Basics of Path Interpolation
2.13 Kinematic adaptation
TO Path Interpolation
68 Function Manual, 11/2010
$
$
[
]
$
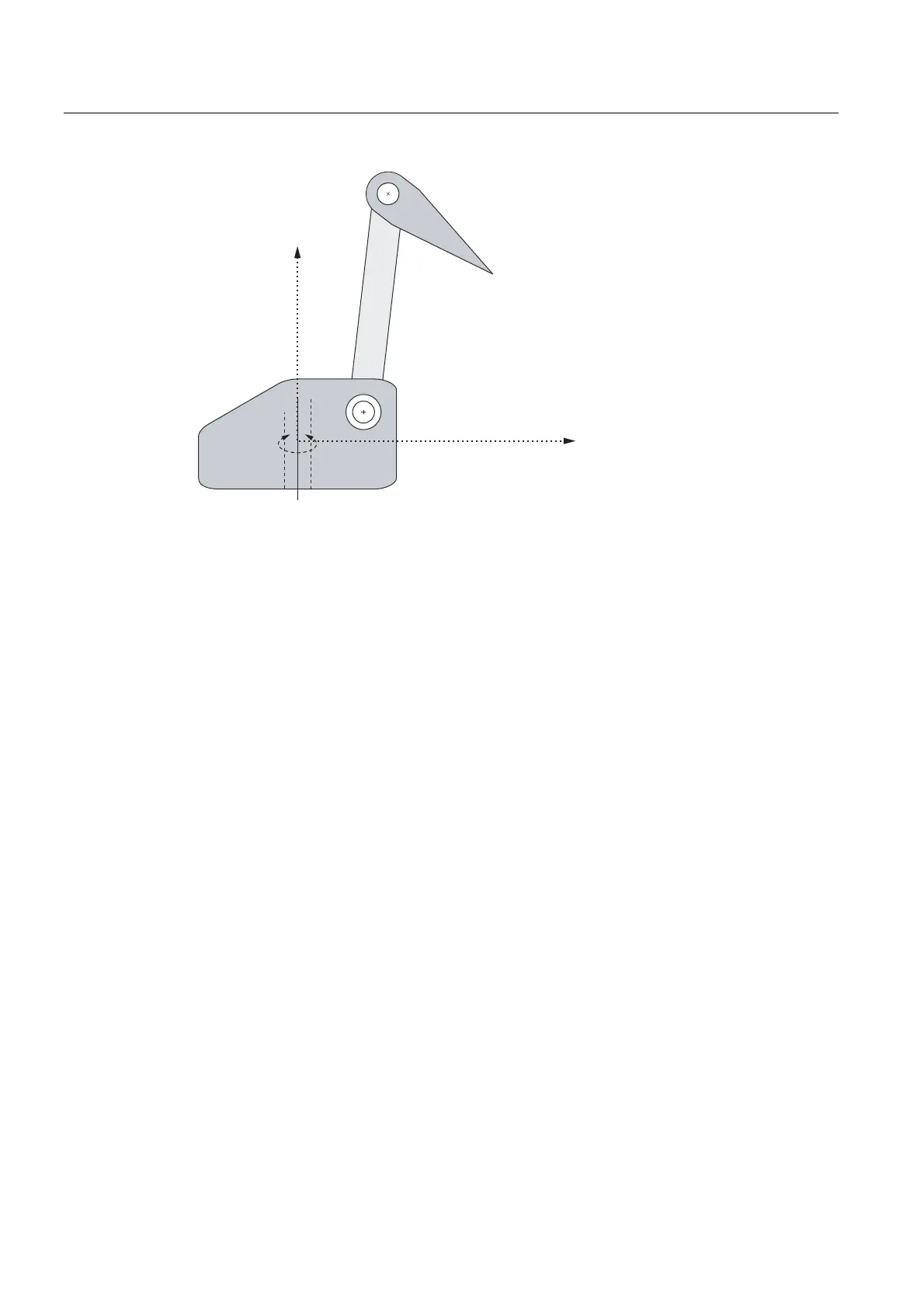
Figure 2-57 Articulated arm kinematics: Axes
● A1 axis: 1. Path axis
● A2 axis: 2. Path axis
● A3 axis: 3. Path axis
If your kinematic system does not provide any axis for the first path axis, you must create a
virtual axis for the first path axis and so interconnect the path object. The path object must
be created on the Z-X main plane (BasicOffset.y:=0) and may only travel there.
2.13.3.12 Specific kinematics
SPECIFIC kinematics type
The SPECIFIC kinematics type can be set using the typeOfKinematics configuration datum.
Example of settings on path object
Kinematics.typeOfKinematics = SPECIFIC (6)
The kinematics and parameters required can then be specified by the TrafoID and a
parameter list.
See also
Appendix A (Page 137)

 Loading...
Loading...











