Basics of Path Interpolation
2.13 Kinematic adaptation
TO Path Interpolation
Function Manual, 11/2010
43
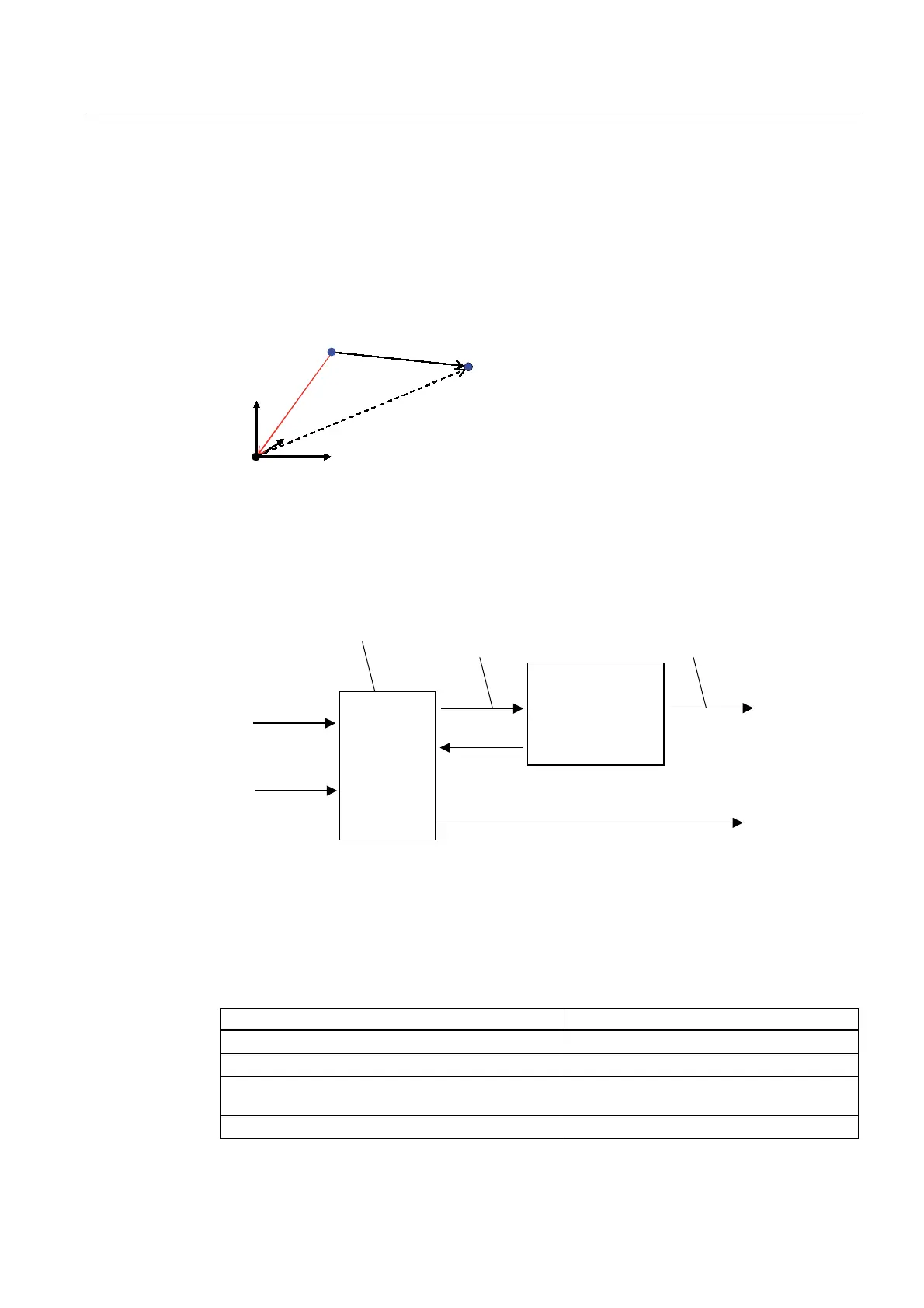
2.13.2.2 Reference points
The following reference points are used in path interpolation:
● Cartesian zero point
● Kinematic zero point
● Kinematic end point
(because a tool is not taken into account, this is equal to the path point)
EDVLF2IIVHW
.LQHPDWLFHQGSRLQW
SDWKSRLQW
&DUWHVLDQ]HURSRLQW
.LQHPDWLF]HURSRLQW
Figure 2-27 Reference points of the coordinate systems in path interpolation
The path object calculates the position on the path. This is also the kinematic end point.
2.13.2.3 System variables for path interpolation and transformation on the path object
3DWKGDWD
&DUWHVLDQ
GHIDXOWV
'HIDXOWVRQSDWKD[HVIURP
SDWKPRWLRQ
7UDQVIRUPDWLRQ
3DWK
LQWHUSRODWRU
'HIDXOWVRQSRVLWLRQLQJD[LV
IURPV\QFKURQRXVSDWK
PRWLRQ
3DWKFRPPDQGVWDWXVHV
3DWKFRPPDQGV
2YHUULGH
&DUWHVLDQ
DFWXDOYDOXHV
Figure 2-28 Overview of system variables of the path object
The position values and dynamic values can be accessed via a system variable:
Path data
System variables Description
path.acceleration Path acceleration
path.command Status of a motion command
path.dynamicAdaption Indicator that maximum dynamic values of
path axes are being taken into account
path.length Length of the current path

 Loading...
Loading...











