effects.
Rate
Speed of effect modulation.
Length
Length of delay line between signals.
Offset
Offset percentage of delay in signal
Tweaking and trying different settings is encouraged on creative audio
effects. While this is also possible on the process orientated tools, it is also
recommended to get to know these parameters functions and purposes and
have a basic understanding of their operation.
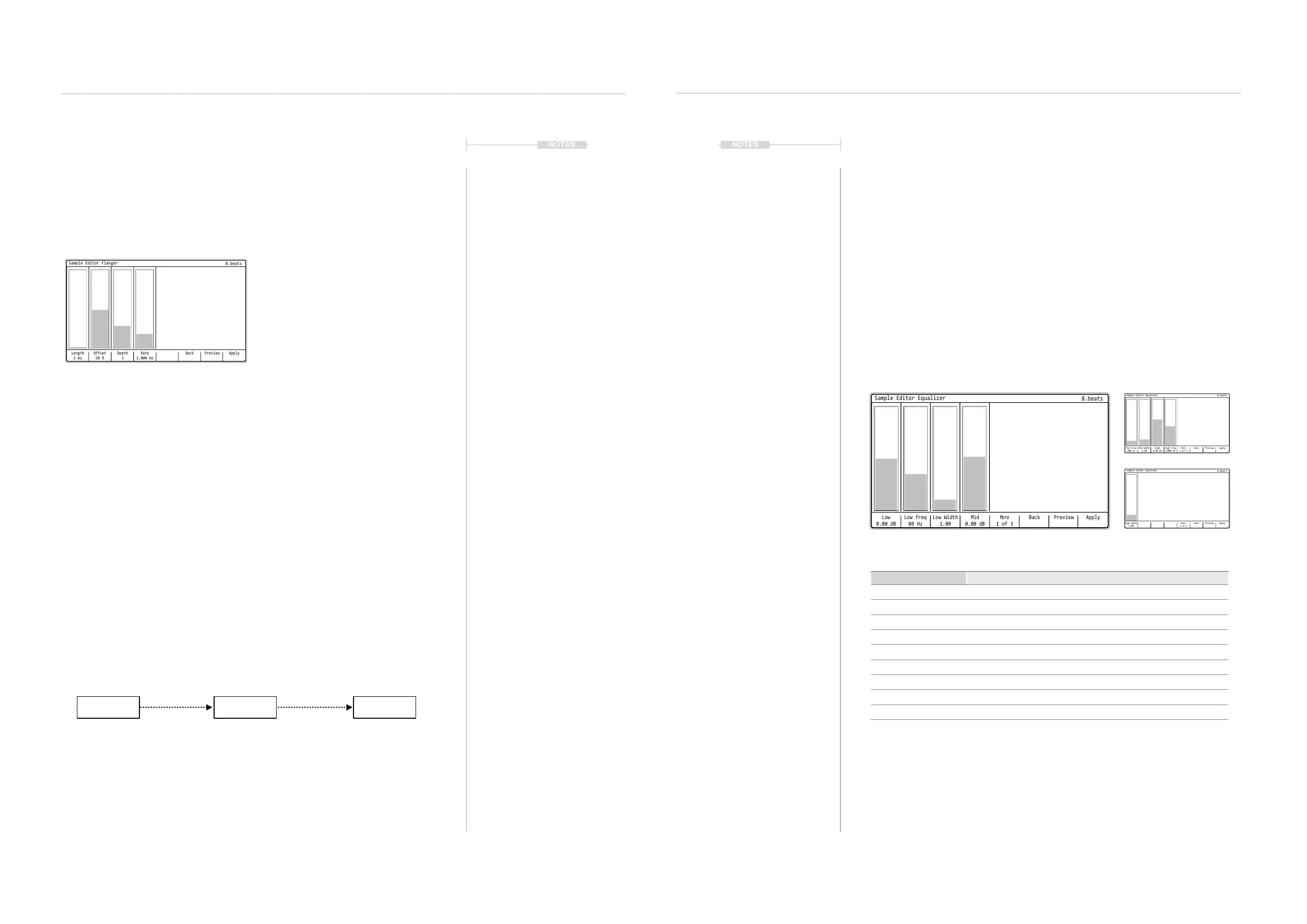
Equalizer
The purpose of an equalizer, also called EQ, is to boost or attenuate
frequencies in an audio signal to either adjust the tonal characteristics or to
x unwanted frequency elements. Equalizers are typically used to shape a
sounds character but also to allow a sound to sit comfortably alongside
another. The sample editor EQ effect has 3 frequency bands. More
coverage of general EQ functions is provided in the Master Effects section.
BackLow
0.00 dB
Low Width
1.00
Mid
0.00 dB
More
1 of 3
Low freq
80 Hz
ApplyPreview
Sample Editor Equalizer
8.beats
BackMid freq
800 Hz
High
0.00 db
High freq
12000 Hz
More
2 of 3
Mid Width
1.00
ApplyPreview
Sample Editor Equalizer
8.beats
BackHigh Width
1.00
More
3 of 3
ApplyPreview
Sample Editor Equalizer
8.beats
Page 1 of 3 Page 2 of 3
Page 3 of 3
EQ Function
Description
Low Low attenuation or boost amount, -12 dB to + 12dB.
Low Freq Low Frequency range, 10Hz - 200Hz
Low Width Width of EQ, also called Q. Range 0.5 to 5.
Mid Mid attenuation or boost amount, -12 dB to + 12dB.
Mid Freq Low Frequency range, 100Hz - 8KHz
Mid Width Width of EQ, also called Q. Range 0.5 to 5.
High High attenuation or boost amount, -12 dB to + 12dB.
High Freq High Frequency range, 8KHz -20KHz
High Width Width of EQ, also called Q. Range 0.5 to 5.
 Loading...
Loading...