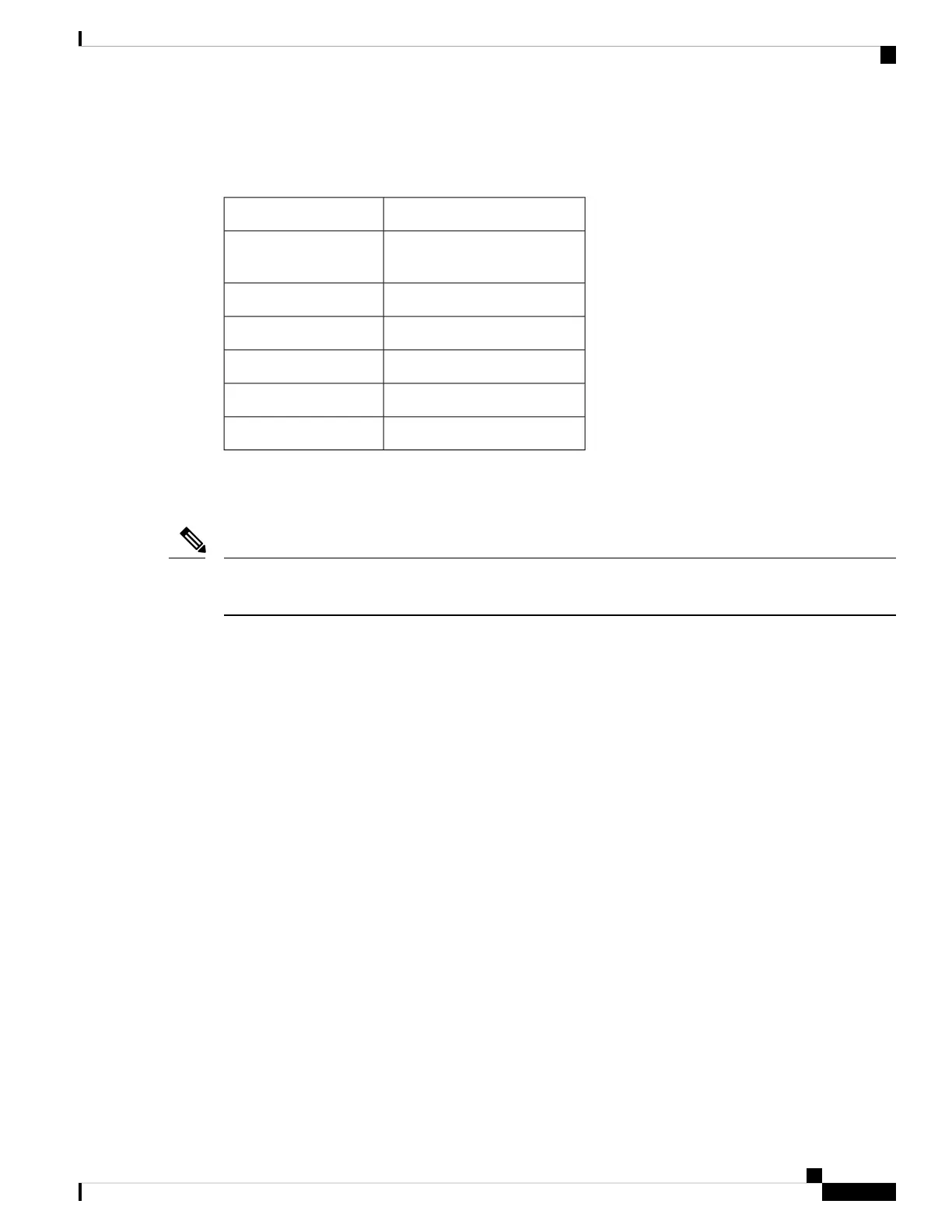
This table lists default administrative distances for the common protocols.
Table 5: Default Administrative Distances
Administrative Distance DefaultProtocol
0Connected or local
routes
1Static routes
20External BGP routes
110OSPF routes
115IS-IS routes
200Internal BGP routes
The administrative distance for some routing protocols (for instance IS-IS, OSPF, and BGP) can be changed.
See the protocol-specific documentation for the proper method to change the administrative distance of that
protocol.
Changing the administrative distance of a protocol on some but not all routers can lead to routing loops and
other undesirable behavior. Doing so is not recommended.
Note
RIB Support for IPv4
In Cisco IOS XR software, RIB tables support unicast routing.
The default routing tables for Cisco IOS XR software RIB are the unicast RIB tables for IPv4 routing.
RIB processes ipv4_rib and ipv6_rib run on the RP card. If process placement functionality is available and
supported by multiple RPs in the router, RIB processes can be placed on any available node.
RIB Statistics
RIB supports statistics for messages (requests) flowing between the RIB and its clients. Protocol clients send
messages to the RIB (for example, route add, route delete, and next-hop register, and so on). RIB also sends
messages (for example, redistribute routes, advertisements, next-hop notifications, and so on). These statistics
are used to gather information about what messages have been sent and the number of messages that have
been sent. These statistics provide counters for the various messages that flow between the RIB server and
its clients. The statistics are displayed using the show rib statistics command.
RIB maintains counters for all requests sent from a client including:
• Route operations
• Table registrations
• Next-hop registrations
Routing Configuration Guide for Cisco NCS 6000 Series Routers, IOS XR Release 6.4.x
355
Implementing and Monitoring RIB
RIB Support for IPv4

 Loading...
Loading...











