Connecting to ECU
To be able to display and log data from the engine management unit, connect the ADU to the CAN
bus of the ECU or its serial port.
When using a CAN bus, you may connect the ECU to the CAN1 (where the ECU CAN bus speed
is 1 Mbps) or to the CAN2 bus where you can define the speed of the CAN bus.
When connecting to an OEM ECU, the typical speed is 500 Kbps (units with a 250 Kbps bus are
rare), which forces us to use a CAN2 bus connection.
Some aftermarket engine management units used in motor sports do not have a CAN bus, but are
equipped with a serial output. This is the case for the EMU, EMU CLASSIC, or Hondata. ADU
supports the following serial formats: AIM, Ecumaster serial protocol, Autronic SM4 and Hondata
serial protocol. For additional information, go to the Serial communication section.
In the case of factory controllers equipped with an OBD2 connector using the CAN BUS (all
vehicles since 2008) it is possible to use the OBD connector to read basic engine operation
parameters. For more information, see OBD2 manual section.
External sensors may be connected to the ADU using the analogue and digital input channels (e.g.
TPS, temperature and oil/fuel pressure sensors, crankshaft position sensor, etc.). As a result, you
can monitor and log parameters that are not supported by the original engine control module.
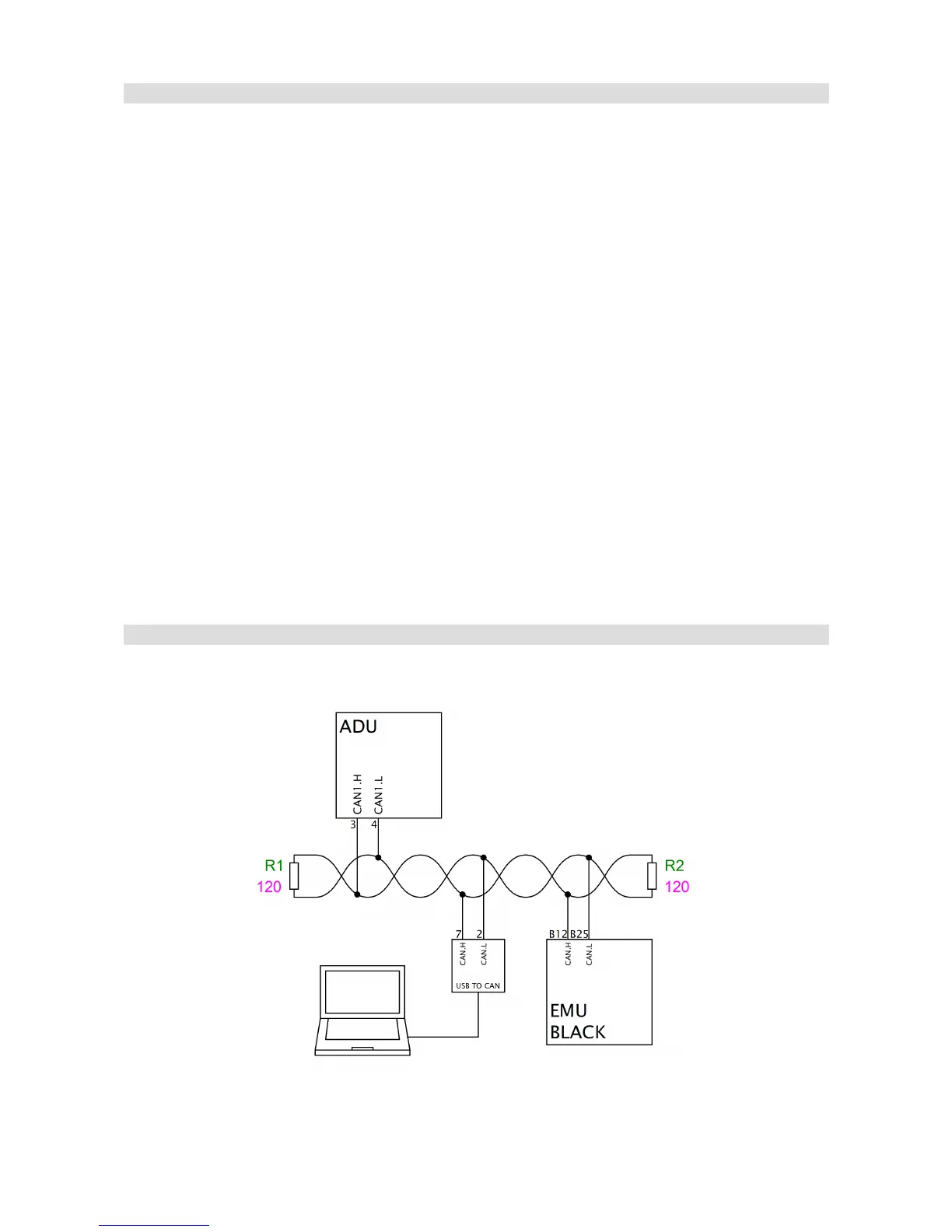
Connecting to CAN bus
The following diagram shows an example connection of an ECU to the ADU using the CAN1 bus.
Page 16/137
 Loading...
Loading...