Basics of Path Interpolation
2.15 Interconnection, interconnection rules
TO Path Interpolation
80 Function Manual, 11/2010
myRetDINT :=
_movePathLinear(
pathObject:=Portal_3D,
pathMode:=ABSOLUTE,
x:=dispose_x,
y:=dispose_y,
z:=dispose_z,
cstype:=BCS
);
2.15 Interconnection, interconnection rules
[
\
]
3DWKREMHFW
3DWKD[LV
3DWKD[LV
3DWKD[LV
3RVLWLRQLQJ
D[LV
3RVLWLRQLQJ
D[LV
&DP
3DWKD[LVLQWHUIDFH
3RVLWLRQLQJD[LVLQWHUIDFHIRU
SDWKV\QFKURQRXVPRWLRQ
0RWLRQ2XW[\]
LQWHUIDFH
&DPLQWHUIDFH
7UDFNLQJ,Q
LQWHUIDFH
HJH[WHUQDO
HQFRGHU
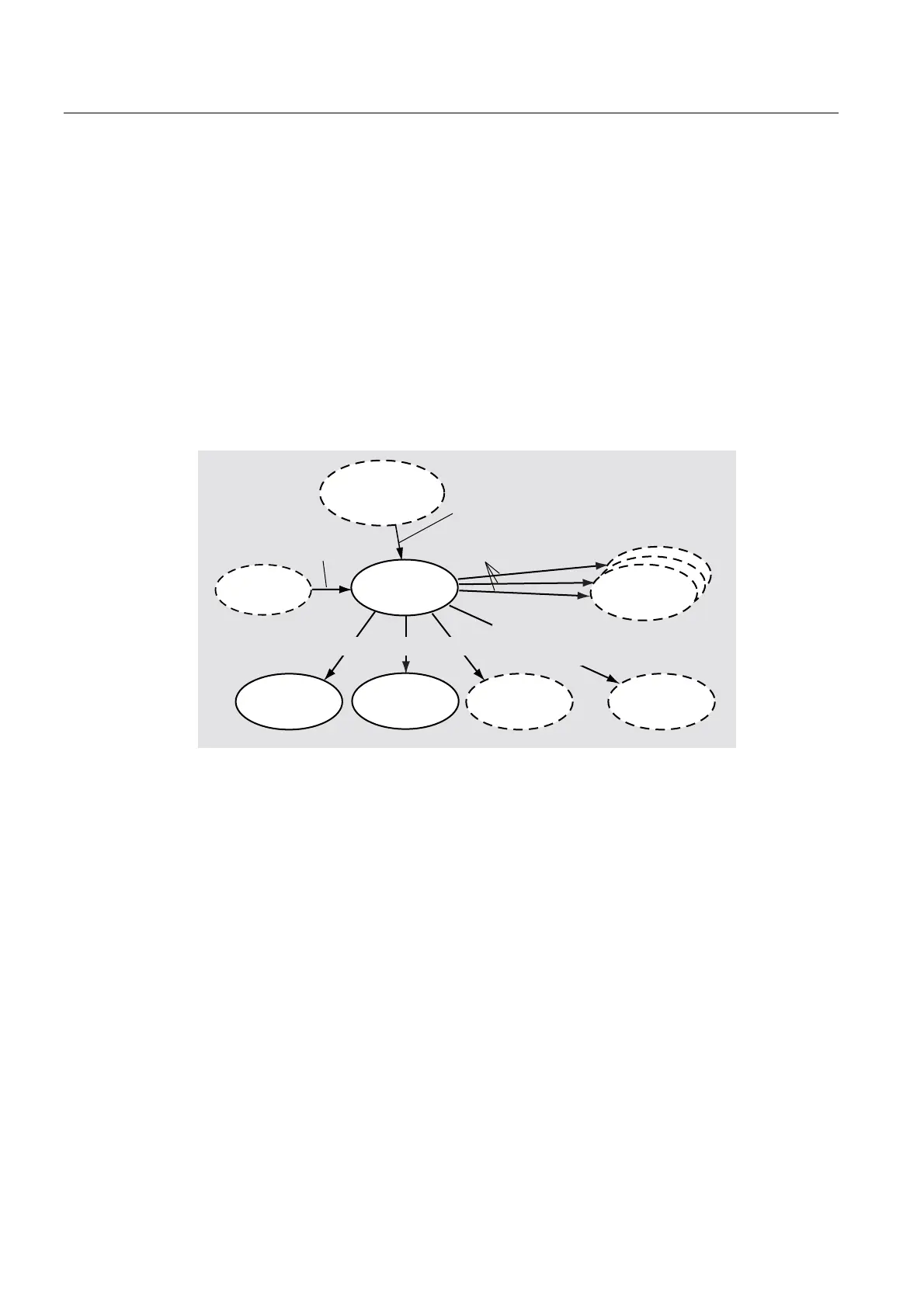
Figure 2-69 Interfaces on the path object
● Path axis interface 1 and path axis interface 2 of a path object must be interconnected
with path axes.
● Path axis interface 3 of the path object can optionally be interconnected with a path axis,
irrespective of the kinematic settings.
● The positioning axis interface for the path-synchronous motion can optionally be
interconnected with a positioning axis.
● The MotionOut.x, MotionOut.y or MotionOut.z interface can optionally be interconnected
with a positioning axis.
● The path object can be interconnected with a cam for specifying a velocity profile.
● To specify a motion sequence reference value, the TrackingIn interface can be
interconnected with a TO that provides an output interface with position value.
For additional information, see Motion Control Basic Functions Function Manual, "Available
technology objects".

 Loading...
Loading...











