xStack® DES-3528/DES-3552 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Fast Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
353
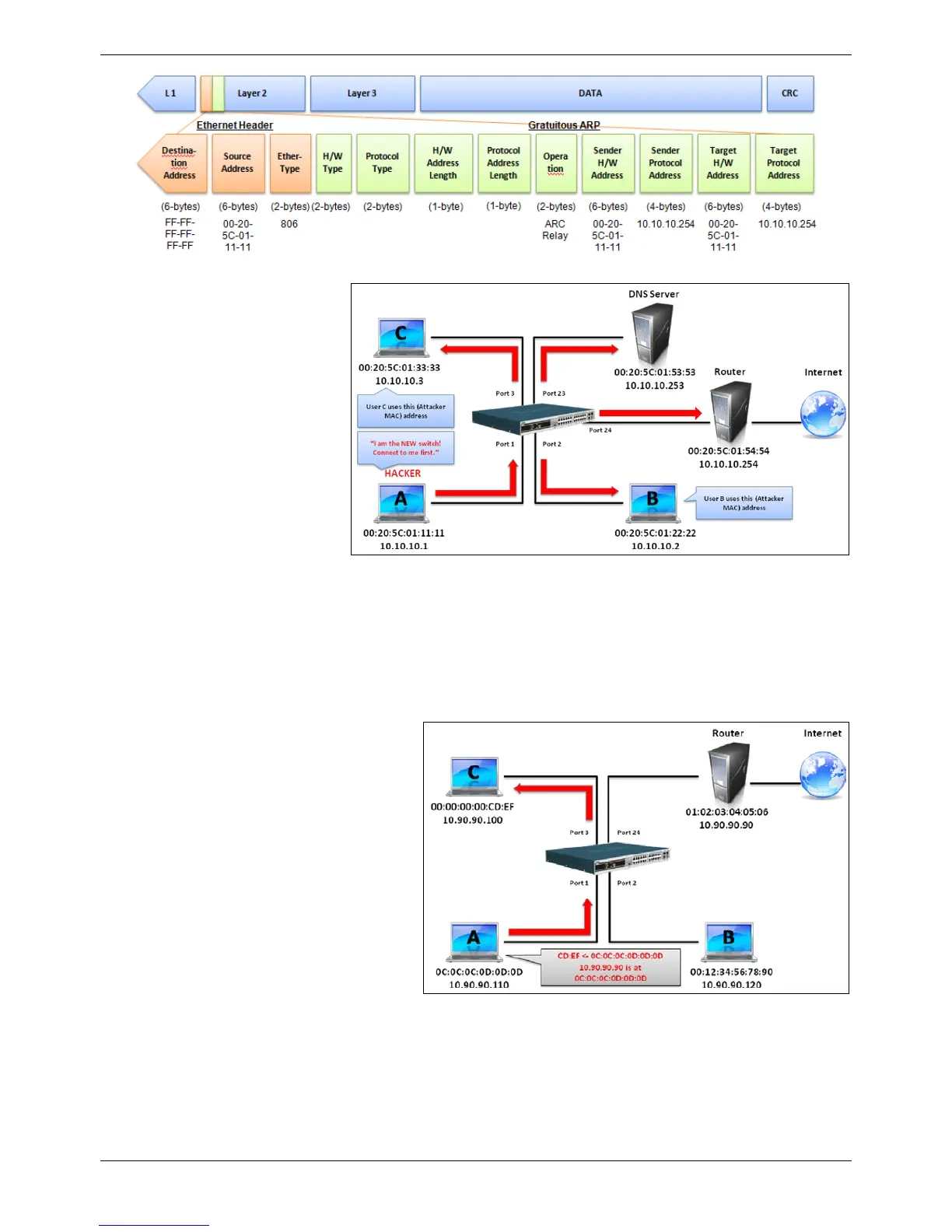
A common DoS attack today can
be done by associating a
nonexistent or any specified MAC
address to the IP address of the
network’s default gateway. The
malicious attacker only needs to
broadcast one Gratuitous ARP to
the network claiming it is the
gateway so that the whole
network operation will be turned
down as all packets to the
Internet will be directed to the
wrong node.
Likewise, the attacker can either
choose to forward the traffic to the
actual default gateway (passive
sniffing) or modify the data before
forwarding it (man-in-the-middle
Figure 5
The hacker cheats the victim PC that it is a router and cheats the router that it is the victim. As can be seen in
Figure 5 all traffic will be then sniffed by the hacker but the users will not discover.
Prevent ARP Spoofing via Packet Content ACL
D-Link managed switches can effectively
mitigate common DoS attacks caused by
ARP spoofing via a unique Package Content
ACL.
For the reason that basic ACL can only filter
ARP packets based on packet type, VLAN
ID, Source, and Destination MAC
information, there is a need for further
inspections of ARP packets. To prevent ARP
spoofing attack, we will demonstrate here via
using Packet Content ACL on the Switch to
block the invalid ARP packets which contain
faked gateway’s MAC and IP binding.
Configuration
The configuration logic is as follows:
1. Only if the ARP matches Source MAC address in Ethernet, Sender MAC address and Sender IP address
in ARP protocol can pass through the switch. (In this example, it is the gateway’s ARP.)

 Loading...
Loading...











