Section 7. Installation
264
CRBasicExample61. PT100inFour‐WireFull‐Bridge
'See FIGURE. PT100 in Four-Wire Full-Bridge (p. 263) for wiring diagram.
Public BrFullOut
Public Rs_Ro
Public Deg_C
BeginProg
Scan(1,Sec,0,0)
'BrFull(Dst,Reps,Range,DfChan,Vx1,MPS,Ex,RevEx,RevDf,Settle,Integ,Mult,Offset)
BrFull(BrFullOut,1,mV25,1,Vx1,1,2500,True,True,0,250,.001,.02344)
'BrTrans = Rf*(X/(1-X))
Rs_Ro = 50 * (BrFullOut/(1 - BrFullOut))
'PRTCalc(Destination,Reps,Source,PRTType,Mult,Offset)
PRTCalc(Deg_C,1,Rs_Ro,2,1.0,0)
NextScan
EndProg
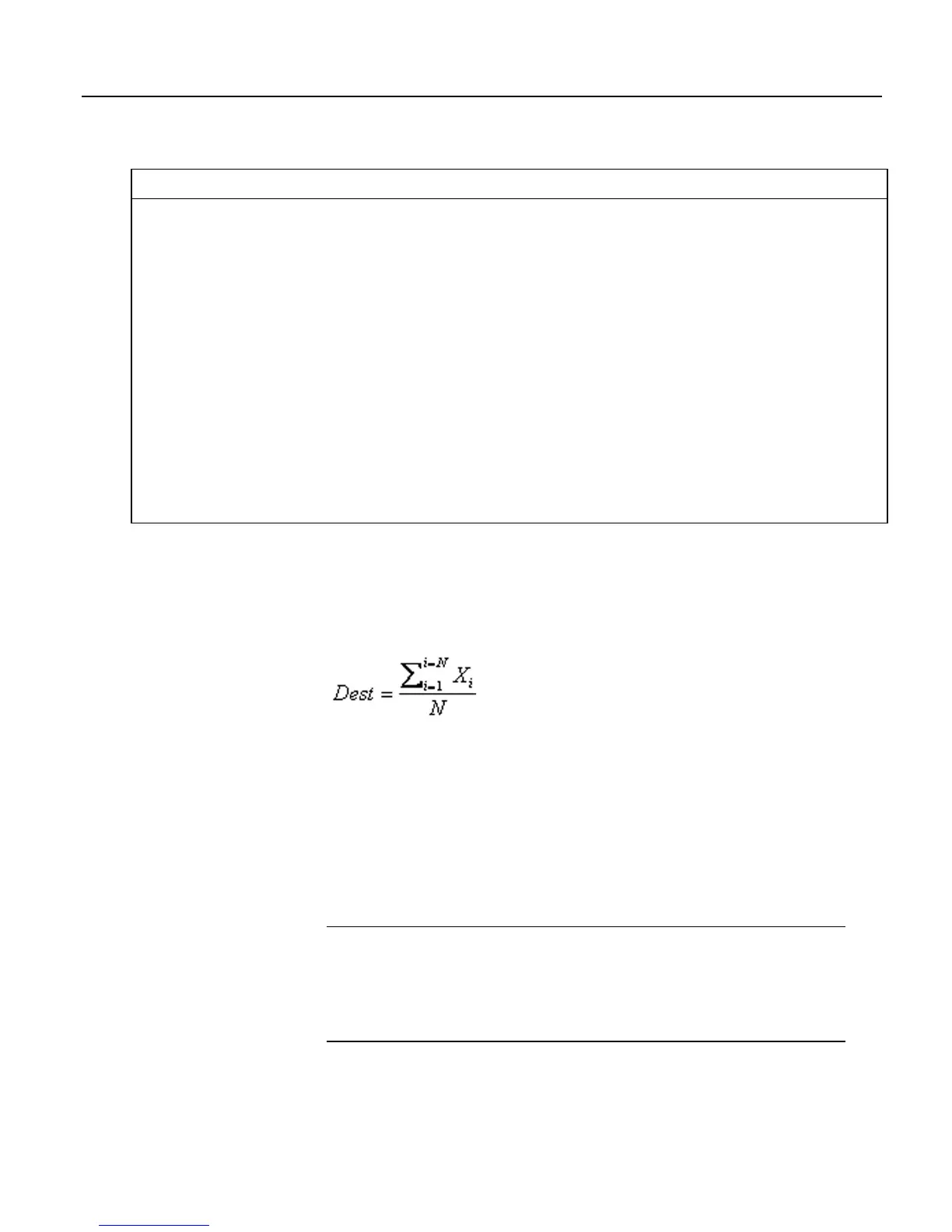
7.8.19 Running Average
The AvgRun() instruction calculates a running average of a measurement or
calculated value. A running average is the average of the last N values where N is
the number of values, as expressed in figure Running-Average Equation
(p. 264),
Figure 82: Running-average equation
where X
N
is the most recent value of the source variable and X
N-1
is the previous
value (X
1
is the oldest value included in the average, i.e., N-1 values back from
the most recent). NANs are ignored in the processing of AvgRun() unless all
values in the population are NAN.
AvgRun() uses high-precision math, so a 32-bit extension of the mantissa is saved
and used internally resulting in 56 bits of precision.
Note This instruction should not normally be inserted within a For/Next
construct with the Source and Destination parameters indexed and Reps set to 1.
Doing so will perform a single running average, using the values of the different
elements of the array, instead of performing an independent running average on
each element of the array. The results will be a running average of a spatial
average of the various source array elements.
A running average is a digital low-pass filter; its output is attenuated as a function
of frequency, and its output is delayed in time. The amounts of attenuation and
phase shift (time delay) depend on the frequency of the input signal and the time
length (which is related to the number of points) of the running average.

 Loading...
Loading...