DNR-X-1G Series RACKtangle and HalfRACK Systems
Chapter 4 45
Installation and Configuration
October 2018 www.ueidaq.com
508.921.4600
© Copyright 2018
United Electronic Industries, Inc.
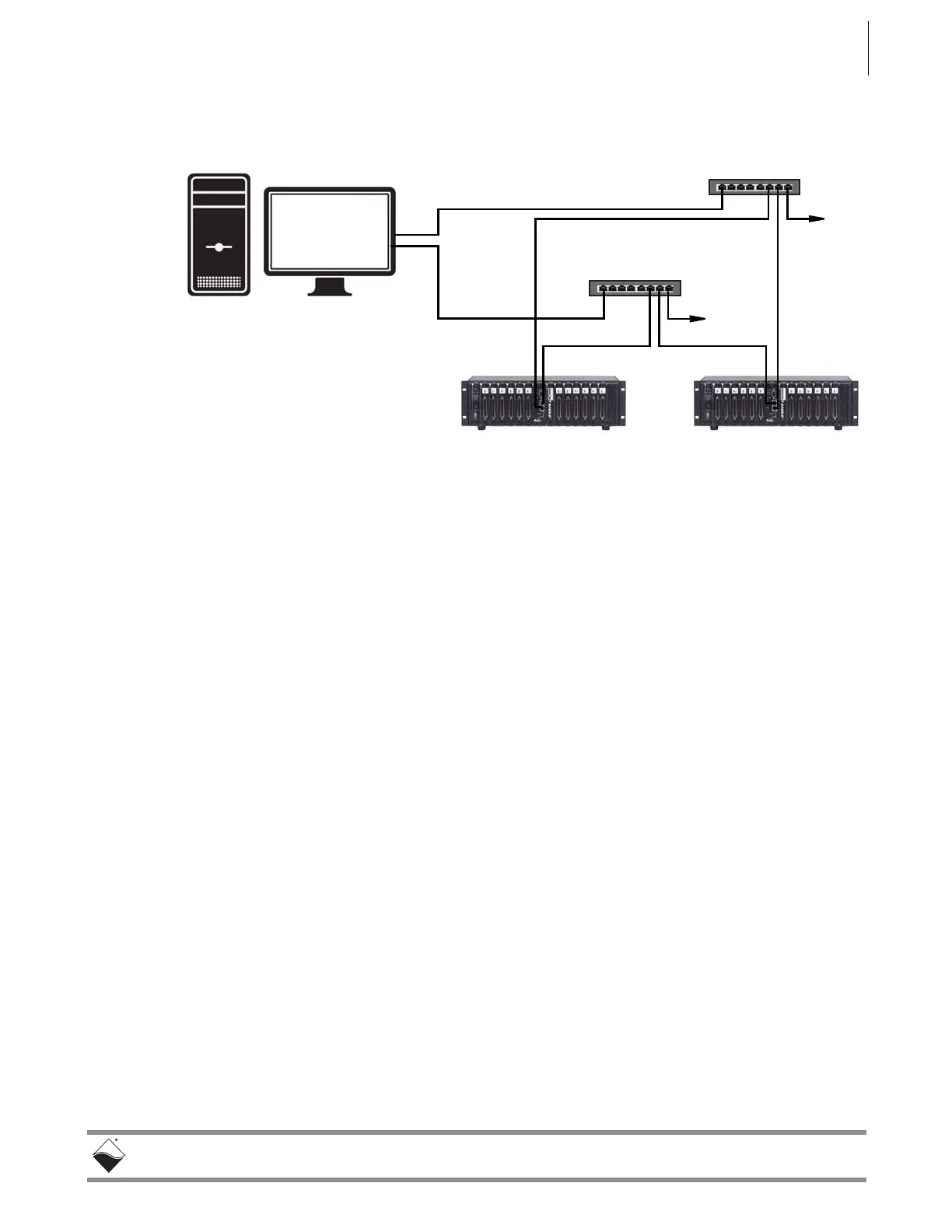
Figure 4-6 shows a two-rack dual network system with two LAN switches that
performs both data acquisition and diagnostic functions.
Figure 4-6. Separate Networks for Operation and Diagnostics: Two
Racks & Two Switches
4.4.1 Example of
Configuring
Network
Settings
This section provides an example of configuring a separate network for
diagnostics.
In this example, we assume that your office uses a Class C network (the class
intended for small networks with fewer than 256 devices) and your host is
configured with a static IP or via DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
STEP 1: Obtain your networking configuration:
• On Windows systems, open the command prompt and type ipconfig to
display the configuration:
Start >> Programs >> ( Accessories >>) Command Prompt
C:\> ipconfig
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.10
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.1
• On Linux systems, use “ifconfig” instead.
In the above example, the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 on NIC1 uses the
subnet range 192.168.1.0 through 192.168.1.255. Refer to the
IP Addressing Side Note on the next page for more information about subnets.
NIC1 - to Intranet
NIC2 -
to diagnostic ports)

 Loading...
Loading...