Section 4. Quickstart Tutorial
37
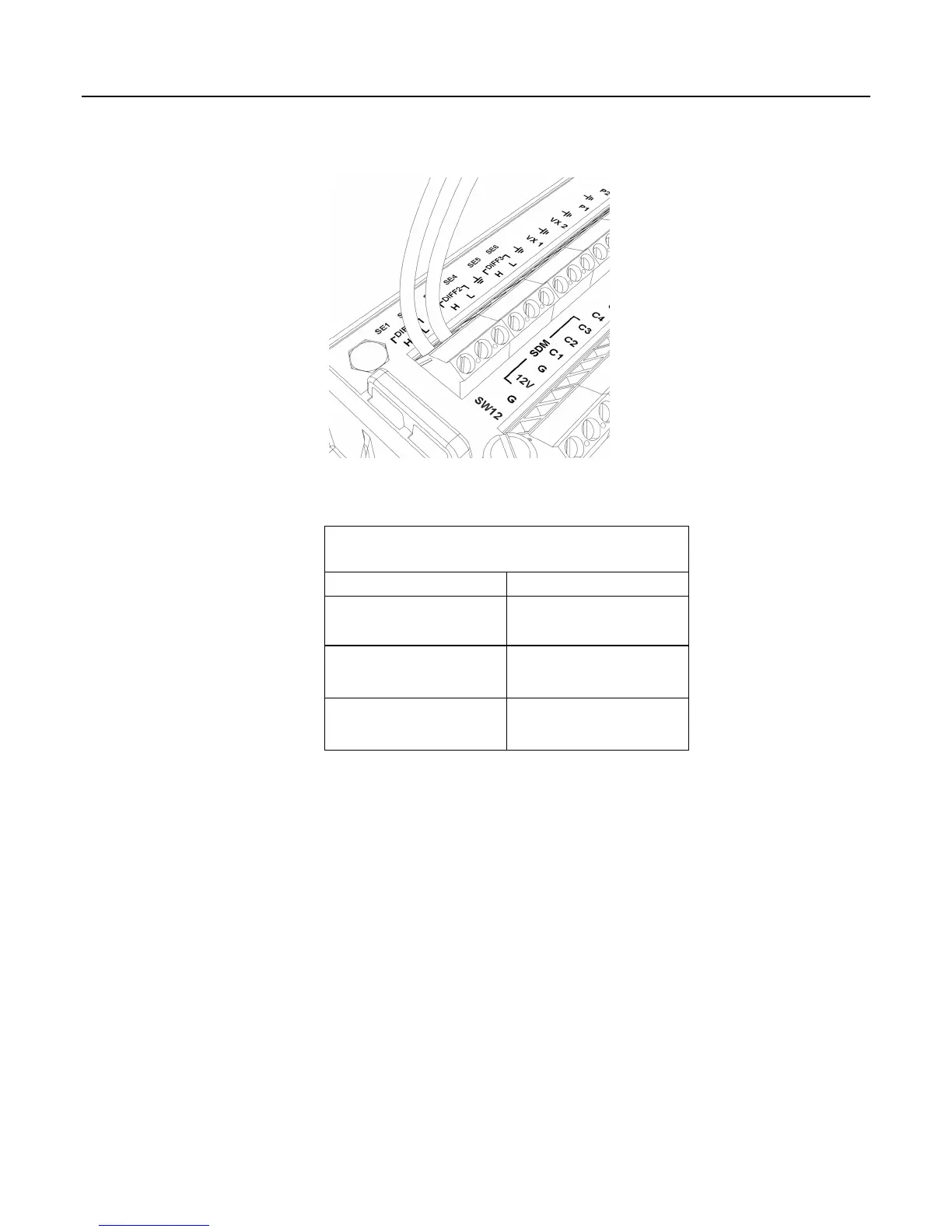
Figure 4: Analog sensor wired to differential channel #1
Table 1. Single-Ended and Differential Input
Channels
Differential Channel Single-Ended Channel
1H 1
1L 2
2H 3
2L 4
3H 5
3L 6
4.1.3.2 Bridge Sensors
Many sensors use a resistive bridge to measure phenomena. Pressure sensors and
position sensors commonly use a resistive bridge. Examples:
• A specific resistance in a pressure transducer strain gage correlates to a
specific water pressure.
• A change in resistance in a wind vane potentiometer correlates to a change in
wind direction.
4.1.3.2.1 Voltage Excitation
Bridge resistance is determined by measuring the difference between a known
voltage applied to a bridge and the measured return voltage. The CR800 supplies
a precise scalable voltage excitation via excitation terminals. Return voltage is
measured on analog terminals. Examples of bridge sensor wiring using voltage
excitation are illustrated in figures Half-Bridge Wiring -- Wind Vane
Potentiometer
(p. 38) and Full-Bridge Wiring -- Pressure Transducer (p. 38).

 Loading...
Loading...