Basics of Path Interpolation
2.13 Kinematic adaptation
TO Path Interpolation
Function Manual, 11/2010
45
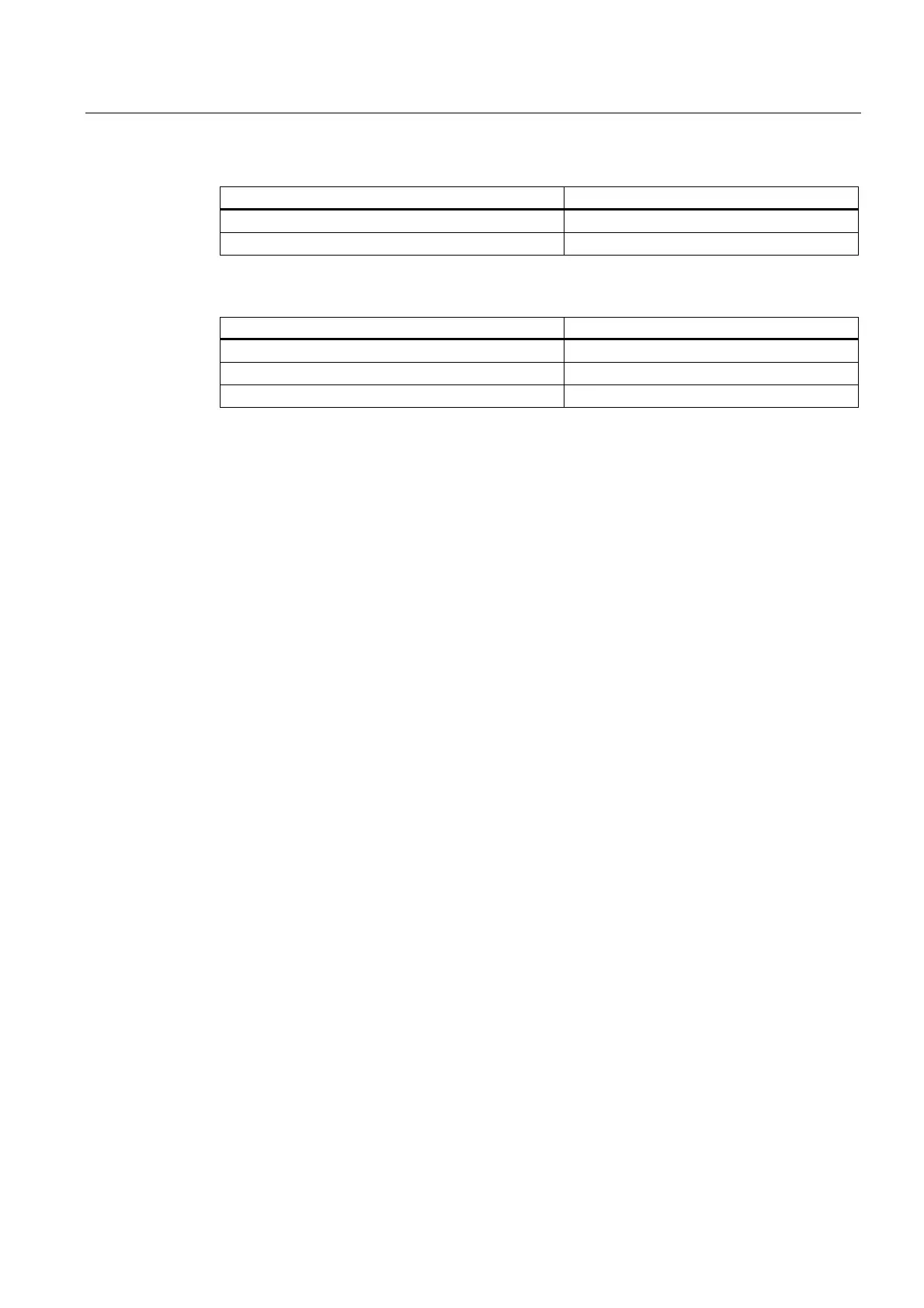
System variables Description
override.acceleration Acceleration override
override.velocity Velocity override
Path command statuses
System variables Description
linearPathCommand.state Status of linear interpolation
circularPathCommand.state Status of circular interpolation
polynomialPathCommand.state Status of polynomial interpolation
2.13.2.4 Transformation of the dynamic values
The kinematicsData.transformationOfDynamics system variable indicates whether a
kinematic transformation supports the dynamics transformation functionality.
2.13.2.5 Differentiation of link constellations
If Cartesian kinematics end points can be reached via various articulation positions,
articulation positioning spaces are defined for the corresponding kinematics.
All path motions take place in the same link constellation. For this reason, a change to
another link constellation is not possible when a path is being executed. A change to another
link constellation is possible through individual axis motions but not via a motion on the path
object.
The current transformation-specific link constellation is indicated on the setpoint side in the
bcs.linkConstellation variable and on the actual value side in the bcs.linkConstellationActual
variable.
The link constellation is defined specifically for each transformation. See Supported
kinem
atics (Page 48).
2.13.2.6 Information commands for the kinematic transformation
In addition to the implicit conversion in the system, the transformation calculations can also
be accessed directly via user commands.
● The _getPathCartesianPosition() command is used to calculate the Cartesian positions
for the axis positions specified in the command.
● The _getPathAxesPosition() command is used to calculate the axis positions from the
Cartesian positions.
● The _getPathCartesianData() command is used to calculate the Cartesian data for the
position, velocity, and acceleration from the axis positions, axis velocities, and axis
accelerations specified in the command.
● The _getPathAxesData() command is used to calculate the axis positions, axis velocities,
and axis accelerations from the Cartesian data for the position, velocity, and acceleration
specified in the command.

 Loading...
Loading...











