xStack® DES-3528/DES-3552 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Fast Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
294
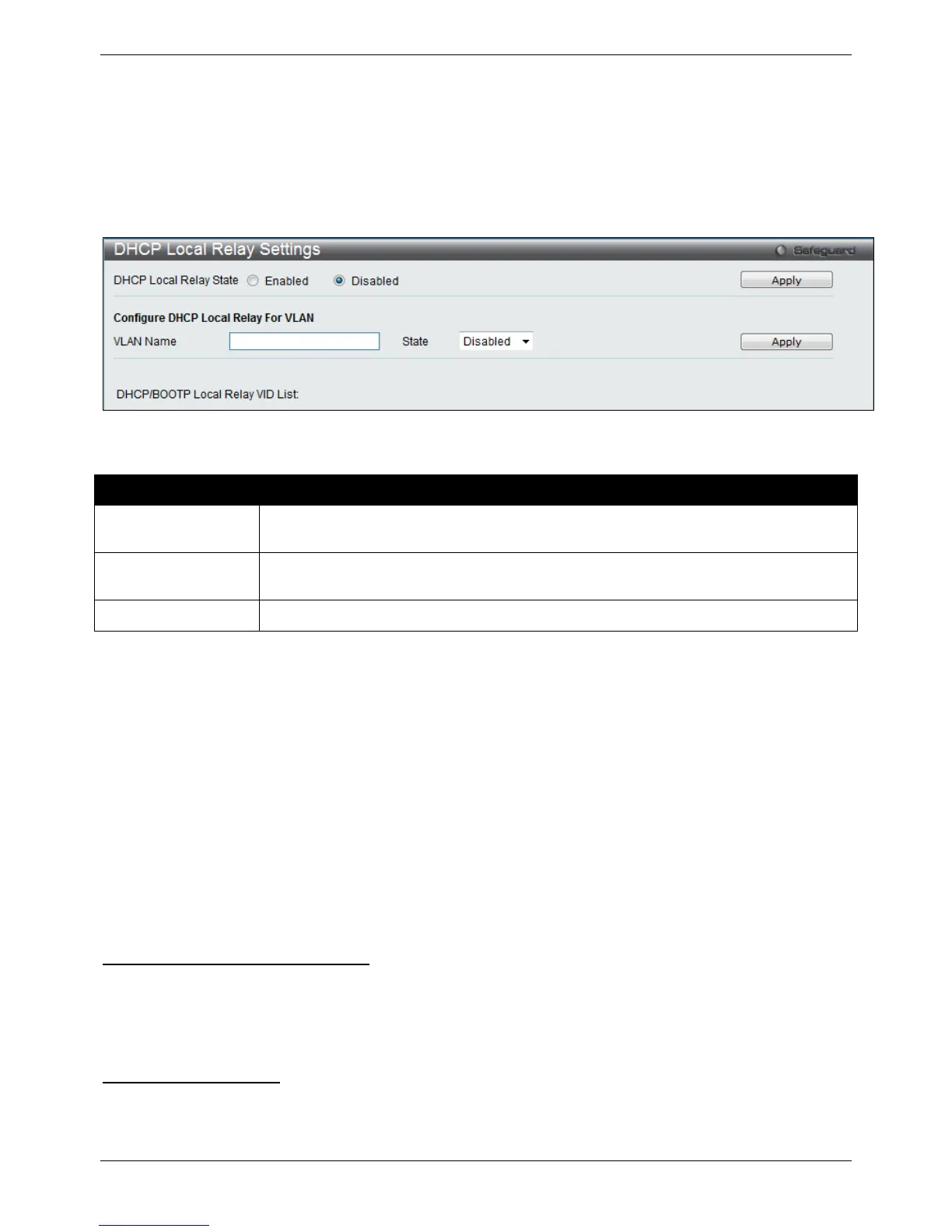
DHCP Local Relay Settings
The DHCP local relay settings allows the user to add option 82 into DHCP request packets when the DHCP client
gets an IP address from the same VLAN. If the DHCP local relay settings are not configured, the Switch will flood
the packets to the VLAN. In order to add option 82 into the DHCP request packets, the DHCP local relay settings
and the state of the Global VLAN need to be enabled.
To view this window, click Network Application > DHCP > DHCP Local Relay Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-19 DHCP Local Relay Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
DHCP Local Relay
Global State
Enable or disable the DHCP Local Relay Global State. The default is Disabled.
VLAN Name
This is the VLAN Name that identifies the VLAN the user wishes to apply the DHCP Local
Relay operation.
State
Enable or disable the configure DHCP Local Relay for VLAN state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made for each individual section.
DNS
DNS Relay
Computer users usually prefer to use text names for computers for which they may want to open a connection.
Computers themselves, require 32 bit IP addresses. Somewhere, a database of network devices’ text names and
their corresponding IP addresses must be maintained.
The Domain Name System (DNS) is used to map names to IP addresses throughout the Internet and has been
adapted for use within intranets.
For two DNS servers to communicate across different subnets, the DNS Relay of the Switch must be used. The
DNS servers are identified by IP addresses.
Mapping Domain Names to Addresses
Name-to-address translation is performed by a program called a Name server. The client program is called a Name
resolver. A Name resolver may need to contact several Name servers to translate a name to an address.
The Domain Name System (DNS) servers are organized in a somewhat hierarchical fashion. A single server often
holds names for a single network, which is connected to a root DNS server - usually maintained by an ISP.
Domain Name Resolution
The domain name system can be used by contacting the name servers one at a time, or by asking the domain
name system to do the complete name translation. The client makes a query containing the name, the type of
answer required, and a code specifying whether the domain name system should do the entire name translation, or
simply return the address of the next DNS server if the server receiving the query cannot resolve the name.

 Loading...
Loading...











