136 Sun Fire V890 Server Owner’s Guide • September 2004
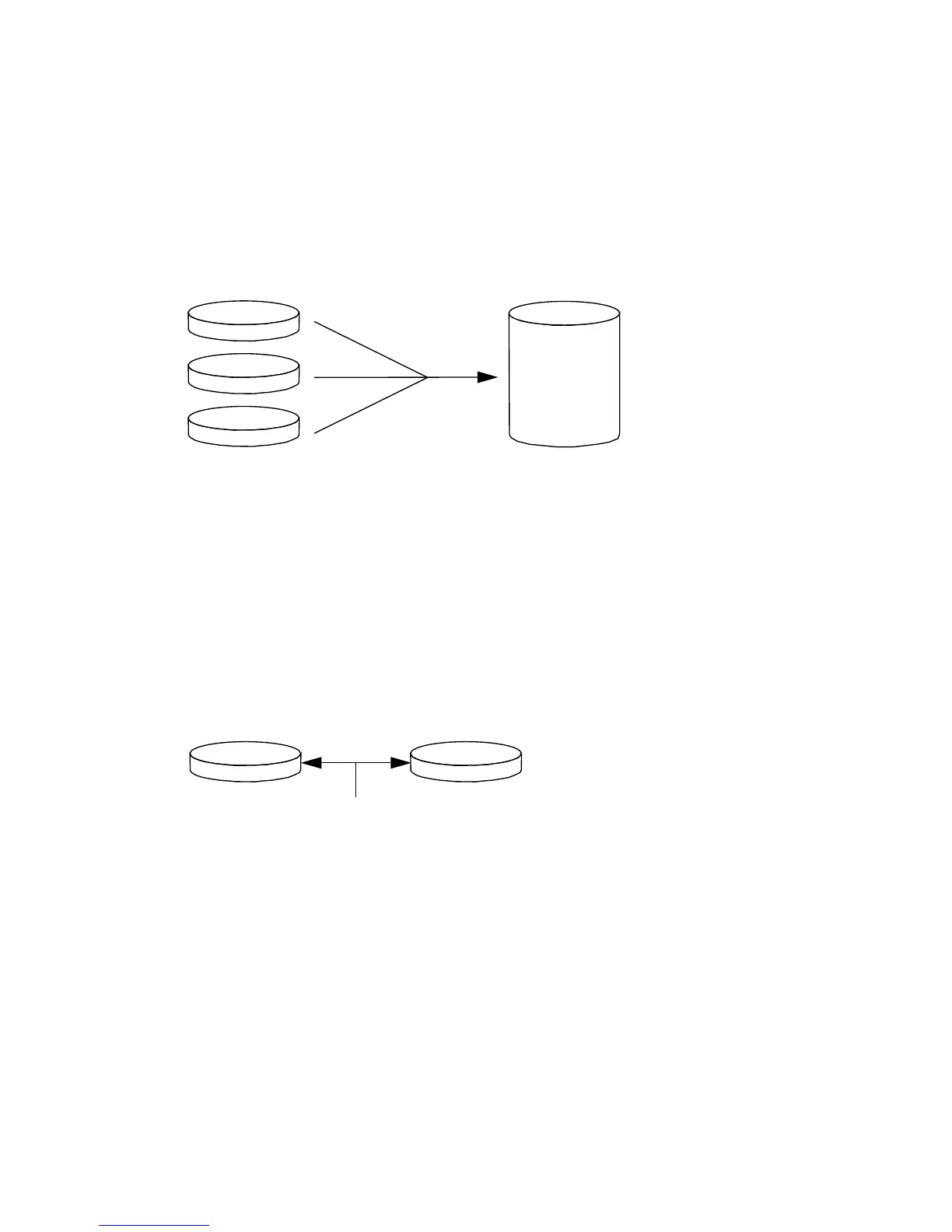
Disk Concatenation
Disk concatenation is a method for increasing logical volume size beyond the
capacity of one disk drive by creating one large volume from two or more smaller
drives. This lets you create arbitrarily large partitions.
Using this method, the concatenated disks are filled with data sequentially, with the
second disk being written to when no space remains on the first, the third when no
room remains on the second, and so on.
RAID 1: Disk Mirroring
Disk mirroring (RAID 1) is a technique that uses data redundancy—two complete
copies of all data stored on two separate disks—to protect against loss of data due to
disk failure. One logical volume is duplicated on two separate disks.
Whenever the operating system needs to write to a mirrored volume, both disks are
updated. The disks are maintained at all times with exactly the same information.
When the operating system needs to read from the mirrored volume, it reads from
whichever disk is more readily accessible at the moment, which can result in
enhanced performance for read operations.
RAID 1 offers the highest level of data protection, but storage costs are high, and
write performance is reduced since all data must be stored twice.

 Loading...
Loading...











