Basics of Path Interpolation
2.5 Path interpolation types
TO Path Interpolation
Function Manual, 11/2010
23
Example of a circular path with radius, end point, and orientation
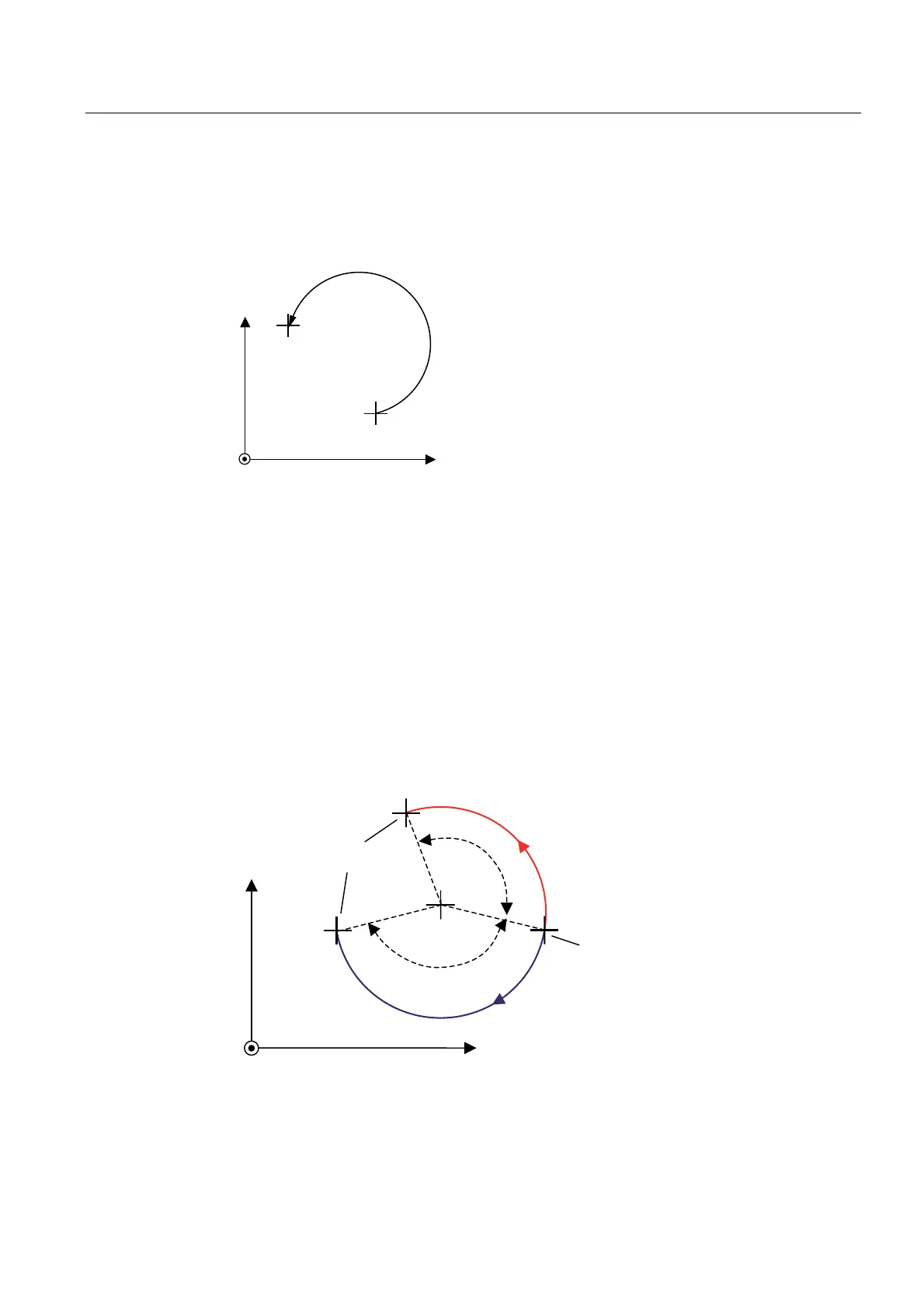
In this example, the current position and the end point lie in the X-Y plane. The end point is
separated from the current position by -10 units along the x-axis and 10 units along the y-
axis. The large circle is traveled in the positive direction.
[
\
(QGSRLQW
&XUUHQWSRVLWLRQ
Figure 2-10 Example of circular path with radius, end point, and orientation
myRetDINT :=
_movePathCircular(
pathObject:=pathIPO,
pathPlane:=X_Y,
circularType:=WITH_RADIUS_AND_ENDPOSITION,
circleDirection:=LONG_RUN_POSITIVE,
pathMode:=RELATIVE,
x:=-10.0,
y:=10.0,
radius:=12.0
);
2.5.4.3 Circle using center and angle
3RVLWLYHRULHQWDWLRQ
(QGSRLQW
&XUUHQWSRVLWLRQ
1HJDWLYHRULHQWDWLRQ
&HQWHUSRLQW
$QJOH
&RRUGLQDWH
&RRUGLQDWH
Figure 2-11 Circular path with center point and angle

 Loading...
Loading...











