DL205 User Manual, 4th Edition, Rev. D
5-172
Chapter 5: Standard RLL Instructions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
B
C
D
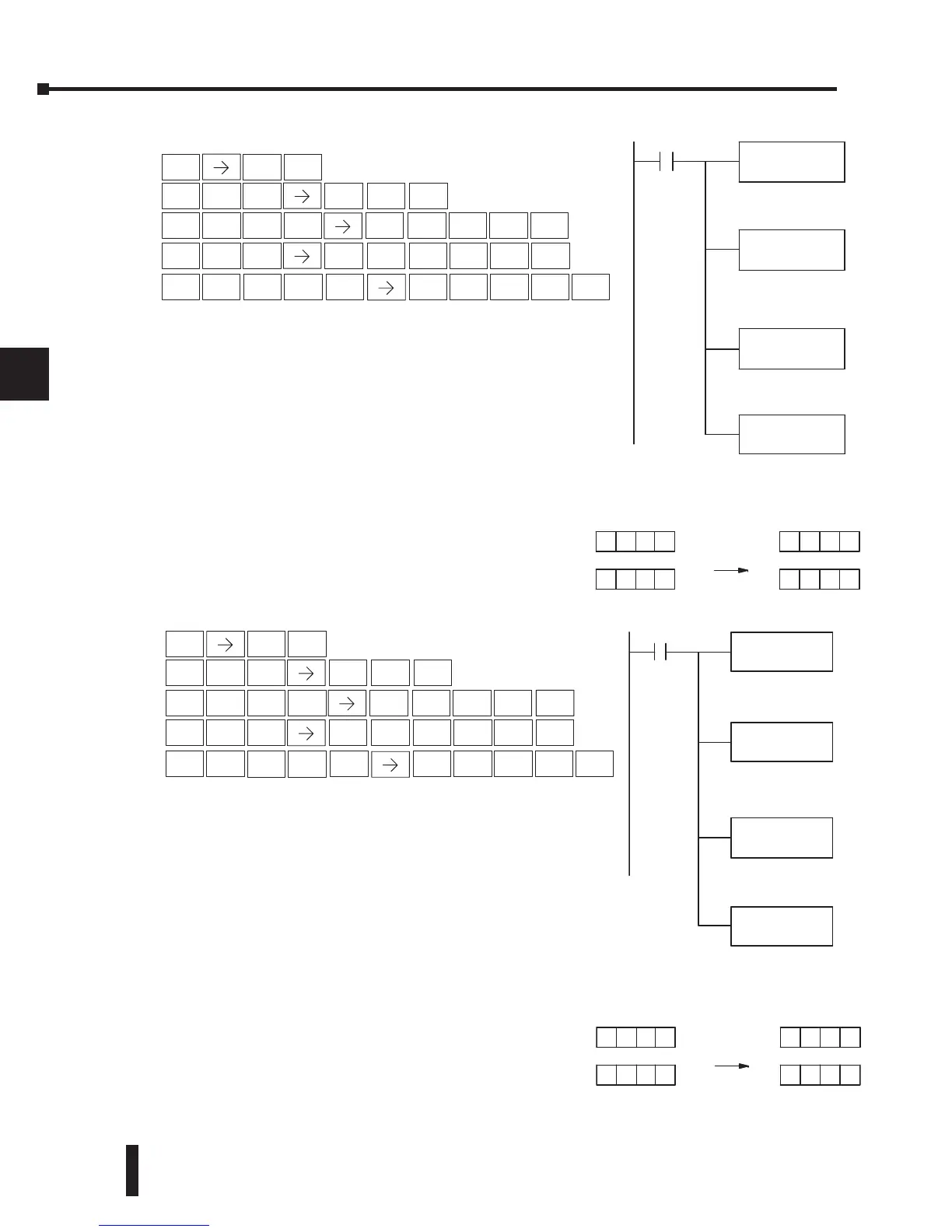
The example to the right shows a table of two words at V3000
and logically ORs it with K8888. The copy of the table at
V3100 shows the result of the OR operation for each word.
The program to the right performs the ORMOV example
above. It assumes that the data in the table at V3000 –
V3001 already exists. First we load the table length (two
words) into the accumulator. Next we load the starting
address of the source table, using the LDA instruction.
Then we load the data into the accumulator to be ORed
with the table. In the ORMOV command, we specify
the table destination, V3100.
The example to the right shows a table of two words at
V3000 and logical XORs it with K3333. The copy of the
table at V3100 shows the result of the XOR operation for
each word.
The ladder program example for the XORMOV is similar
to the one above for the ORMOV. Just use the XORMOV
instruction. On the Handheld Programmer, you must use
the SHFT key and spell “XORMOV” explicitly.
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
9 9 9 9
9 9
of the accumulator.
Convert octal 3000 to HEX
and load the value into the
accumulator. This is the
table beginning.
Load the constant value
8888 (Hex.) into the lower
16 bits of the accumulator.
Copy the table to V3100,
ORing its contents with the
Load the constant value 2
(Hex.) into the lower 16
bits of the accumulator.
Convert otal 3000 to HEX
and load the value into the
accumulator. This is the
table beginning.
Load the constant value
6666 (Hex.) into the lower
16 bits of the accumulator.
Copy the table to V3100,
ANDing its contents with th
 Loading...
Loading...