Protocol Analysis
R&S
®
RTM20xx
155User Manual 1317.4726.02 ─ 01
Position
Defines the position of the frame table on the screen: top right, bottom right, or full screen.
With full screen setting, the frame table covers nearly the complete righthand half of the
screen.
Save
Opens the "Save" menu to save the decoded data in a CSV file (comma-separated list).
Remote command:
BUS<b>:LIST? on page 376
BUS<b>:LIST:SAVE on page 376
11.2 SPI/SSPI Bus (Option R&S RTM-K1)
11.2.1 The SPI Protocol
A 4-channel instrument is required for full support of the SPI protocol.
The Serial Peripheral Interface SPI is used for communication with slow peripheral devi-
ces, in particular, for transmission of data streams.
Main characteristics of SPI are:
●
Master-slave communication
●
No device addressing; The slave is accessed by a chip select, or slave select line.
●
No acknowledgement mechanism to confirm receipt of data
●
Duplex capability
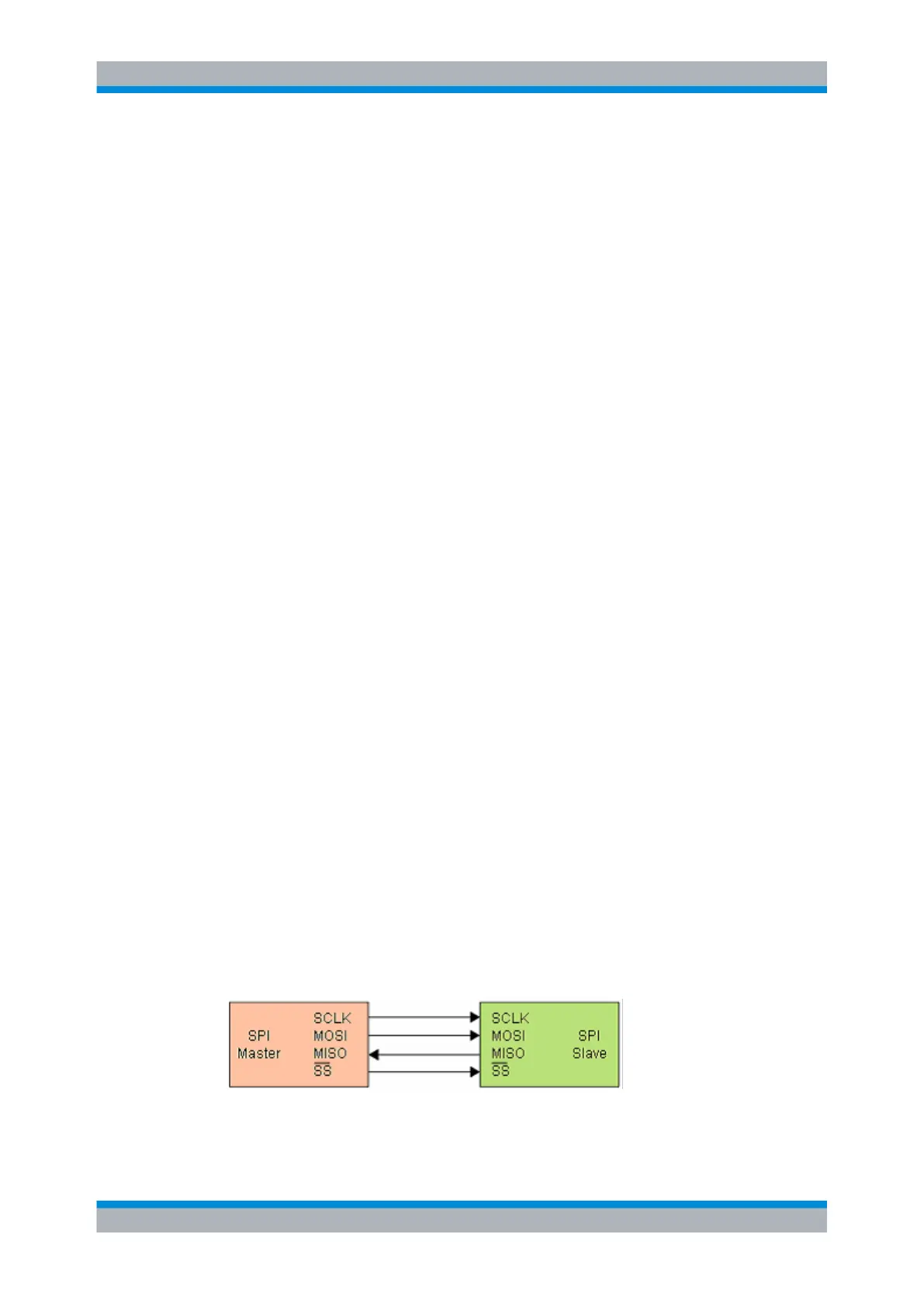
Most SPI buses have four lines, two data and two control lines:
●
Clock line to all slaves (SCLK)
●
Slave Select or Chip Select line (SS or CS)
●
Master data output, slave data input (MOSI or SDI)
●
Master data input, slave data output (MISO or SDO)
When the master generates a clock and selects a slave device, data may be transferred
in either or both directions simultaneously.
As SPI is very simple and efficient for single master - single slave applications, the
R&S RTM provides also an SSPI (simple SPI) configuration that does not have a chip
select line.
Fig. 11-1: Simple configuration of SPI bus
SPI/SSPI Bus (Option R&S RTM-K1)

 Loading...
Loading...











