28
Interrupt Functions Section 1-4
If the Counter Mode is not used, these SR bits can be used as work bits.
2. With the INT(89) instruction, refresh the Counter Mode set value and en-
able interrupts.
The input interrupt for which the set value is refreshed will be enabled in
Counter Mode. When the counter reaches the set value, an interrupt will
occur, the counter will be reset, and counting/interrupts will continue until the
counter is stopped.
Note 1. If the INT(89) instruction is used during counting, the present value (PV)
will return to the set value (SV). You must, therefore, use the differentiated
form of the instruction or an interrupt may never occur.
2. The set value will be set when the INT(89) instruction is executed. If inter-
rupts are already in operation, then the set value will not be changed just
by changing the content of SR 244 to SR 247, i.e., if the contents is
changed, the set value must be refreshed by executing the INT(89) instruc-
tion again.
Interrupts can be masked using the same process as for the Input Interrupt
Mode, but if the masks are cleared using the same process, the Counter
Mode will not be maintained and the Input Interrupt Mode will be used
instead. Interrupt signals received for masked interrupts can also be cleared
using the same process as for the Input Interrupt Mode.
Counter PV in Counter Mode
When input interrupts are used in Counter Mode, the counter PV will be
stored in the SR word corresponding to input interrupts 0 to 3. Values are
0000 to FFFE (0 to 65,534) and will equal the counter PV minus one.
Example: The present value for an interrupt whose set value is 000A will be
recorded as 0009 immediately after INT(89) is executed.
Note Even if input interrupts are not used in Counter Mode, these SR bits cannot be
used as work bits.
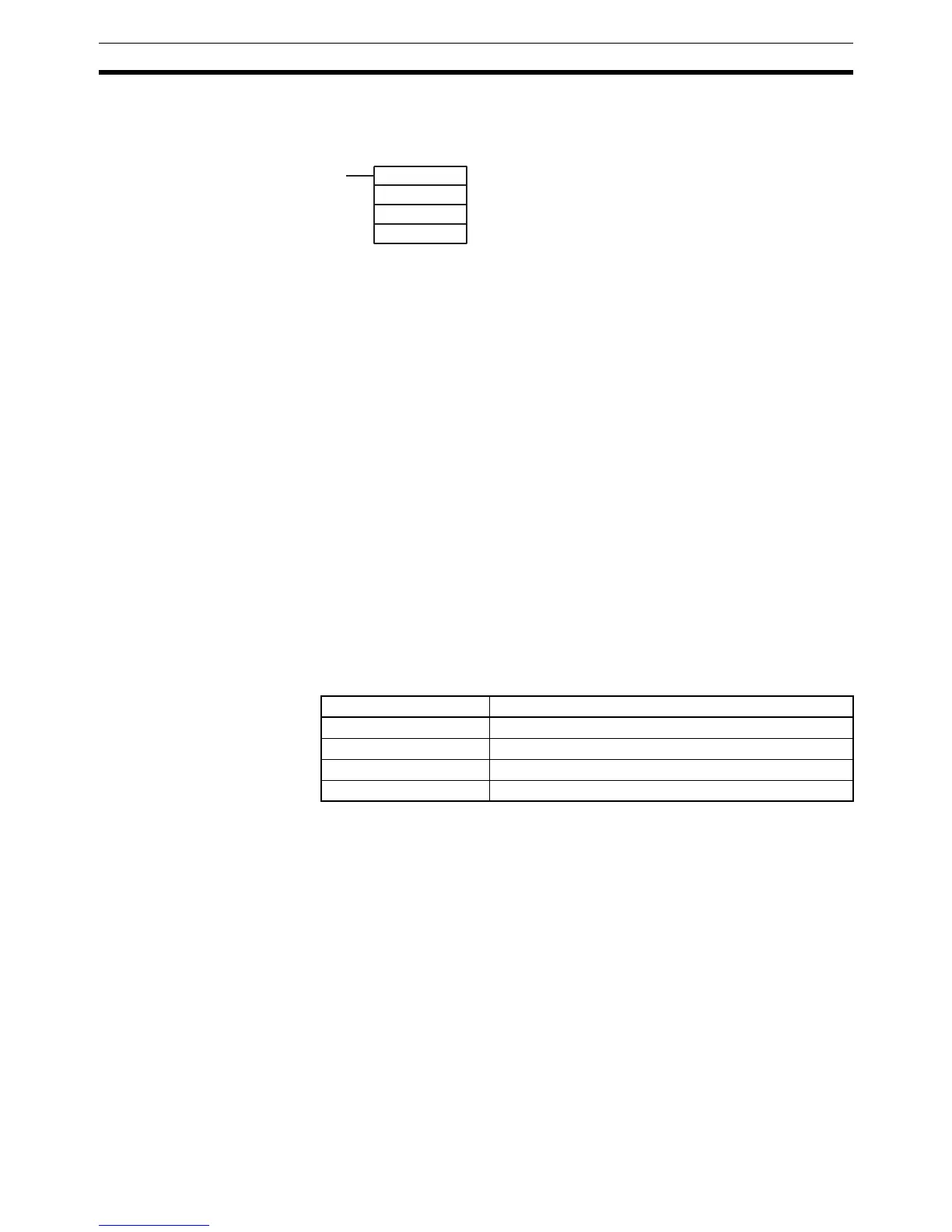
(@)INT(89)
003
000
D
If D bits 0 to 3, which correspond to input interrupts 0 to 3,
are set to "0," then the set value will be refreshed and inter-
rupts will be permitted.
0: Counter mode set value refreshed and mask cleared.
1: Nothing happens. (Set to 1 the bits for all interrupts
that are not being changed.)
Interrupt Word containing counter PV – 1
Input interrupt 0 SR 248
Input interrupt 1 SR 249
Input interrupt 2 SR 250
Input interrupt 3 SR 251
 Loading...
Loading...