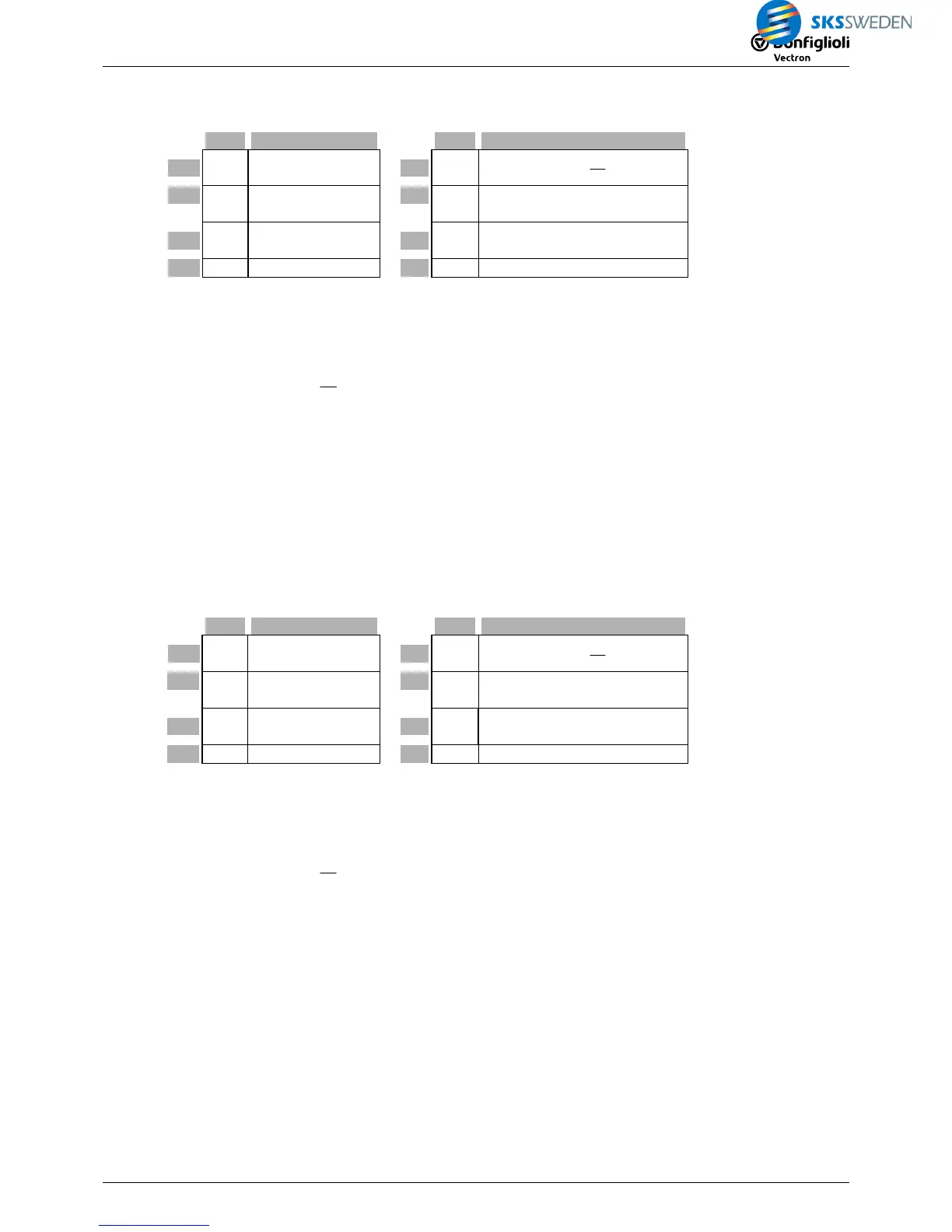
5.4.2 [371] PI controller (Tn in milliseconds)
Type Function
Type Function
I1 %
Input (reference
value)
O1 %
()
()
d t2 I1 I
2P
1P
2 I 1 I 1 PO 1
∫
−+ − × =
I2
%
Input (actual val-
ue)
O2
% inverted output = -1
I3 %
Limitation of out-
put values
P1 i P amplification
I4 b Master Reset
P2 i Integral time in ms
Description:
The control deviation (I1- I2) is multiplied by the amplification P1. The I controller adds up the
control deviation over time. The I component is added. When the integral time has elapsed, the
I component reaches the same value again so that the output value is doubled.
()
()
d t2 I1 I
2P
1P
The output value is limited to the value at input I3.
As long as status TRUE is present at I4 (Master Reset), the output value I1 and the I compo-
nent are 0.
Note:
Percentages [%] have two decimals.
For example: Value 12345
IN
= 123.45% = 1.2345
5.4.3 [372] PI controller (Tn in seconds)
Type Function
Type Function
I1 %
Input (reference
value)
O1 %
()
()
d t2 I1 I
2P
1P
2 I 1 I 1 PO 1
∫
−+ − × =
I2
%
Input (actual val-
ue)
O2
% inverted output = -1
I3 %
Limitation of out-
put values
P1 i P amplification
I4 b Master Reset
P2 i Integral time in s
Description:
The control deviation (I1 - I2) is multiplied by the amplification P1. The I controller adds up the
control deviation over time. The I component is added. When the integral time has elapsed, the
I component reaches the same value again so that the output value is doubled.
()
()
d t2 I1 I
2
1P
∫
−
P
+−× =− =
The output value is limited to the value at input I3.
As long as status TRUE is present at I4 (Master Reset), the output value O1 and the I compo-
nent are 0.
Note:
Percentages [%] have two decimals.
For example: Value 12345
IN
= 123.45% = 1.2345

 Loading...
Loading...











