Revision 14
30 August 02, 2019
2.9 Total Sulfur Option
The system is available with an oven that converts sulfur compounds to H
2
S, so that the total
sulfur content of a sample gas stream can be determined. With a dual stream setup, it is
possible to measure both the H
2
S and the total sulfur content of the same stream on the
same system.
The sample gas is mixed with hydrogen in a quartz reaction tube at a temperature of 900°C.
At this temperature, the hydrogen reacts with all sulfur components to form H
2
S, and most
hydrocarbons to form methane. The conversion of total sulfur to hydrogen sulfide is covered
in ASTM Method D4468-85: Total Sulfur in Gaseous Fuels by Hydrogenolysis and
Rateometric Colorimetry. A few typical reactions are shown in Table 2-2.
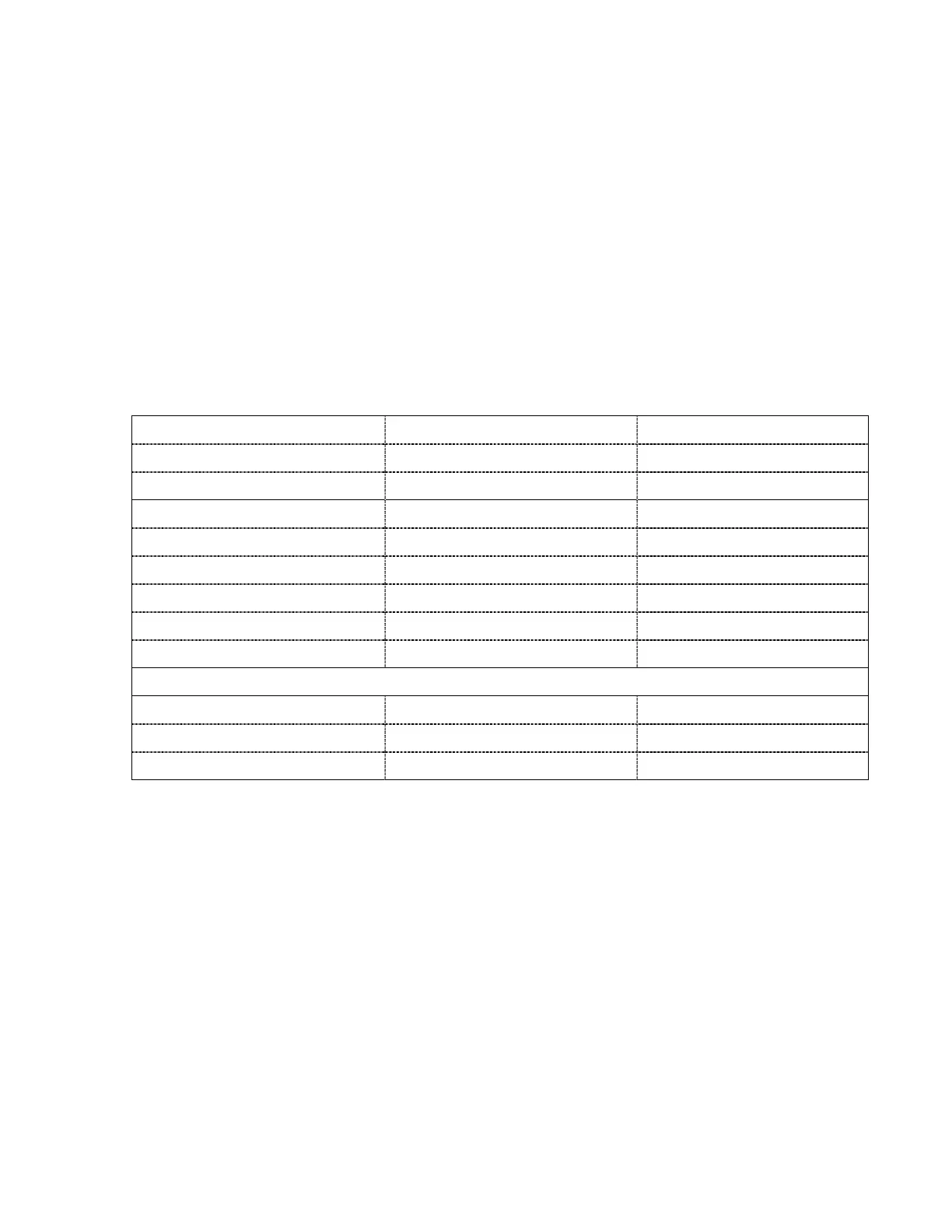
Table 2-2: Total Sulfur Reactions
Carbonyl Sulfide
COS + 4H
2
H
2
S + CH
4
+ H
2
O
900°C
Ethyl Sulfide
(C
2
H
5
)
2
S + 4H
2
H
2
S + 4CH
4
900°C
Methyl Sulfide
(CH
3
)
2
S + 2H
2
H
2
S + 2CH
4
900°C
Example of cracking:
Butane
C
4
H
10
+ 3H
2
4CH
4
900°C
Because the sulfur compounds are converted into hydrogen sulfide, a measurement of the
hydrogen sulfide content formed by these reactions will be directly equivalent to the total
sulfur content in the sample gas stream.
The formation of H
2
S takes place in an external total sulfur furnace that is mounted below the
electronics enclosure. The total sulfur furnace is shown in Figure 2-14.

 Loading...
Loading...