Page 46
Example 2 Level Monitoring and Control (up or down)
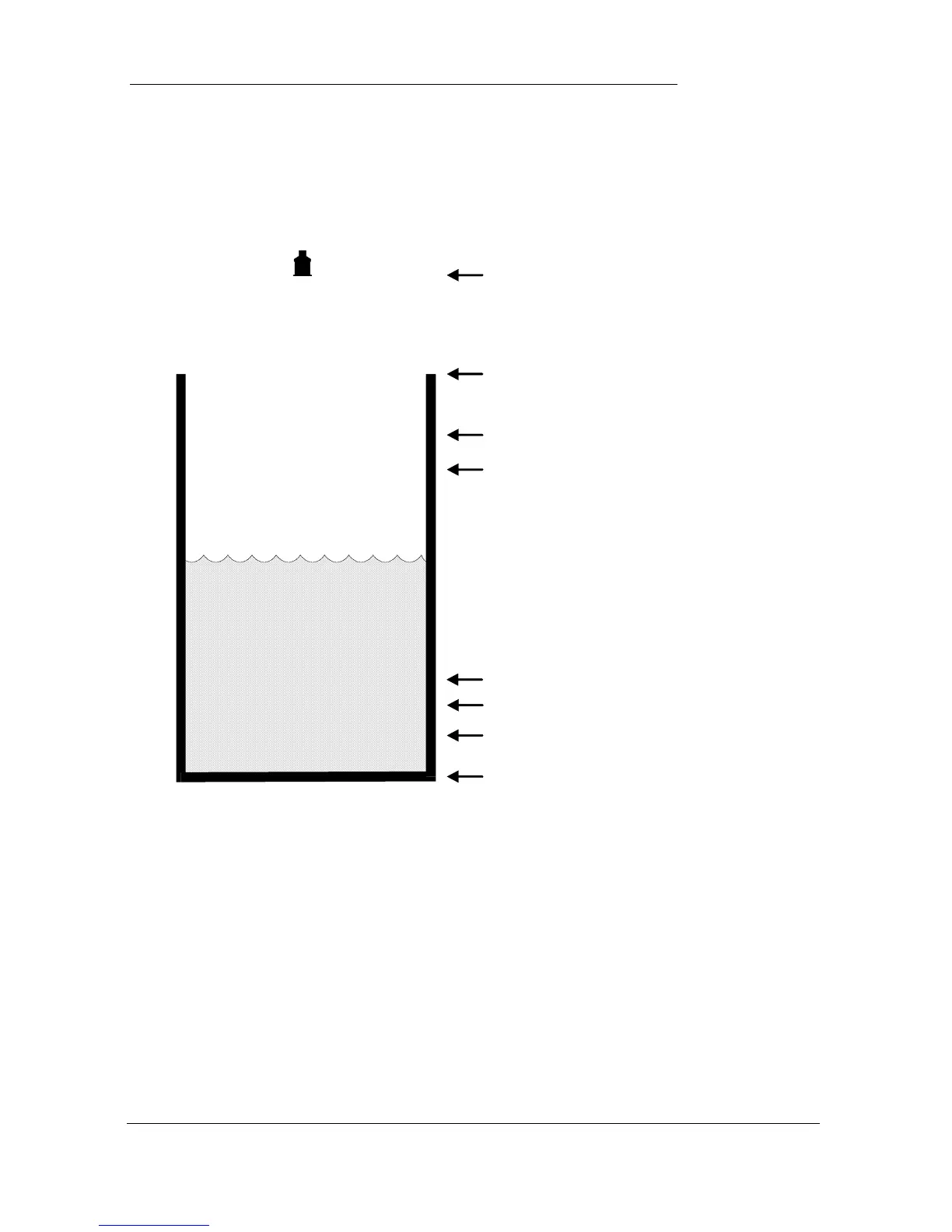
A vessel, containing a liquid that has a variation in level that is to be
monitored, and when the level reaches a specific point, the vessel is pumped
down, with the fluid being transferred to another process. The pump will be
assigned to Relay 1 a High Alarm to Relay 2 and Low Alarm to Relay 5.
The application is to be assigned to Point (transducer) 2.
empty distance (P2-105), 11.0 feet
100%, span (P2-106), 10.0 feet
85%, high alarm on (P*223), 8.5 feet
80%, high alarm off (P*224), 8.0 feet
80%, control (down) on (P*213), 8.0 feet
15% , low alarm off (P*254), 1.5 feet
10%, low alarm on (P*253), 1.0 feet
20%, control (down) off (P*214), 2.0 feet
In this example, there is a pump (Relay 1), which will come on if the level
rises to 8.0 feet, and go off when the level drops to 2.0 feet. (control down).
If the level rises to 8.5 feet, then the high level alarm (Relay 2) will come on
until the level drops to 8.0 feet. If the level falls to 1.0 feet, then the low
level alarm (Relay 5) will come on until the level rises to 1.5 feet.
Alternatively, if it is a control up application, then the on and off points for
the control relay are reversed, so the pump comes on when the level is at
2.0 feet and goes off when it rises to 8.0 feet.
The display will show the level in the tank and mA output 2 will be
representative of level where 4mA = empty level (0%) and 20mA = 10.0
feet (100%).

 Loading...
Loading...