RL78/F13, F14 CHAPTER 15 SERIAL ARRAY UNIT
R01UH0368EJ0210 Rev.2.10 896
Dec 10, 2015
SPI function performs the following three types of communication operations.
• Master transmission (See 15.6.1 Master transmission.)
• Master reception (See 15.6.2 Master reception.)
• Master transmission/reception (See 15.6.3 Master transmission/reception.)
• Slave transmission (See 15.6.4 Slave transmission.)
• Slave reception (See 15.6.5 Slave reception.)
• Slave transmission/reception (See 15.6.6 Slave transmission/reception.)
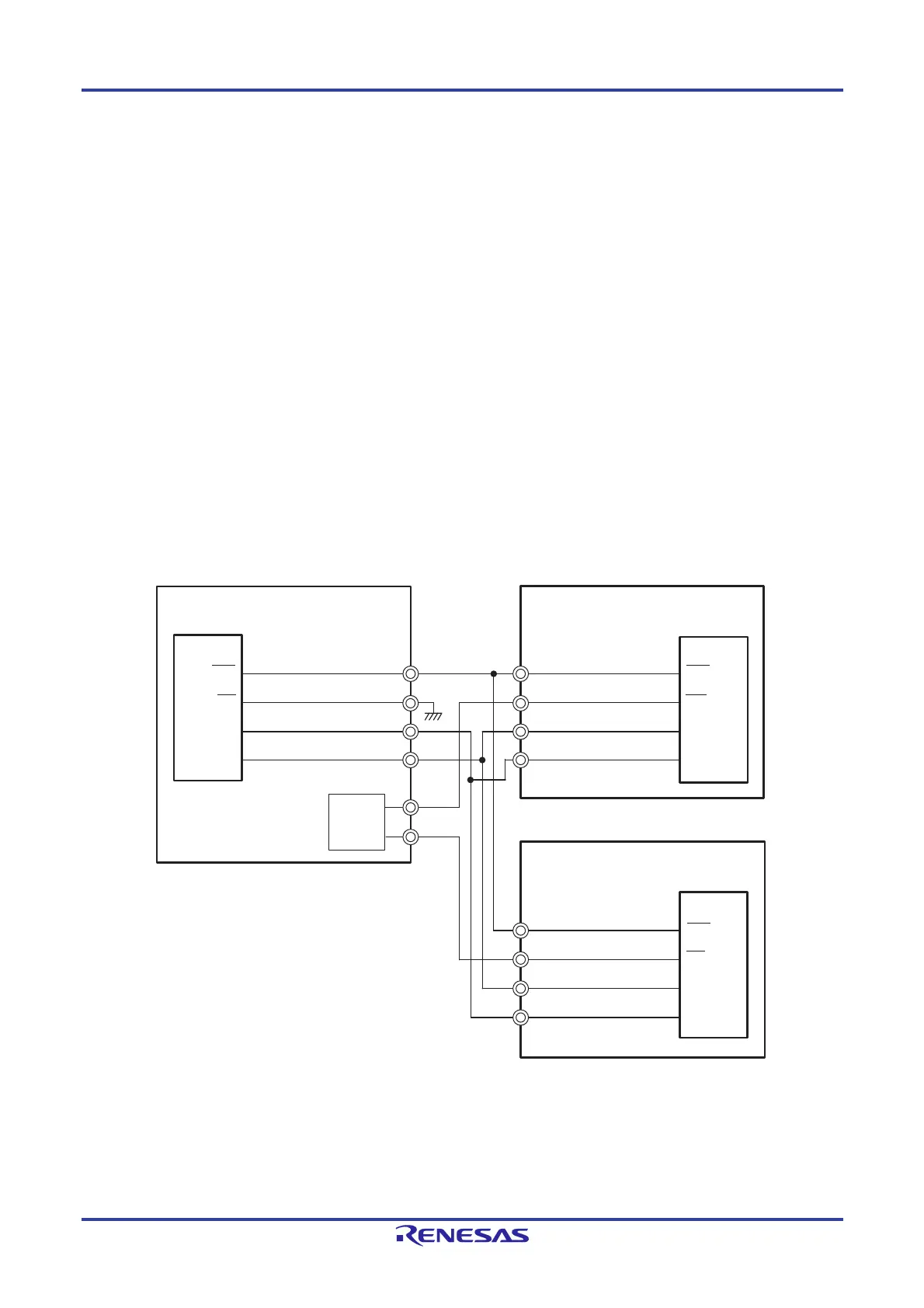
Multiple slaves can be connected to a master and communication can be performed by using the slave select input
function. The master outputs a slave select signal to the slave (one) that is the other party of communication, and each
slave judges whether it has been selected as the other party of communication and controls the SO pin output. When a
slave is selected, the SO pin is set to output state and transmit data can be communicated from the SO pin to the master.
When a slave is not selected, the SO pin is set to Hi-Z state and prevents the short circuit with the output from the SO pin
of other slaves. Therefore, in an environment where multiple slaves are connected, it is necessary set the SO pin to N-ch
open-drain and pull up the node. Furthermore, when a slave is not selected, no transmission/reception operation is
performed even if a serial clock is input from the master.
Caution Output the slave select signal by port manipulation.
Figure 15-72. Example of Slave Select Input Function Configuration
SAU
SAU
SCK
SSI
SI
SO
SAU
Master
Slave
Slave
Port
SCK
SSI
SI
SO
SCK
SSI
SI
SO

 Loading...
Loading...











