1-13
1 Overview and Specifications
CP1E CPU Unit Hardware User’s Manual(W479)
1-3 Specifications
1
1-3-3 Functional Specifications
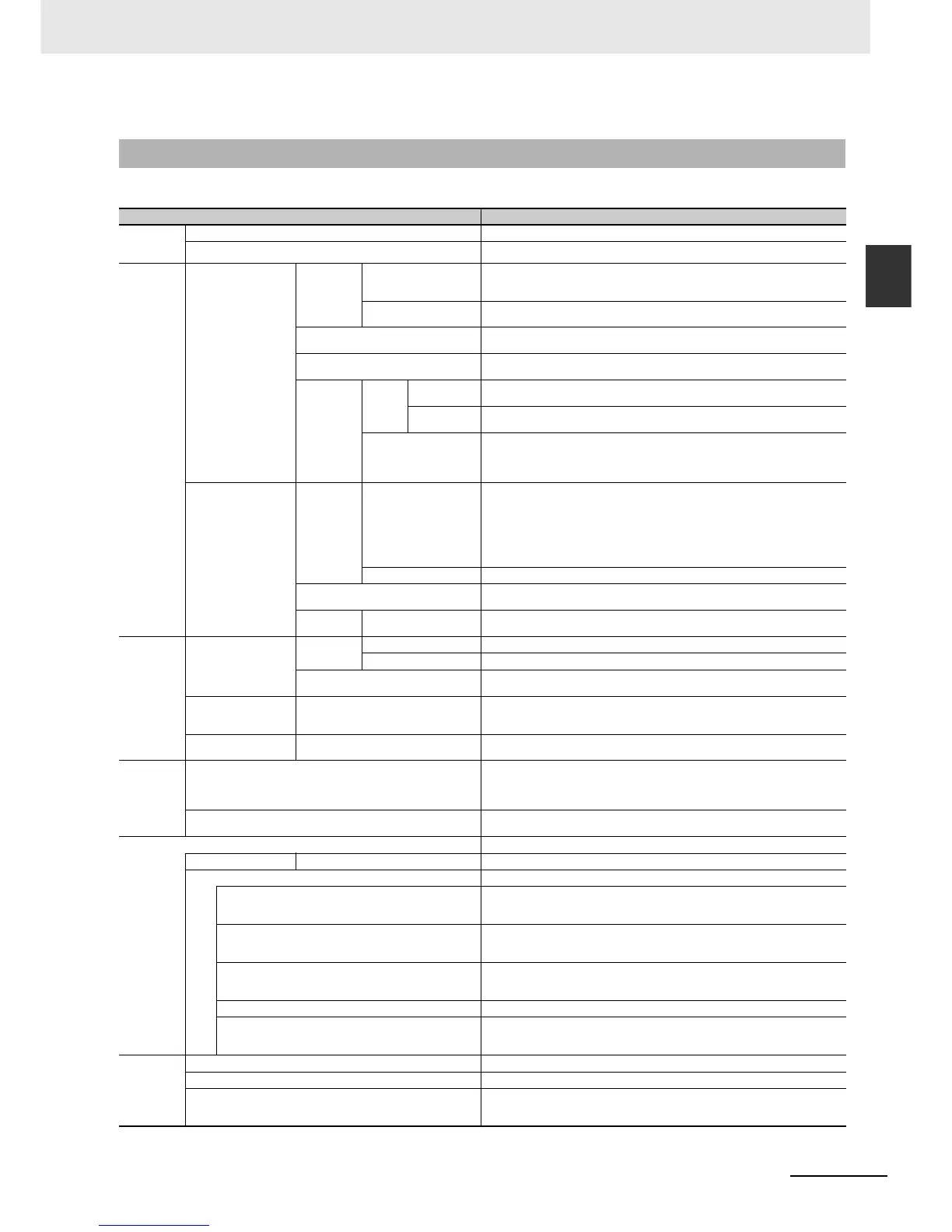
The following table gives the functional specifications of CP1E CPU Units.
1-3-3 Functional Specifications
Function Description
Cycle time
manage-
ment
Minimum cycle time Makes the cycle time consistent.
Monitoring the cycle time Monitors the cycle time.
CPU Unit
built-in
functions
Inputs High-
speed
counters
inputs
High-speed pulse
inputs
High-speed pulses from devices such as a rotary encoder are counted. The
counted values are stored in the Auxiliary Area.Interrupt tasks can be executed
when target is reached or by range comparison.
Input pulse fre-
quency measurement
The frequency of pulses input by the PRV instruction is measured.
Interrupt inputs Relevant interrupt tasks are executed during the cycle when the CPU Unit
built-in inputs turn ON or turn OFF.
Quick-response inputs Inputs can be read without being affected by cycle time.
Use the quick-response inputs to read signals shorter than the cycle time.
Normal
inputs
I/O
refres
hing
Cyclic
refreshing
The CPU Unit’s built-in I/O are cyclically refreshed.
Immediate
refreshing
I/O refreshing by immediate refreshing instructions.
Input response times Input constants can be set for Basic I/O Units.
The response time can be increased to reduce the effects of chattering and
noise at input contacts. The response time can be decreased to enable detect-
ing shorter input pulses.
Outputs Pulse out-
puts (Mod-
els with
transistor
outputs
only )
Pulse control A pulse signal is output and positioning or speed control is performed with a
servo driver that accepts a pulse input.
Continuous mode for speed control or independent mode for position control
can be used. There are functions for changing to positioning during speed con-
trol and for changing the target value during positioning.
* It is not possible to change the target speed, acceleration/deceleration set-
tings, or direction during positioning.
Origin positioning Origin searches and origin returns.
PWM outputs (Models with transis-
tor outputs only )
Pulses for which the duty ratio (ratio between ON time and OFF time during
one pulse cycle) can be set are output.
Normal
outputs
Load OFF function All of the outputs on the CPU Unit’s I/O can be turned OFF when an error
occurs in RUN or MONITOR mode.
Expansion
I/O Units
and
Expansion
Units
Functions sup-
ported by both
Expansion I/O Unit
and Expansion Unit
I/O refresh-
ing
Cyclic refreshing The Expansion I/O Units and Expansion Units are cyclically refreshed.
Refreshing by IORF I/O refreshing by IORF instruction.
Load OFF function All of the outputs on Expansion I/O Units and Expansion Units are turned OFF
(0000 hex) when an error occurs in RUN or MONITOR mode.
Expansion I/O Units Input response times The response time can be increased to reduce the effects of chattering and
noise at input contacts.
The response time can be decreased to enable detecting shorter input pulses.
Expansion Units Unit error detection Errors in Expansion Units are detected.
The CPU Unit is notified that the Expansion Unit stopped due to an error.
Memory
manage-
ment func-
tions
Holding I/O memory when changing operating modes The status of I/O memory can be held when the operating mode is changed or
power is turned ON.
The forced-set/reset status can be held when the operating mode is changed
or power is turned ON.
Automatic backup to the backup memory
(built-in EEPROM)
Automatic backup of ladder programs and parameter area to the backup mem-
ory (built-in EEPROM).
Communications −
Peripheral USB port Peripheral bus (toolbus) For communications with computer.
Serial port (N-type only) −
Host Link (SYSWAY) communications Host Link commands or FINS commands placed between Host Link headers
and terminators can be sent from a PT to read/write I/O memory, read/control
the operating mode, and perform other operations for PLC.
No-protocol communications I/O instructions for communications ports (such as TXD/RXD instructions) can
be used for data transfer with peripheral devices such as bar code readers and
printers.
NT Link communications I/O memory in the PLC can be allocated and directly linked to various PT func-
tions, including status control areas, status notification areas, touch switches,
lamps, memory tables, and other objects.
Serial PLC Links Up to 10 words of data per Unit can be shared between up to nine CPU Units.
Modbus-RTU Easy Master function Modbus-RTU commands are sent by the Modbus-RTU Master function. Mod-
bus slaves, such as inverters, can be easily controlled with serial communica-
tions.
Interrupt Scheduled interrupts Tasks can be executed at a specified interval (0.5 ms min., Unit: 0.1 ms).
Input interrupts Interrupt tasks are processed when the built-in input turns ON or OFF.
High-speed counter interrupts This function counts input pulses with the CPU Unit’s built-in high-speed
counter and executes an interrupt task when the count reaches the preset
value or falls within a preset range (target value or zone comparison).

 Loading...
Loading...