Basics of Path Interpolation
2.5 Path interpolation types
TO Path Interpolation
Function Manual, 11/2010
27
Smooth-path transition between two linear paths
[
\
33
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
33
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
BPRYH3DWK3RO\QRPLDO
'LUHFWLRQRIPRWLRQ
)LUVWDQGVHFRQG
GHULYDWLYHDWVWDUWSRLQW
)LUVWDQGVHFRQG
GHULYDWLYHDWHQGSRLQW
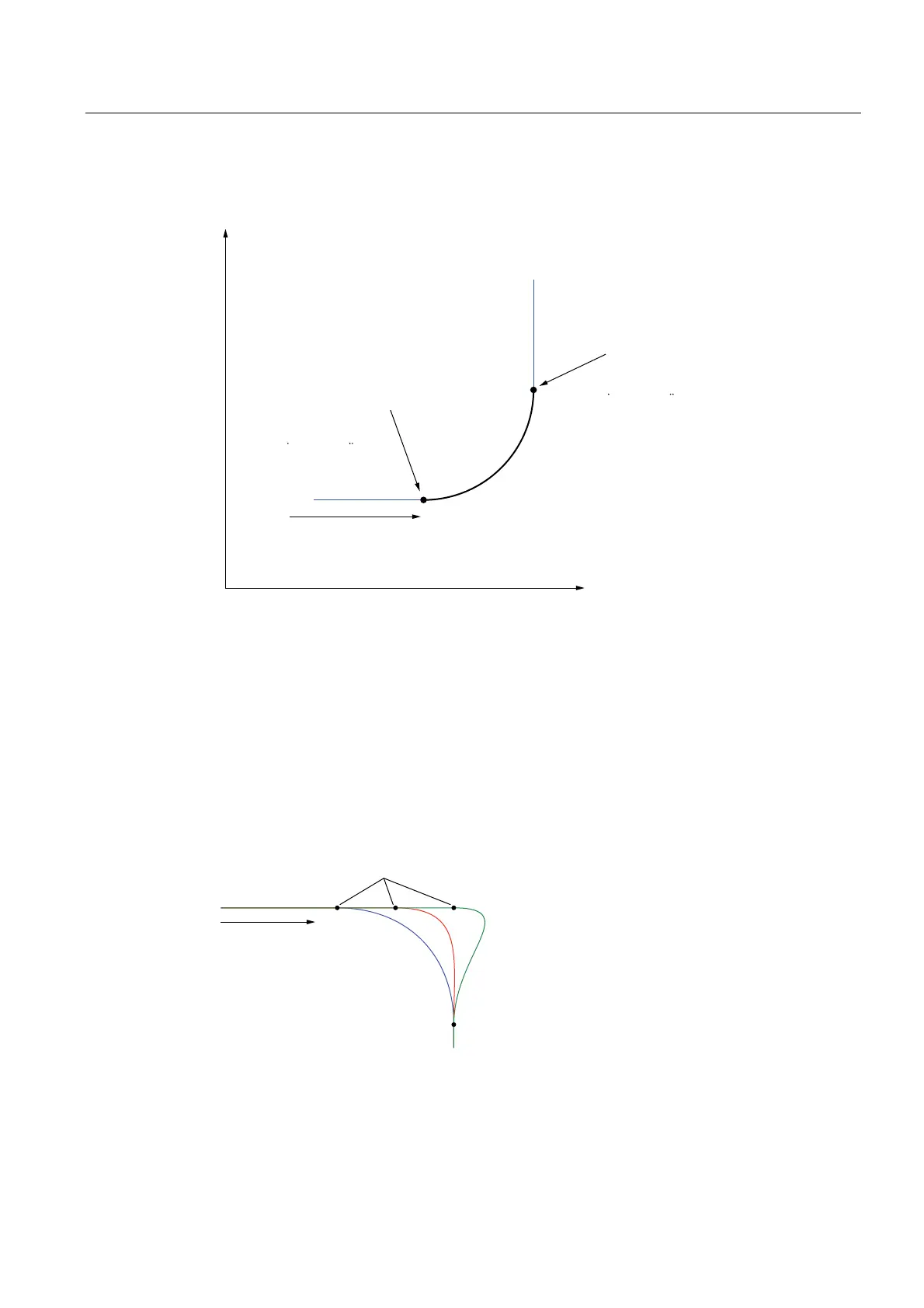
Figure 2-16 Specification of derivatives for polynomial transition between two linear paths
The derivatives at the end point of the previous geometry and at the start point of the
following geometry can be calculated with the _getLinearPathGeometricData(),
_getCircularPathGeometricData() and _getPolynomialPathGeometricData() commands.
If a polynomial path is not traversed because of the geometry, the 50002 error will be issued.
Effect of the start and end points
When polynomials are used, they must be linked smoothly to the previous and subsequent
path segment. Depending on the choice of the start and end points, there are consequently
different polynomial curves that can deviate significantly from a circular path.
The following graphic shows the curve of a polynomial path with different start points:
3RO\QRPLDOVWDUWSRLQW
'LUHFWLRQRIPRWLRQ
3RO\QRPLDOHQGSRLQW
Figure 2-17 Behavior of a polynomial path with different start points

 Loading...
Loading...











