DL205 User Manual, 4th Edition, Rev. D
5-54
Chapter 5: Standard RLL Instructions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
B
C
D
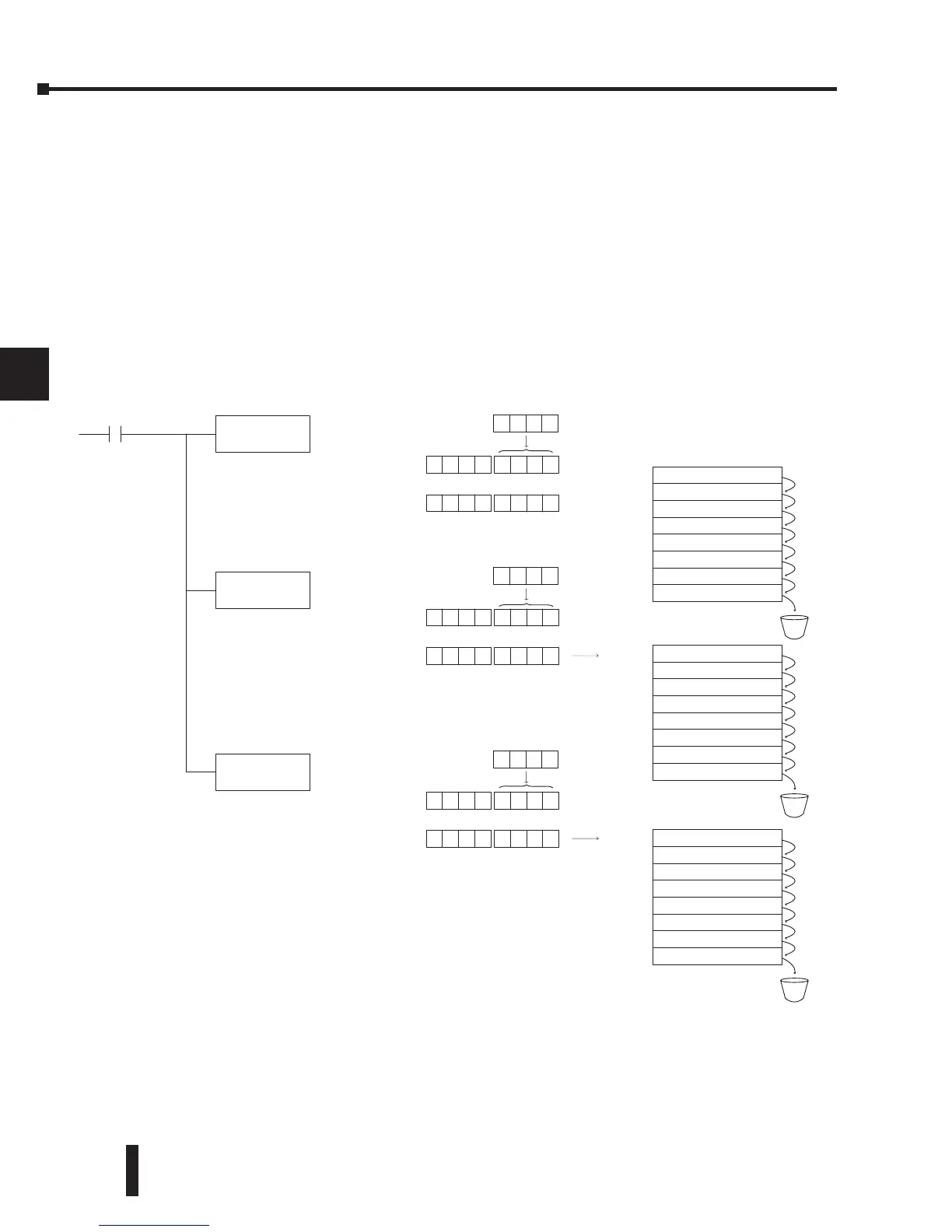
Using the Accumulator Stack
The accumulator stack is used for instructions that require more than one parameter to
execute a function or for user-defined functionality. The accumulator stack is used when more
than one Load instruction is executed without the use of an Out instruction. The first Load
instruction in the scan places a value into the accumulator. Every Load instruction thereafter
without the use of an Out instruction places a value into the accumulator and the value that
was in the accumulator is placed onto the accumulator stack. The Out instruction nullifies the
previous Load instruction and does not place the value that was in the accumulator onto the
accumulator stack when the next Load instruction is executed. Every time a value is placed
onto the accumulator stack, the other values in the stack are pushed down one location. The
accumulator is eight levels deep (eight 32-bit registers). If there is a value in the eighth location
when a new value is placed onto the stack, the value in the eighth location is pushed off the
stack and cannot be recovered.
The POP instruction rotates values upward through the stack into the accumulator. When
a POP is executed, the value that was in the accumulator is cleared and the value that was on
top of the stack is in the accumulator. The values in the stack are shifted up one position in
the stack.
Acc.
Load the value 3245 into the accumu-
lator
Load the value 5151 into the accumu-
lator, pushing the value 3245 onto the
stack
Load the value 6363 into the accumu-
lator, pushing the value 5151 to the 1st
stack location and the value 3245 to
the 2nd stack location
LD
K3245
 Loading...
Loading...