DL205 User Manual, 4th Edition, Rev. D
4-43
Chapter 4: System Design and Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
B
C
D
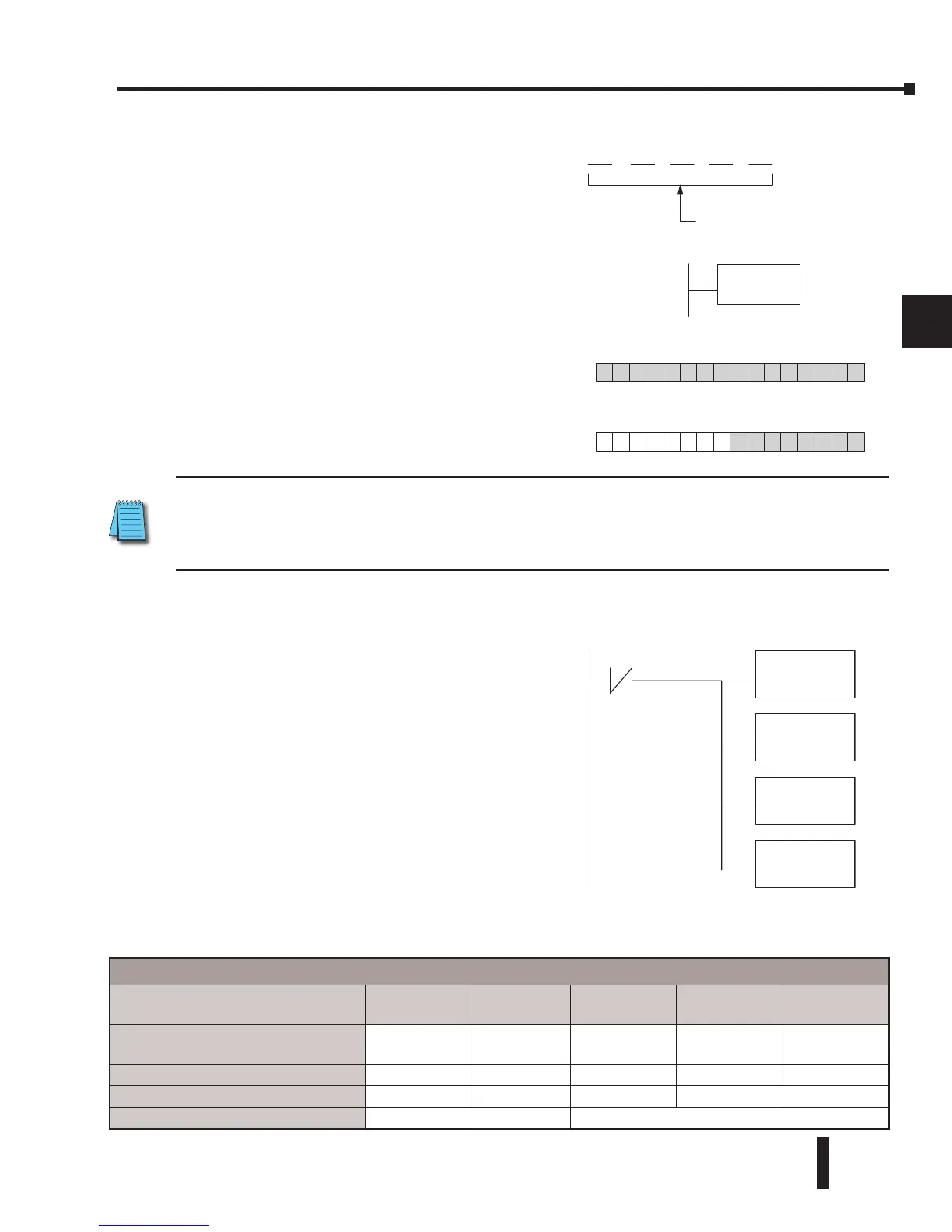
Step 3: Specify Master Memory Area
The third instruction in the RX or WX sequence is
a Load Address (LDA) instruction. Its purpose is to
load the starting address of the memory area to be
transferred. Entered as an octal number, the LDA
instruction converts it to hex and places the result
in the accumulator.
For a WX instruction, the DL250-1/260 CPU
sends the number of bytes previously specified from
its memory area beginning at the LDA address
specified.
For an RX instruction, the DL250-1/260 CPU
reads the number of bytes previously specified from
the slave, placing the received data into its memory
area beginning at the LDA address specified.
NOTE: Since V-memory words are always 16 bits, you may not always use the whole word. For example,
if you only specify 3 bytes and you are reading Y outputs from the slave, you will only get 24 bits of data.
In this case, only the 8 least significant bits of the last word location will be modified. The remaining 8 bits
are not affected.
Step 4: Specify Slave Memory Area
The last instruction in our sequence is the WX
or RX instruction itself. Use WX to write to the
slave, and RX to read from the slave. All four of
our instructions are shown to the right. In the last
instruction, you must specify the starting address
and a valid data type for the slave.
• DirectNET slaves – specify the same address in the
WX and RX instruction as the slave’s native I/O
address.
• Modbus DL405 or DL205 slaves – specify the same
address in the WX and RX instruction as the slave’s
native I/O address.
• Modbus 305 slaves – use the following table to
convert DL305 addresses to Modbus addresses.
 Loading...
Loading...