Basics of Path Interpolation
2.5 Path interpolation types
TO Path Interpolation
Function Manual, 11/2010
21
● Mode of path-synchronous motion in wMode
● Direction of path-synchronous motion in
wDirection
● End point of path-synchronous motion in
w
Details of the object coordinate system
(see Object coordinate system (OCS) on the path objec
t (Page 69) )
● Specification of the coor
dinate system in
csType
This parameter is used to set whether the motion should be performed in the base
coordinate system or in an object coordinate system.
● Specification of the object coordinate system in
csNumber
This parameter is used to set which object coordinate system should be used for the
motion.
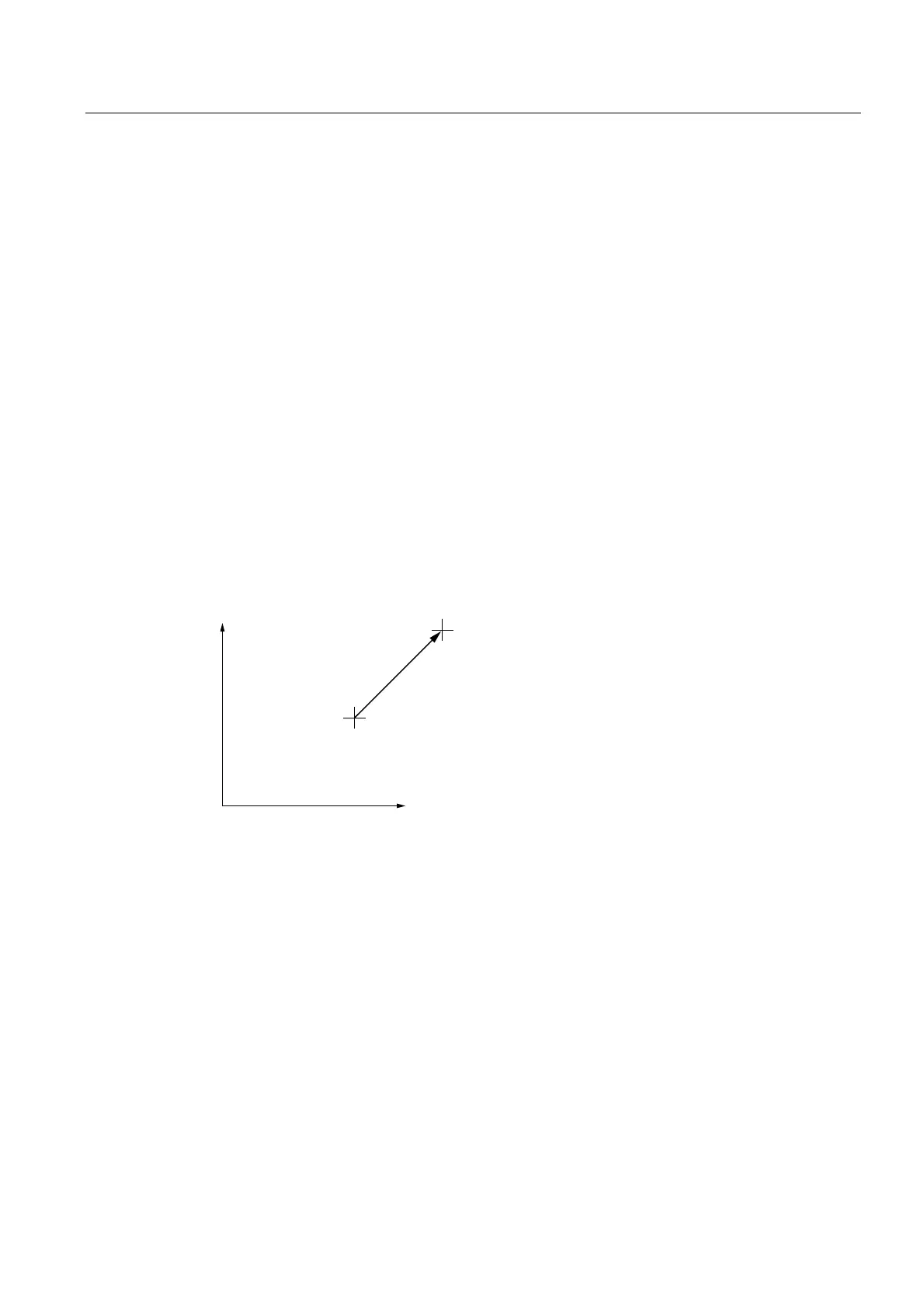
2.5.3 Linear paths
In the case of linear path interpolation, an end point is approached on a straight line starting
from the current position.
Linear paths are traversed with the _movePathLinear() command.
[
\
&XUUHQWSRVLWLRQ
(QGSRLQW
Figure 2-8 Example of a linear path
Example of a linear path in ST
In this example, the current position and the end point lie in the X-Y plane. Each end point is
separated by 10 units in the positive direction from the current position along both axes.
myRetDINT :=
_movePathLinear(
pathObject:=pathIPO,
pathPlane:=X_Y,
pathMode:=relative,
x:=10.0,
y:=10.0
);

 Loading...
Loading...











