Basics of Path Interpolation
2.7 Stopping and resuming path motion
TO Path Interpolation
Function Manual, 11/2010
35
[
\
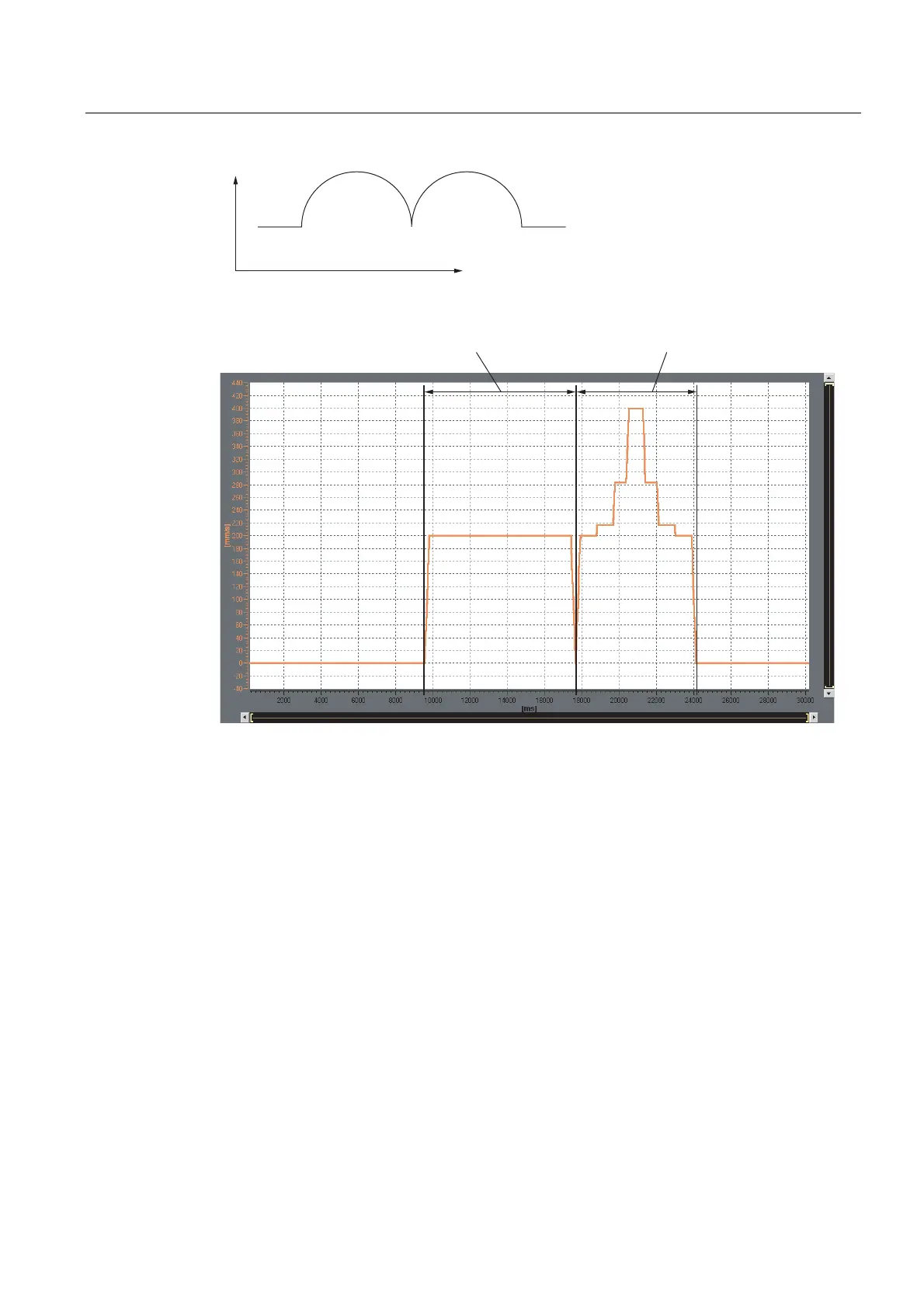
Figure 2-22 Example: Limiting the path dynamics
$&7,9(B:,7+B&2167$17B/,0,76
$&7,9(B:,7+B9$5,$%/(B/,0,76
Figure 2-23 Trace: ACTIVE_WITH_CONSTANT_LIMITS, ACTIVE_WITH_VARIABLE_LIMITS
Override
A velocity override (system variable override.velocity) and an acceleration override (system
variable override.acceleration) are available on the path object.
2.7 Stopping and resuming path motion
The _stopPath() command can be used to stop the current path motion. A stopped, but not
canceled, path motion can be continued with the _continuePath() command.
When the path motion is resumed, the motion properties (velocity profile, acceleration, etc.)
of the interrupted path command are applied. With SIMOTION V4.2 and higher, other
dynamism parameters can be specified directly at the command _continuePath().
In the case of canceled path motions, if you want the application to start at the abort position,
the last calculated setpoint position on the path is indicated in the abortPosition system
variable.
Dynamic response for _stopPath()

 Loading...
Loading...











