Section 8. Operation
293
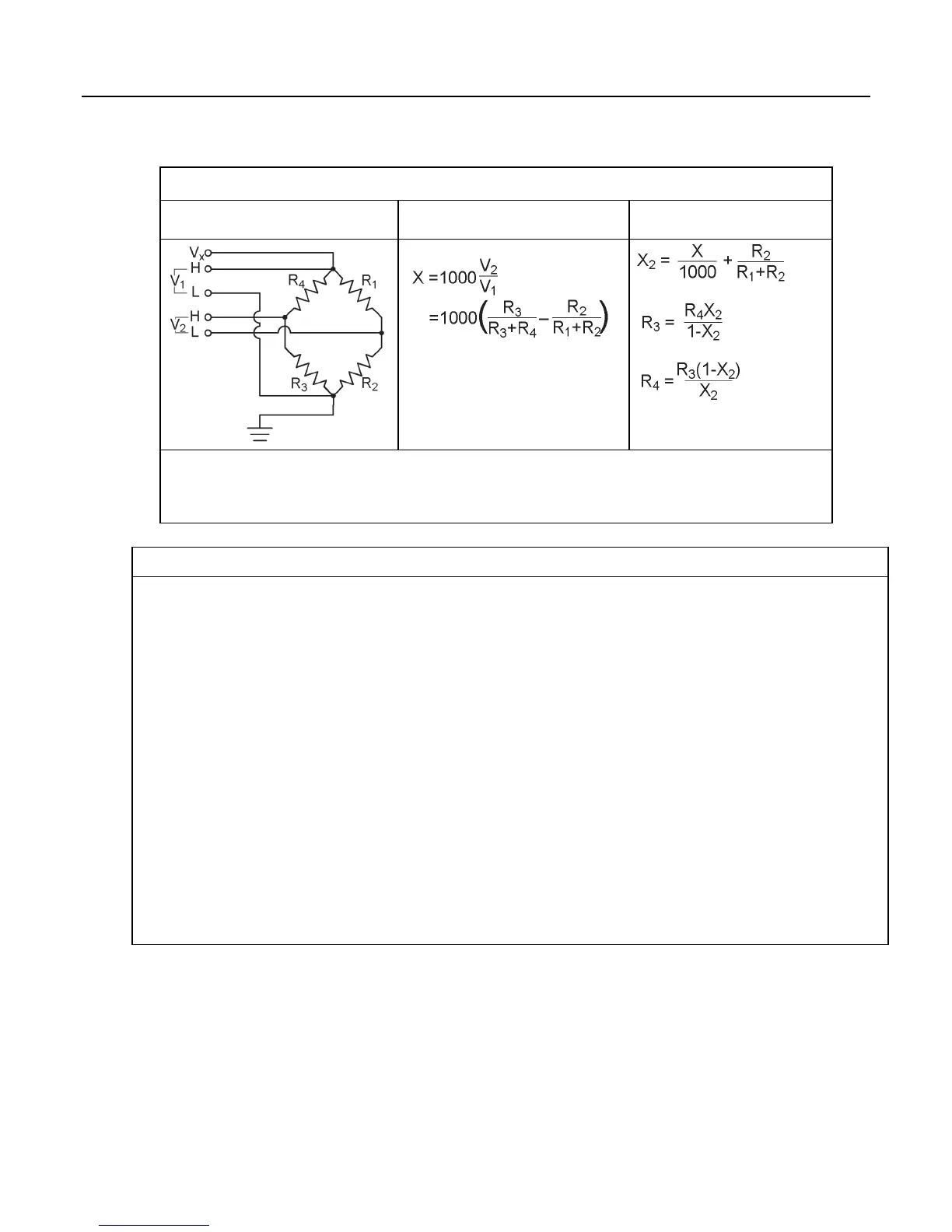
Table 61. Resistive-Bridge Circuits with Voltage Excitation
Resistive-Bridge Type and
Circuit Diagram
CRBasic Instruction and
Fundamental Relationship
Relationships
1
Key: V
x
= excitation voltage; V
1
, V
2
= sensor return voltages; R
f
= "fixed", "bridge" or "completion" resistor; R
s
= "variable" or
"sensing" resistor.
2
Where X = result of the CRBasic bridge measurement instruction with a multiplier of 1 and an offset of 0.
3
See the appendix Resistive Bridge Modules (p. 539) for a list of available terminal input modules to facilitate this measurement.
CRBasicExample64. Four‐WireFull‐BridgeMeasurementandProcessing
'Declare Variables
Public X
Public X1
Public R1
Public R2
Public R3
Public R4
'Main Program
BeginProg
R2 = 1000 'Resistance of R2
R3 = 1000 'Resistance of R3
R4 = 1000 'Resistance of R4
Scan(500,mSec,1,0)
'Full Bridge Measurement:
BrFull(X,1,mV2500,1,1,1,2500,True,True,0,_60Hz,1.0,0.0)
X1 = ((-1 * X) / 1000) + (R3 / (R3 + R4))
R1 = (R2 * (1 - X1)) / X1
NextScan
EndProg
8.1.3.1 ac Excitation
Some resistive sensors require ac excitation. These include electrolytic tilt
sensors, soil moisture blocks, water conductivity sensors, and wetness sensing
grids. The use of dc excitation with these sensors can result in polarization, which
will cause erroneous measurement, shift calibration, or lead to rapid sensor decay.
 Loading...
Loading...