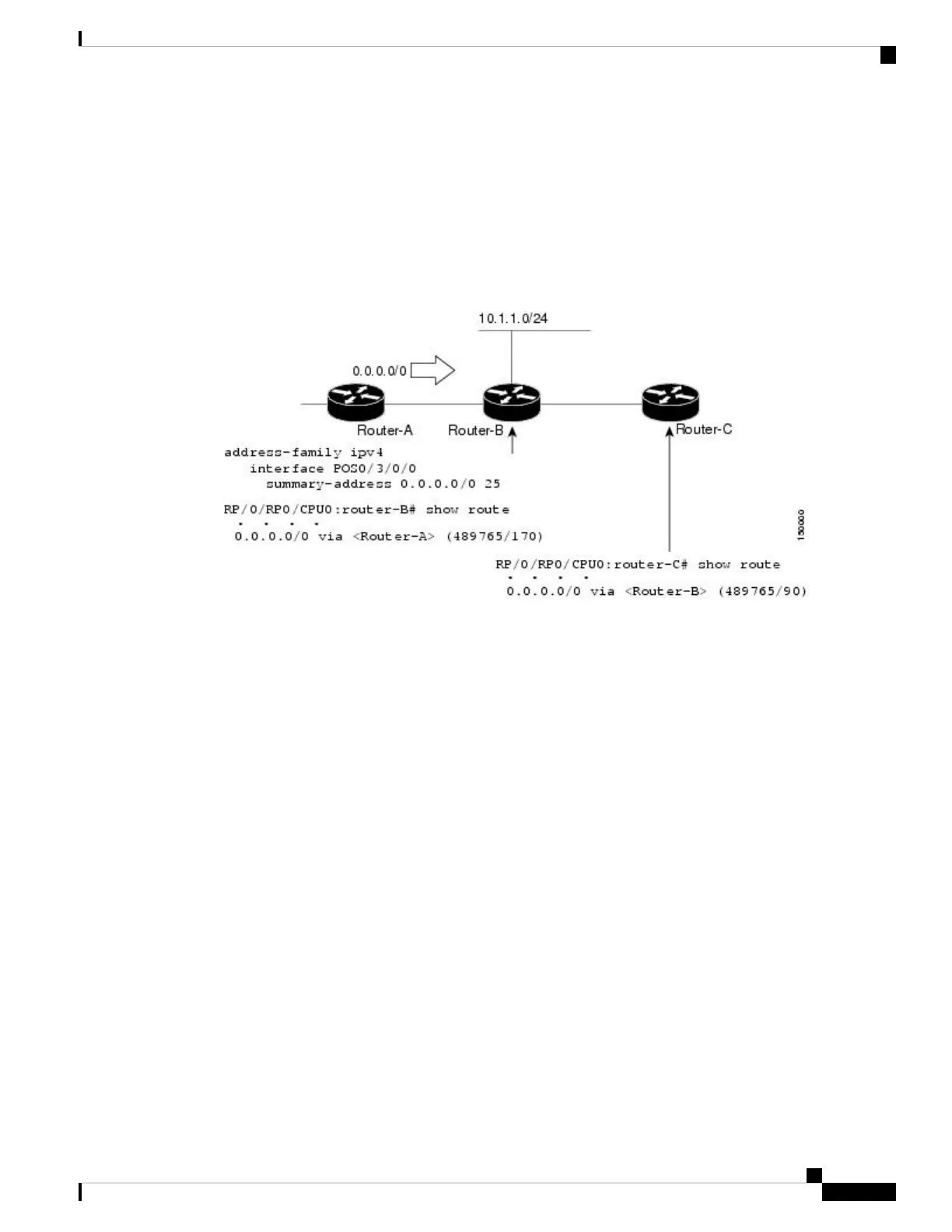
advertises this route to Router-B. Router-B is configured so that only a default summary route is advertised
to Router-C. The default summary route is applied to interface 0/1 on Router-B with the following configuration:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config)# router eigrp 100
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-eigrp)# address-family ipv4
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-eigrp-af)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/3/0/0
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-eigrp-af-if)# summary-address 100.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
Figure 11: Floating Summary Route Is Applied to Router-B
The configuration of the default summary route on Router-B sends a 0.0.0.0/0 summary route to Router-C
and blocks all other routes, including the 10.1.1.0/24 route, from being advertised to Router-C. However, this
configuration also generates a local discard route on Router-B, a route for 0.0.0.0/0 to the null 0 interface with
an administrative distance of 5. When this route is created, it overrides the EIGRP learned default route.
Router-B is no longer able to reach destinations that it would normally reach through the 0.0.0.0.0/0 route.
This problem is resolved by applying a floating summary route to the interface on Router-B that connects to
Router-C. The floating summary route is applied by relating an administrative distance to the default summary
route on the interface of Router-B with the following statement:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-if)# summary-address 100 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 250
The administrative distance of 250, applied in the above statement, is now assigned to the discard route
generated on Router-B. The 0.0.0.0/0, from Router-A, is learned through EIGRP and installed in the local
routing table. Routing to Router-C is restored.
If Router-A loses the connection to Router-B, Router-B continues to advertise a default route to Router-C,
which allows traffic to continue to reach destinations attached to Router-B. However, traffic destined for
networks to Router-A or behind Router-A is dropped when the traffic reaches Router-B.
Figure 12: Floating Summary Route Applied for Dual-Homed Remotes, on page 186 shows a network with
two connections from the core: Router-A and Router-D. Both routers have floating summary routes configured
on the interfaces connected to Router-C. If the connection between Router-E and Router-C fails, the network
continues to operate normally. All traffic flows from Router-C through Router-B to the hosts attached to
Router-A and Router-D.
Routing Configuration Guide for Cisco NCS 6000 Series Routers, IOS XR Release 6.4.x
185
Implementing EIGRP
Floating Summary Routes for an EIGRP Process

 Loading...
Loading...











