Mathematics
R&S
®
RTM20xx
107User Manual 1317.4726.02 ─ 01
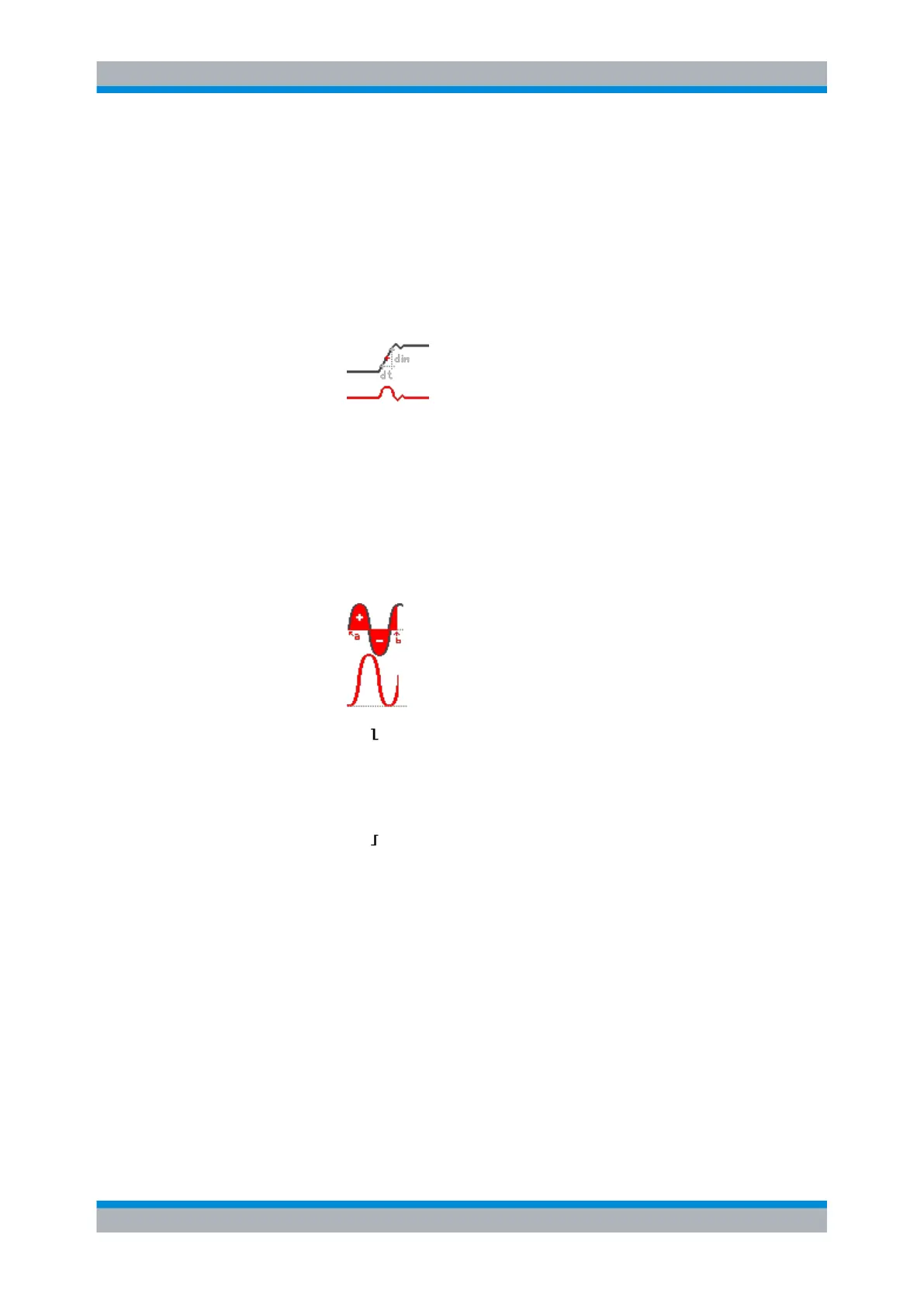
"Derivative"
f'(Op1)
The derivative corresponds to the rise of the tangent through a function
point and indicates the dimension of the change in quantity of the oper-
and in time. The larger the quantity change of the operand per time
becomes, the larger the result of the derivative is.
The calculation is approximated using the secant based on the current
calculated value and a value with a distance of 0.1 DIV. Due to this, the
time axis has a finitely small resolution. Therefore, scale the input signal
to display the required area appropriately.
"Integral"
Calculates the definite integral of the operand.
The calculation is displayed in the illustration. The integration starts at
point "a" and adds the area beneath the waveform. Point "b" indicates
the currently calculated value. At the end of the positive alternation, the
integral function reaches its maximum. Due to the homopolar operand
used in this example, the waveform of the area reaches zero after the
negative alternation.
Use a V-Marker to measure the area for an extract of the waveform.
See also: "Meas.Type" on page 83.
"IIR low pass"
IIR (Op1,fg=Op2)
Calculates a low-pass filtered waveform of "Operand 1". The cut-off
frequency is set with constant "Operand 2". Signal components with
frequencies higher than the cut-off frequency are attenuated signifi-
cantly.
"IIR high pass"
IIR (Op1,fg=Op2)
Calculates a high-pass filtered waveform of "Operand 1". The cut-off
frequency is set with constant "Operand 2". Signal components with
frequencies below the cut-off frequency are attenuated significantly.
Remote command:
CALCulate:MATH<m>[:EXPRession][:DEFine] on page 346
Operand 1 ← Edit Equations
Defines the first operand for the mathematical operation. The source can be any active
channel signal, a constant value, or a mathematical waveform with lower number than
the one to be defined.
"CH1 | CH2 |
CH3 | CH4"
An active channel waveform
"Const."
A constant value
Reference for Mathematics

 Loading...
Loading...











