4-63
BUS OPERATION
Figure 4-42 also shows the system asserting RDY# to indicate a non-burst line-fill cycle. Burst
cache line-fill cycles behave similarly to non-burst cache line-fill cycles when snooping using
BOFF#. If the system snoop hits the same line as the line being filled (burst or non-burst), the
Write-Back Enhanced IntelDX4 processor does not assert HITM# and does not issue a snoop
write-back cycle, because the line was not modified, and the line fill resumes upon the de-asser-
tion of BOFF#. However, the line fill is cached only if INV is driven low during the snoop cycle.
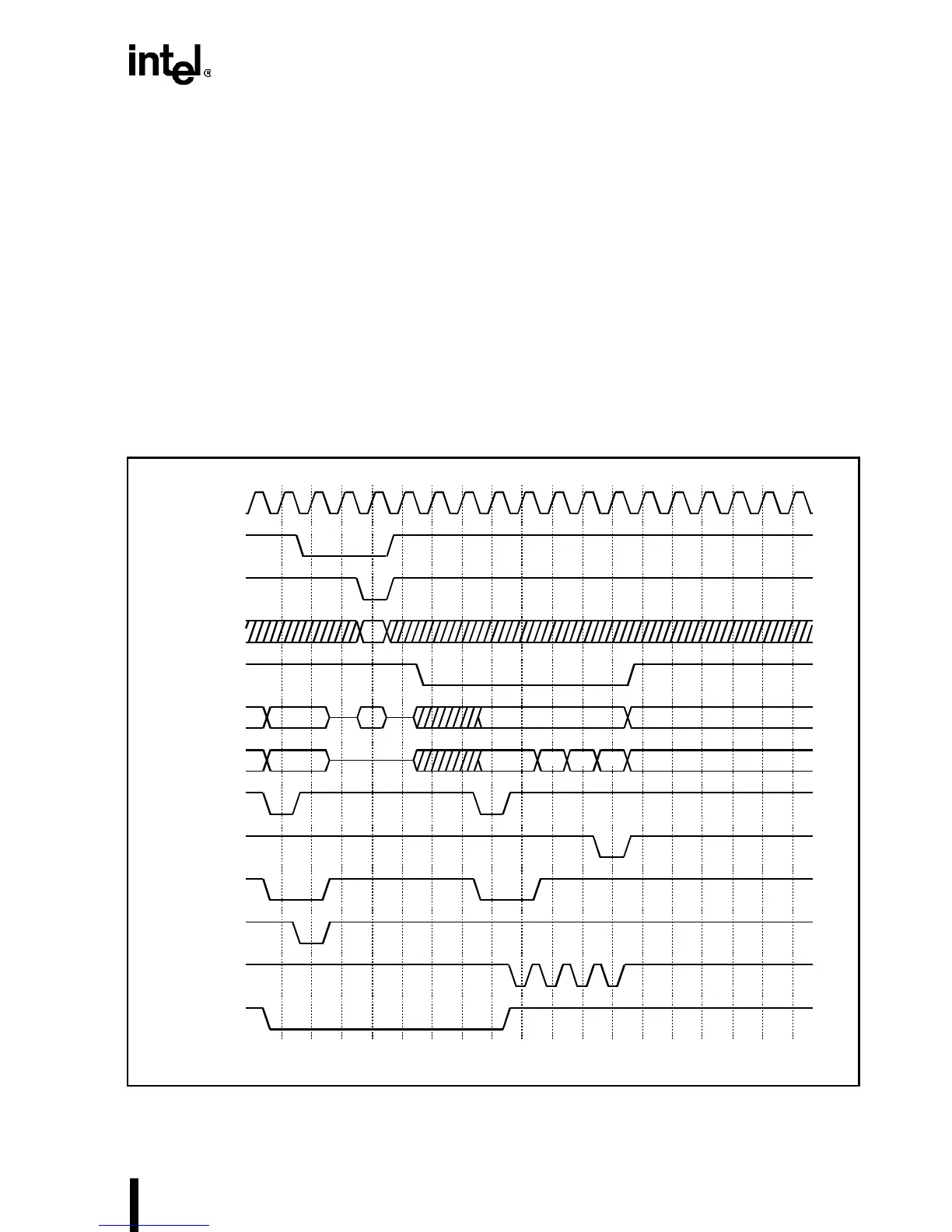
Snoop under BOFF# during Replacement Write-Back
If the system snoop under BOFF# hits the line that is currently being replaced (burst or non-
burst), the entire line is written back as a snoop write-back line, and the replacement write-back
cycle is not continued. However, if the system snoop hits a different line than the one currently
being replaced, the replacement write-back cycle continues after the snoop write-back cycle has
been completed. Figure 4-43 shows a system snoop hit to the same line as the one being replaced
(non-burst).
Figure 4-43. Snoop under BOFF# to the Line that is Being Replaced
CLK
BOFF#
EADS#
INV
HITM#
A31–A4
A3–A2
ADS#
12345678910111213141516171819
BLAST#
CACHE#
RDY#
BRDY#
To Processor
W/R#
0 4 8 C
Repl Wb
Repl Wb
Write Back Cycle
†
†
 Loading...
Loading...











