Basics of Path Interpolation
2.13 Kinematic adaptation
TO Path Interpolation
Function Manual, 11/2010
63
\
RIIVHW$
$
[
.LQHPDWLF
HQGSRLQW
0HFKDQLFDO
=HURSRVLWLRQ
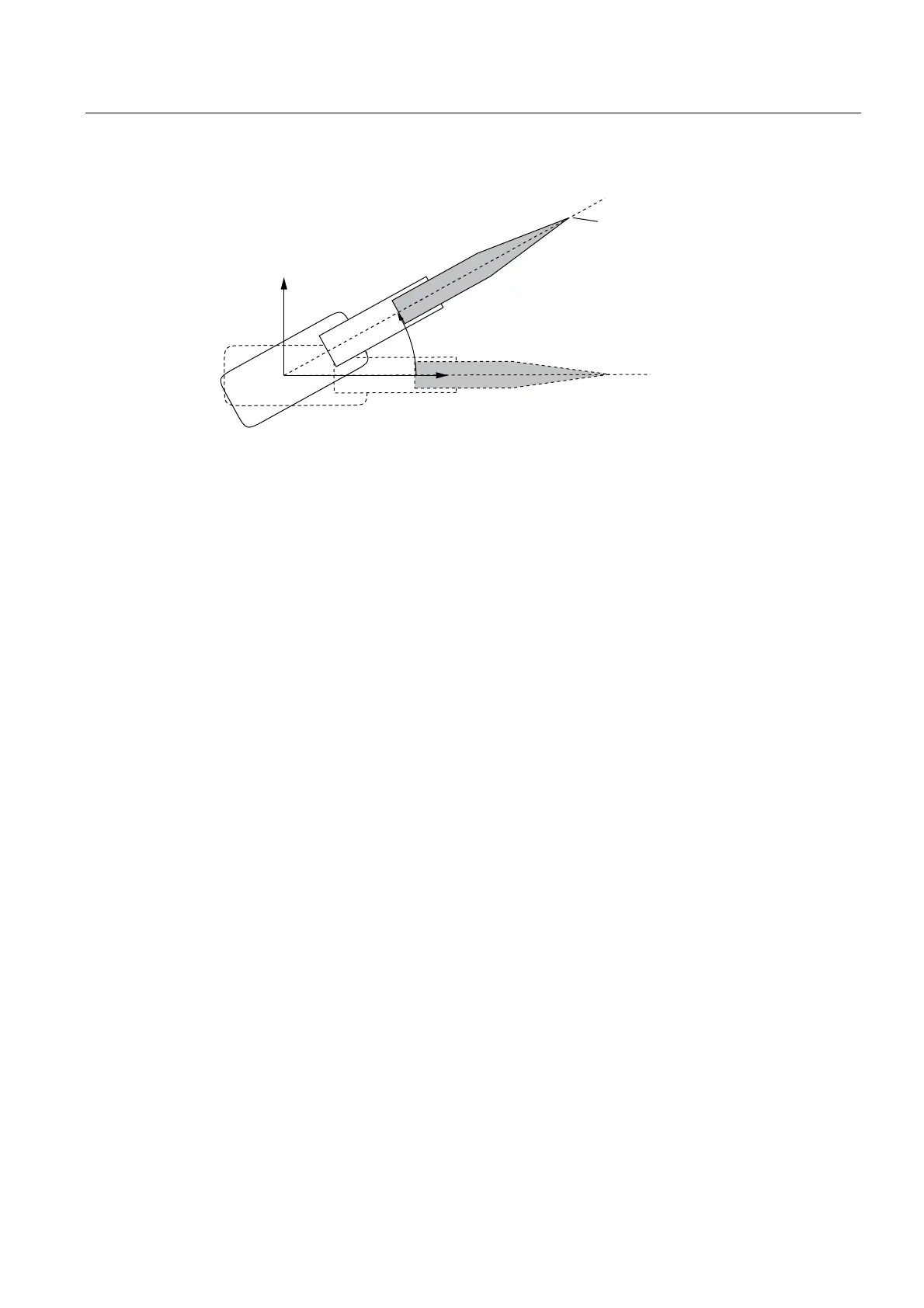
Figure 2-52 Articulated arm: Axis A1 zero position
The domain of the single A1 to A3 axes is limited to [-180°; 180°).
Coupled axes
If a positive coupling factor between two axes is specified, the transformation assumes that a
positive motion on the first axes leads to a negative motion on the second axis.
Configuration data for articulated arm kinematics
typeOfKinematics:
ARTICULATED_ARM
Articulated arm kinematics type
basicOffset.x Offset of the kinematic zero point relative to the
Cartesian zero point, x-coordinate
basicOffset.y Offset of the kinematic zero point relative to the
Cartesian zero point, y-coordinate
basicOffset.z Offset of the kinematic zero point relative to the
Cartesian zero point, z-coordinate
offsetA1 Offset of axis zero point axis A1 relative to zero position
of axis A1 in the transformation
distanceA1A2 A1-A2 separation
offsetA2 Offset of axis zero point axis A2 relative to zero position
of axis A2 in the transformation
distanceA2A3 A2 - A3 separation
offsetA3 Offset of axis zero point axis A3 relative to zero position
of axis A3 in the transformation
distanceA3Endpoint A3 - end point separation
linkCompensation.enableA2A3 Compensate A3 articulated joint positioning dependence
for A2
linkCompensation.factorA2A3 Factor

 Loading...
Loading...











