Developing Methods
User Information 111
Varying Event Times
Vial equilibration time
The time that the sample vial spends in the oven determines the
amount of analyte in the headspace gas and the presence or
absence of equilibrium. The Headspace Sampler can be
programmed to analyze a series of samples to determine if
equilibrium is reached.
To determine if equilibrium is reached, use Chain Methods (see
Chaining Methods on page 104) to increase the Vial
Equilibration Time for each method in the chain, or use Param
Increment (see Parameter Increment on page 68) to increase
the Vial Equilibration Time for each successive sample in the
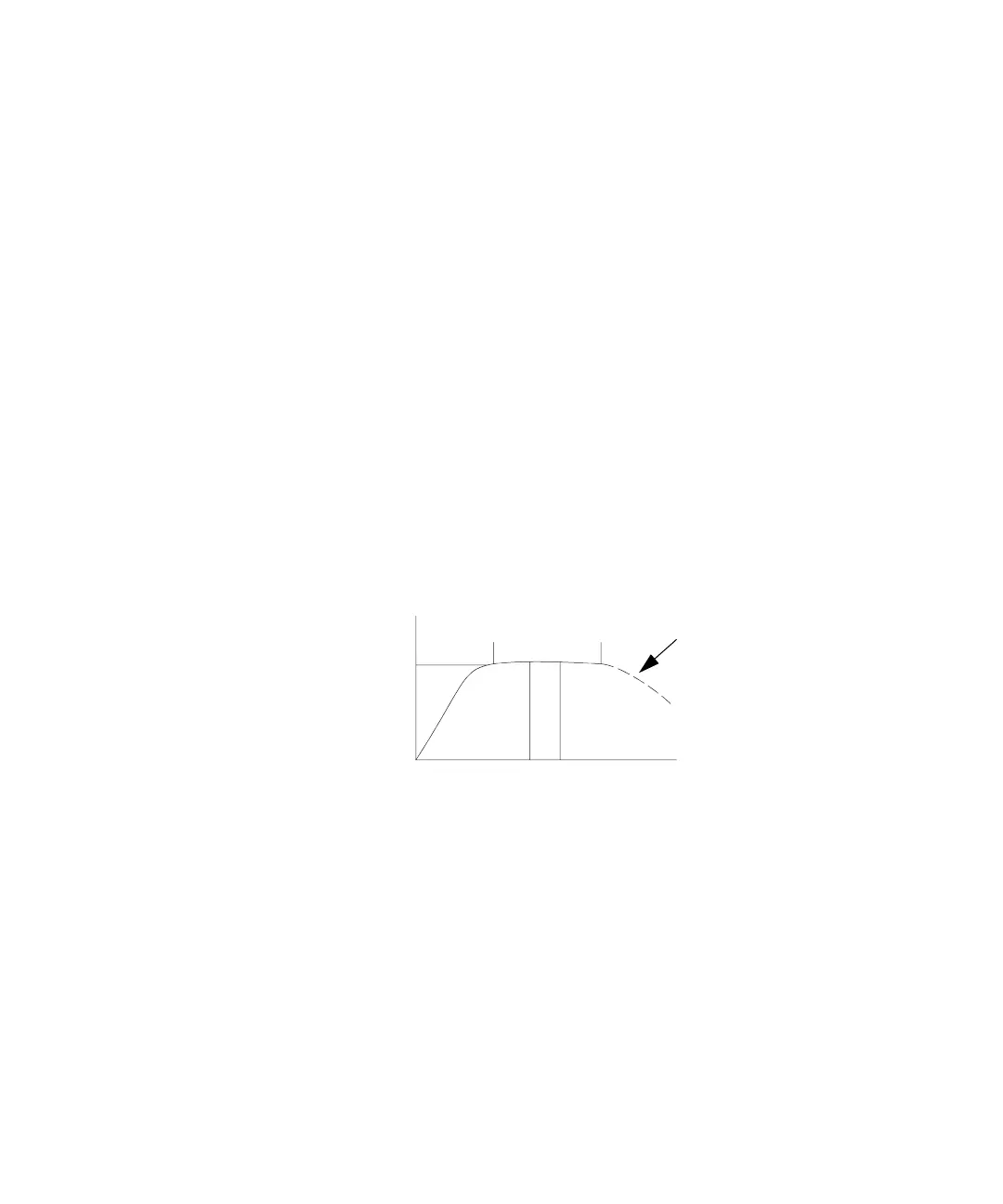
series. Then plot the peak area versus equilibration time for a
certain peak. The system is at equilibrium when this curve
flattens out. See Figure 16.
Loop fill time
Normally, set the loop fill time to 10 seconds.
A very short loop–fill time (one or two seconds) may help
increase sensitivity in headspace analysis. The headspace gas
purges the sample loop, but the vent valve is closed before the
sample vial falls to atmospheric pressure. The loop is
Figure 16 Equilibration curve
[X]
G
∆[X]
G
≈ 0
Equilibrium
∆T
Heating Time
Degradation
Condition
Where:
X is the component of interest
[X]
G
is the concentration of X
medium_standard.book Page 111 Tuesday, February 17, 2004 10:14 AM

 Loading...
Loading...











