Oscilloscope Reference Spectral analyzer window types
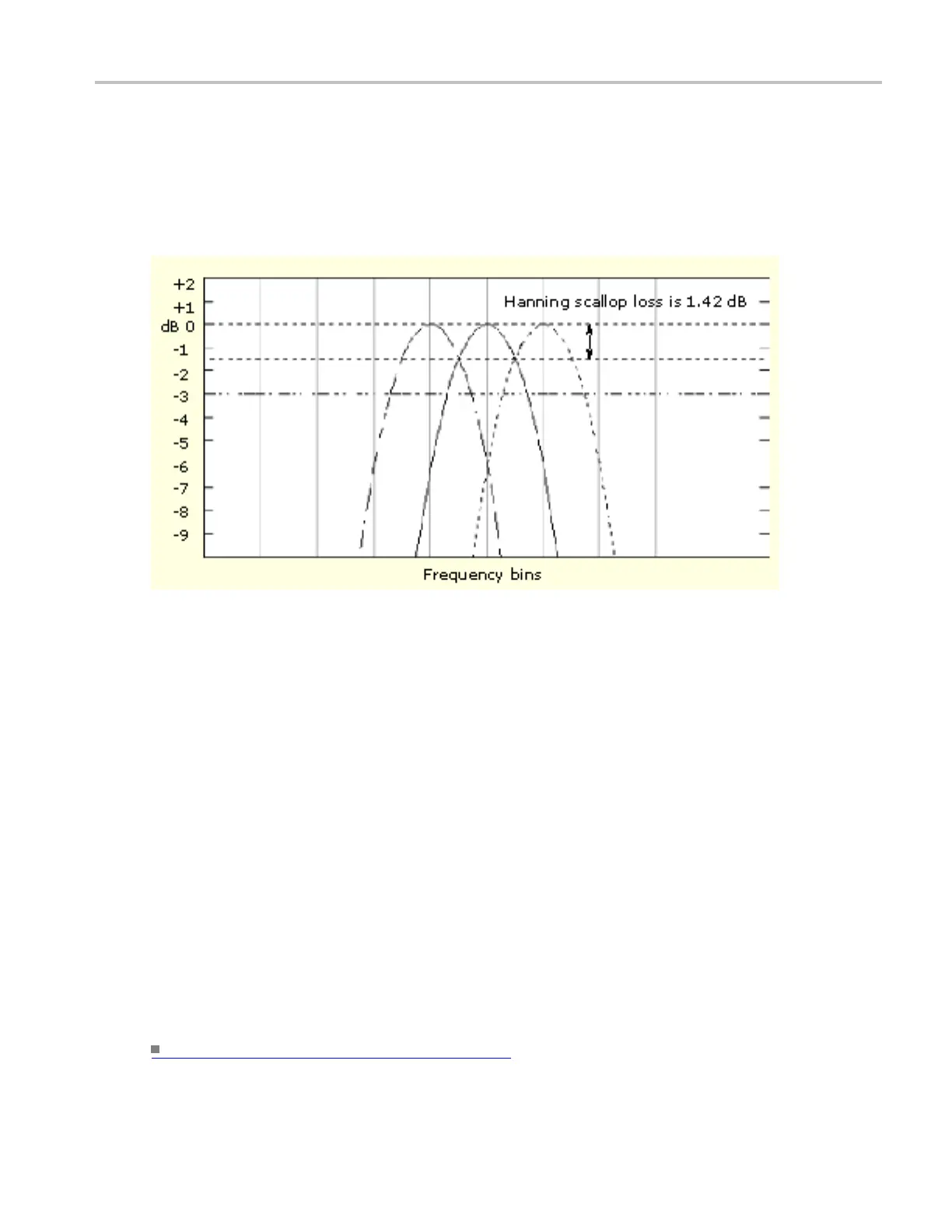
Scallop l oss
This is the magnitude error of the spectral analyzer when the frequency of the observed signal is exactly
half way between two frequency samples of the spectrum when the interpolation ratio due to zero fill of the
FFT is one. When zero fill is in effect, scallop loss is essentially eliminated because of the interpolation in
the frequenc
y domain due to zero fill. If you work with span settings less than full and you work with
larger resolution bandwidth settings, zero fill is in effect most of the time.
Nearest side lobe
This is the difference in magnitude between the spectral lobe peak in the spectrum and the next side lobe
that occurs due to energy leakage. Different windows have different leakage characteristics. The more
narro
w the resolution bandwidth of the window the more leakage in the spectrum.
Zero phase reference
This is the position in the time domain gate that is the reference point for phase in the output spectrum.
That is, if a sine wave input has its peak at the zero phase reference position, then it reads out as zero phase
in the spectrum. If the phase is to be correct when doing impulse response testing, the impulse in the time
domain must be located at this position in the gate interval.
C
oefficients
These are used to generate the windows that are constructed from a cosine series. For the Gaussia n window,
t
he value of "a" is given instead of a set of coefficients. You can find descriptions of cosine series windows
in the Handbook of Digital Signal Processing Engineering Applications by Elliot. ISBN 0-12-237075-9.
What do you want to do next?
Learn about recognizing aliasing. (see page 780)
DSA/DPO70000D, MSO/DPO/DSA70000C, DPO7000C, and MSO/DPO5000 Series 773

 Loading...
Loading...